
What was Gregor Mendel's experiment with pea plants?
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: Gregor Johann Mendel was an astronomer and plant breeder who was a monk and teacher. He was born in 1822 and entered a monastery in Brünn at the age of 21. The monastery was a centre for science, religion, and culture, including a botanical garden and library.
Complete answer:
With his pea plants, Mendel investigated the pattern of inheritance.
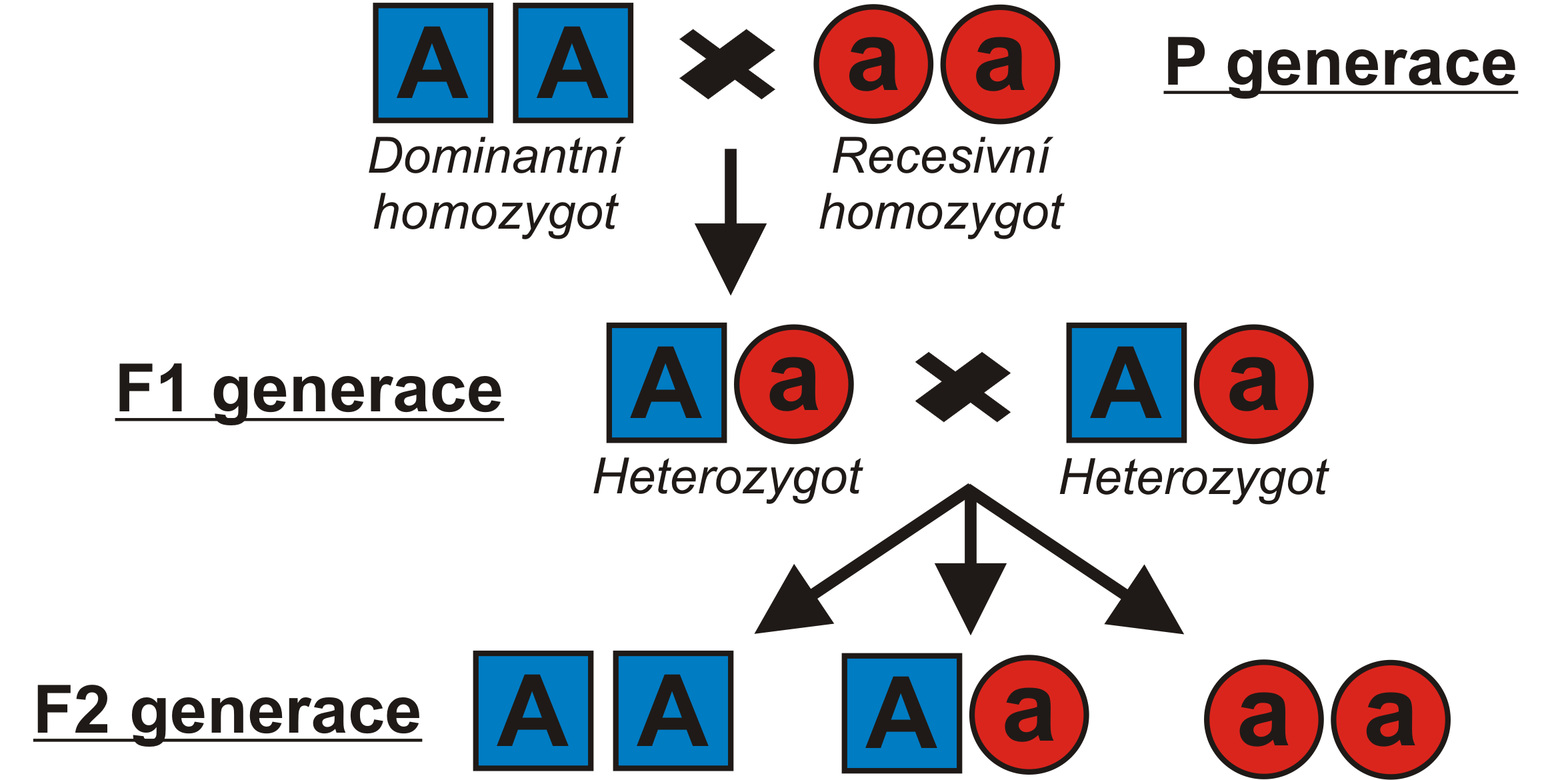
PARENTAL GENERATION : Pea plants were chosen as Mendel's specimen because they have different features that may be easily detected from one generation to the next (e.g. colour, height). First and foremost, he guaranteed that each kind bred according to type (e.g. only tall plants yield tall plants).
He mated the two opposing qualities for each attribute once he got these purebred seeds. Mendel had to emasculate the blossoms and physically transfer pollen because pea plants self-pollinate.
GENERATION F1: The offspring produced by crossing the two opposing traits was heterozygous. (For instance, TT, tt = Tt.) After that, the hybrids were self-pollinated.
Mendel researched pea inheritance (Pisum sativum). Peas were chosen because they had previously been used in comparable trials, are easy to grow, and may be planted every year. Pea flowers have both male and female components, known as stamen and stigma, and self-pollinate most of the time. Self-pollination occurs before the flowers open, resulting in several plants from a single plant.
Peas can also be cross-pollinated by hand, by removing the pollen-producing stamen from the flower buds (to avoid self-pollination) and dusting pollen from one plant onto the stigma of another.
Note:-
The garden pea, Pisum sativum, was used to examine heredity in Mendel's key work. This species spontaneously self-fertilizes, which means pollen comes into contact with eggs within the same flower. To prevent cross-pollination, the flower petals remain tightly closed until pollination is complete.
Complete answer:
With his pea plants, Mendel investigated the pattern of inheritance.
PARENTAL GENERATION : Pea plants were chosen as Mendel's specimen because they have different features that may be easily detected from one generation to the next (e.g. colour, height). First and foremost, he guaranteed that each kind bred according to type (e.g. only tall plants yield tall plants).
He mated the two opposing qualities for each attribute once he got these purebred seeds. Mendel had to emasculate the blossoms and physically transfer pollen because pea plants self-pollinate.
GENERATION F1: The offspring produced by crossing the two opposing traits was heterozygous. (For instance, TT, tt = Tt.) After that, the hybrids were self-pollinated.

Mendel researched pea inheritance (Pisum sativum). Peas were chosen because they had previously been used in comparable trials, are easy to grow, and may be planted every year. Pea flowers have both male and female components, known as stamen and stigma, and self-pollinate most of the time. Self-pollination occurs before the flowers open, resulting in several plants from a single plant.
Peas can also be cross-pollinated by hand, by removing the pollen-producing stamen from the flower buds (to avoid self-pollination) and dusting pollen from one plant onto the stigma of another.
Note:-
The garden pea, Pisum sativum, was used to examine heredity in Mendel's key work. This species spontaneously self-fertilizes, which means pollen comes into contact with eggs within the same flower. To prevent cross-pollination, the flower petals remain tightly closed until pollination is complete.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




