
Give the structural differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
Answer
529.8k+ views
Hint: Hydrocarbons are molecules which contain hydrogen and carbon atoms mainly that are bonded to each other and may or may not contain other atoms. They are classified into two distinct categories on the basis of their bonding: saturated and unsaturated.
Complete step by step solution:
While saturated hydrocarbons only have a single bond between its hydrogen and carbon atoms, unsaturated hydrocarbons have double and even triple bonds between the carbon atoms. Thus, unsaturated hydrocarbons are more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons and have fewer hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atoms than saturated hydrocarbons have.
Another point to be noted is that saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons can form cyclic structures also.
Let us learn a little about the different kinds of hydrocarbons.
Alkanes: They are saturated and have hydrogen and carbon atoms bonded to each other by single bonds only. Examples include Paraffin.
Alkenes: They are unsaturated having double bonds between carbons. They are extensively present in the petrochemical industry.
Alkynes: This category of hydrocarbons is unsaturated, and contains at least one carbon-to-carbon triple bond. Example is ethylene.
Cycloalkanes: These are cyclic, closed structures with single bonds between its carbon atoms. So, they are saturated.
Arenes: These are cyclic unsaturated compounds. These are aromatic in nature and contain double bonds.
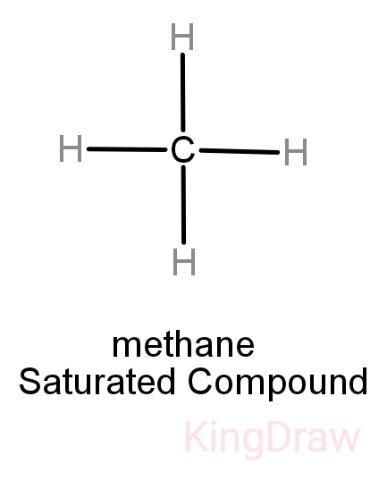
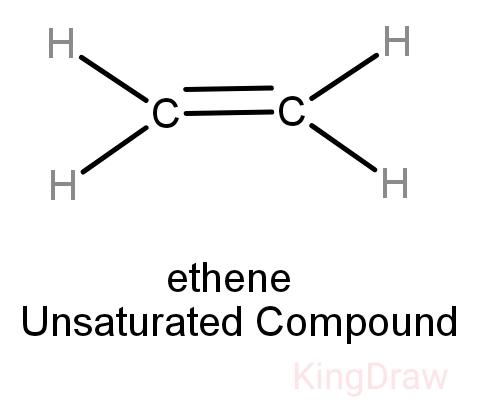
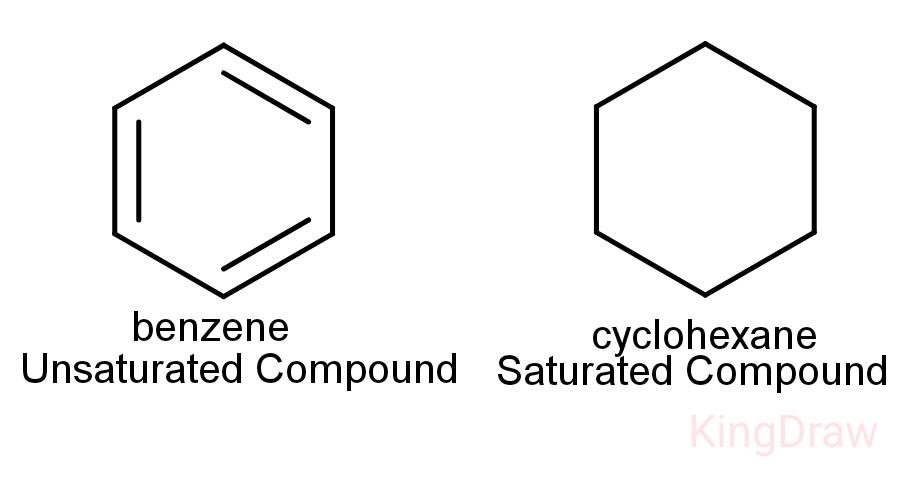
Note: It is important to remember that on burning an unsaturated hydrocarbon, sooty residues are obtained hence they are unclean. But the saturated hydrocarbons always burn with a blue flame and are generally preferred to be used as fuel over unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Complete step by step solution:
While saturated hydrocarbons only have a single bond between its hydrogen and carbon atoms, unsaturated hydrocarbons have double and even triple bonds between the carbon atoms. Thus, unsaturated hydrocarbons are more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons and have fewer hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atoms than saturated hydrocarbons have.
Another point to be noted is that saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons can form cyclic structures also.
Let us learn a little about the different kinds of hydrocarbons.
Alkanes: They are saturated and have hydrogen and carbon atoms bonded to each other by single bonds only. Examples include Paraffin.
Alkenes: They are unsaturated having double bonds between carbons. They are extensively present in the petrochemical industry.
Alkynes: This category of hydrocarbons is unsaturated, and contains at least one carbon-to-carbon triple bond. Example is ethylene.
Cycloalkanes: These are cyclic, closed structures with single bonds between its carbon atoms. So, they are saturated.
Arenes: These are cyclic unsaturated compounds. These are aromatic in nature and contain double bonds.



Note: It is important to remember that on burning an unsaturated hydrocarbon, sooty residues are obtained hence they are unclean. But the saturated hydrocarbons always burn with a blue flame and are generally preferred to be used as fuel over unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




