
Give an example of incomplete linkage.
Answer
605.7k+ views
Hint: Linkage was first discovered by Bateson and Punnett. They noticed two pairs of alleles which did not sort independently.
Complete answer:
First let us see what is incomplete linkage. Homologous chromosomes undergo recombination during gametogenesis (meiosis) . Post chiasma in homologous non-sister chromatids during pachytene of Prophase-1, new non-parental combinations are produced which give rise to variation. Crossing over between chromosomes will cause linked genes which are located far from each other to separate thus rendering the linkage incomplete. Incomplete linkage is commonly seen in almost all organisms. Let us take the example of maize:
In the diagram below we see a cross between, Colored-Full seed [CCFF] and colorless-shrunken seed [ccff]
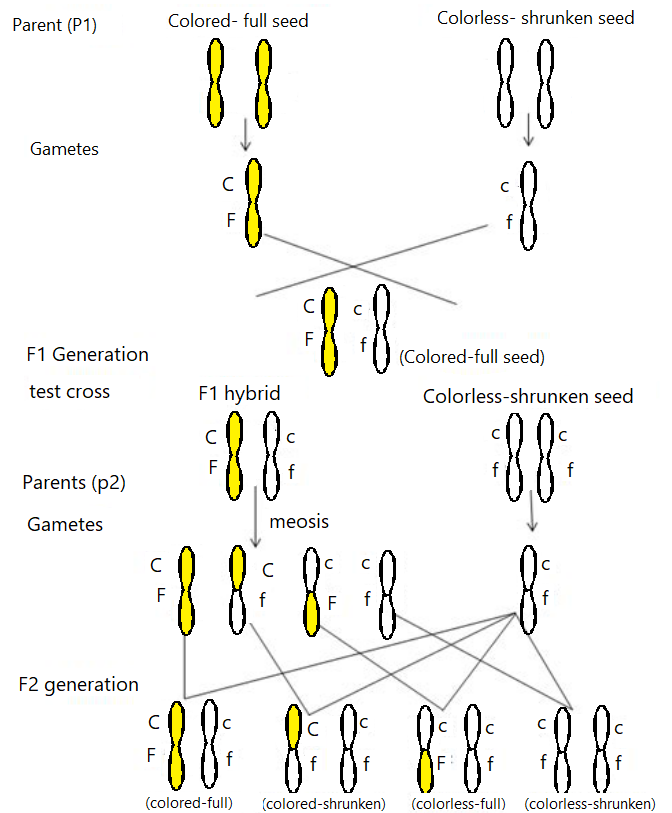
From the above cross we get the $F_2$ phenotypic ratio 1:1:1:1.
In this cross we see incomplete linkage between two genes, the gene responsible for colour and the gene responsible for shape of the seed, when these crossing over happens during meiosis it leads to a variation in the phenotype on the $F_2$ generation where we see non-parental combinations which are colored but shrunken seeds and colorless but full seeds.
This experiment shows us that the genes for color and shape of seed are linked and located far from each other. During gametogenesis these linked genes tend to remain together but because they are far away they are separated due to crossing over.Incomplete linkage has been studied in female Drosophila, maize, tomato and many other organisms.
Notes: To easily differentiate between complete linkage and incomplete linkage you should check the inherited characters of the $F_2$ generation. Complete linkage shows only parental combinations because the genes aren't separated during chiasma since they are located close to each other whereas incomplete linkage shows non-parental combinations due to their distant locations.
Complete answer:
First let us see what is incomplete linkage. Homologous chromosomes undergo recombination during gametogenesis (meiosis) . Post chiasma in homologous non-sister chromatids during pachytene of Prophase-1, new non-parental combinations are produced which give rise to variation. Crossing over between chromosomes will cause linked genes which are located far from each other to separate thus rendering the linkage incomplete. Incomplete linkage is commonly seen in almost all organisms. Let us take the example of maize:
In the diagram below we see a cross between, Colored-Full seed [CCFF] and colorless-shrunken seed [ccff]

From the above cross we get the $F_2$ phenotypic ratio 1:1:1:1.
In this cross we see incomplete linkage between two genes, the gene responsible for colour and the gene responsible for shape of the seed, when these crossing over happens during meiosis it leads to a variation in the phenotype on the $F_2$ generation where we see non-parental combinations which are colored but shrunken seeds and colorless but full seeds.
This experiment shows us that the genes for color and shape of seed are linked and located far from each other. During gametogenesis these linked genes tend to remain together but because they are far away they are separated due to crossing over.Incomplete linkage has been studied in female Drosophila, maize, tomato and many other organisms.
Notes: To easily differentiate between complete linkage and incomplete linkage you should check the inherited characters of the $F_2$ generation. Complete linkage shows only parental combinations because the genes aren't separated during chiasma since they are located close to each other whereas incomplete linkage shows non-parental combinations due to their distant locations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




