
Give one function of each part of the embryo
1. Plumule
2. Radicle
3. Cotyledons
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: The seed coat consists of an embryo that is differentiated into plumule, radical, and cotyledons.
Complete answer: Function of Plumule (shoot tip): The plumule is the part of the embryo that develops into the shoot bearing the leaves of the plant. The plumule gives rise to aerial shoots.
The function of radical (root tip): The radical when elongates gives rise to the primary root. It is the part that appears first when a seed germinates. It grows along with them down into the soil giving an anchor to seedlings. In dicotyledonous plants, they develop into taproot whereas in monocotyledonous plat it develops into the fibrous root
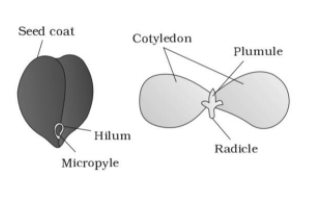
The function of cotyledon: They store reserve food material or serve as photosynthetic organs in young seedlings. In beans (in dicotyledons) they reserve food material in the form of carbohydrates and proteins to provide nourishment to the embryonal axis at the time of seed germination and growth of young seedlings.
In monocotyledons, they are known as scutellum which helps in the translocation of nutrients from the endosperm to the growing embryo at the time of germination and seedling growth.
Additional Information: The embryonic shoot known as plumule has two main parts, the epicotyls, and the hypocotyls.
The epicotyls are the portion of the embryonic stem above the point at which the stem is attached to the cotyledons.
The hypocotyls are the portion below the point of attachment.
Note: The mature embryo consists of an embryonic root known as radical, an embryonal axis, and one or two cotyledons.
Complete answer: Function of Plumule (shoot tip): The plumule is the part of the embryo that develops into the shoot bearing the leaves of the plant. The plumule gives rise to aerial shoots.
The function of radical (root tip): The radical when elongates gives rise to the primary root. It is the part that appears first when a seed germinates. It grows along with them down into the soil giving an anchor to seedlings. In dicotyledonous plants, they develop into taproot whereas in monocotyledonous plat it develops into the fibrous root

The function of cotyledon: They store reserve food material or serve as photosynthetic organs in young seedlings. In beans (in dicotyledons) they reserve food material in the form of carbohydrates and proteins to provide nourishment to the embryonal axis at the time of seed germination and growth of young seedlings.
In monocotyledons, they are known as scutellum which helps in the translocation of nutrients from the endosperm to the growing embryo at the time of germination and seedling growth.
Additional Information: The embryonic shoot known as plumule has two main parts, the epicotyls, and the hypocotyls.
The epicotyls are the portion of the embryonic stem above the point at which the stem is attached to the cotyledons.
The hypocotyls are the portion below the point of attachment.
Note: The mature embryo consists of an embryonic root known as radical, an embryonal axis, and one or two cotyledons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




