
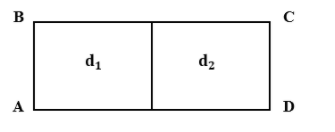
Half of the uniform rectangular plate of length ‘L’ is made up of material of density ${d}_{1}$ and the other half with density ${d}_{2}$. The perpendicular distance of mass from AB is
A. $\dfrac {2{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}} \times \dfrac {L}{4}$
B. $\dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}} \times \dfrac {L}{4}$
C. $\dfrac {3{d}_{1}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}} \times \dfrac {L}{4}$
D. $\dfrac {3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}} \times \dfrac {L}{4}$

Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, first find the mass of each half of the plate in terms of density and volume. Then, substitute the value of volume in terms of area and thickness. Find the distance of center of mass for both halves of the plate. Then, use the formula for position of center of mass, Substitute the values in the formula and find the perpendicular distance of the mass from AB.
Formula used:
$Density= \dfrac {Mass}{Volume}$
$V= At$
${X}_{CM}= \dfrac {{m}_{1}{x}_{1}+{m}_{2}{x}_{2}}{{m}_{1}+{m}_{2}}$
Complete answer:

Given: Length of the rectangular plate= L
Density of materials are ${d}_{1}$ and ${d}_{2}$ respectively.
The formula for density is given by,
$Density= \dfrac {Mass}{Volume}$
$\Rightarrow d= \dfrac {m}{V}$ …(1)
Where, d is the density of the plate
m is the mass of the plate
V is the volume of the plate
Let the area of the rectangular plate be A
The thickness of the plate be t
We know, volume of a rectangular plate is given by,
$V= At$ …(2)
Where, V is the volume of the rectangular plate
A is the area off the plate
t is the thickness of the plate
Substituting equation. (2) in equation. (1) we get,
$d= \dfrac {m}{At}$
Density of first half of the plate can be given by,
${d}_{1}= \dfrac {{m}_{1}}{\dfrac {At}{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{1}={d}_{1}\dfrac {At}{2}$
Similarly, the density of second half of the plate can be given by,
${d}_{2}= \dfrac {{m}_{2}}{\dfrac {At}{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{2}={d}_{2}\dfrac {At}{2}$
From the diagram we can infer, ${x}_{1}= \dfrac {L}{4}$ and ${x}_{2}= \dfrac{3L}{4}$.
The position for center of mass is given by,
${X}_{CM}= \dfrac {{m}_{1}{x}_{1}+{m}_{2}{x}_{2}}{{m}_{1}+{m}_{2}}$
Substituting values in above equation we get,
${X}_{CM}= \dfrac {{d}_{1}(\dfrac {At}{2})\dfrac {L}{4}+ {d}_{2}(\dfrac {At}{2})\dfrac {3L}{4}}{{ d}_{1}\dfrac {At}{2}+ { d}_{2}\dfrac {At}{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {X}_{CM}= \dfrac {\dfrac {{d}_{1}AtL+ 3{d}_{2}AtL}{8}}{\dfrac {{d}_{1}At+{d}_{2}At}{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {X}_{CM}= \dfrac {2}{8} . (\dfrac {{d}_{1}AtL+ 3{d}_{2}AtL}{{d}_{1}At+ {d}_{2}At})$
$\Rightarrow {X}_{CM}= \dfrac {2AtL}{8At} .\dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {X}_{CM}= \dfrac {L}{4} .\dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}}$
Hence, the perpendicular distance of mass from AB is $\dfrac {L}{4} .\dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}}$.
So, the correct answer is option B i.e. $ \dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}} \times \dfrac {L}{4}$
Note:
Students must understand that if they do not substitute the value of volume in terms of area and thickness, still they will get the same answer as the term At gets cancelled any way. So, if they don’t write that step, the length of the solution gets reduced. Students must try to solve a given problem in a shorter method, this will save their time and they can go to the next question.
Formula used:
$Density= \dfrac {Mass}{Volume}$
$V= At$
${X}_{CM}= \dfrac {{m}_{1}{x}_{1}+{m}_{2}{x}_{2}}{{m}_{1}+{m}_{2}}$
Complete answer:

Given: Length of the rectangular plate= L
Density of materials are ${d}_{1}$ and ${d}_{2}$ respectively.
The formula for density is given by,
$Density= \dfrac {Mass}{Volume}$
$\Rightarrow d= \dfrac {m}{V}$ …(1)
Where, d is the density of the plate
m is the mass of the plate
V is the volume of the plate
Let the area of the rectangular plate be A
The thickness of the plate be t
We know, volume of a rectangular plate is given by,
$V= At$ …(2)
Where, V is the volume of the rectangular plate
A is the area off the plate
t is the thickness of the plate
Substituting equation. (2) in equation. (1) we get,
$d= \dfrac {m}{At}$
Density of first half of the plate can be given by,
${d}_{1}= \dfrac {{m}_{1}}{\dfrac {At}{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{1}={d}_{1}\dfrac {At}{2}$
Similarly, the density of second half of the plate can be given by,
${d}_{2}= \dfrac {{m}_{2}}{\dfrac {At}{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {m}_{2}={d}_{2}\dfrac {At}{2}$
From the diagram we can infer, ${x}_{1}= \dfrac {L}{4}$ and ${x}_{2}= \dfrac{3L}{4}$.
The position for center of mass is given by,
${X}_{CM}= \dfrac {{m}_{1}{x}_{1}+{m}_{2}{x}_{2}}{{m}_{1}+{m}_{2}}$
Substituting values in above equation we get,
${X}_{CM}= \dfrac {{d}_{1}(\dfrac {At}{2})\dfrac {L}{4}+ {d}_{2}(\dfrac {At}{2})\dfrac {3L}{4}}{{ d}_{1}\dfrac {At}{2}+ { d}_{2}\dfrac {At}{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {X}_{CM}= \dfrac {\dfrac {{d}_{1}AtL+ 3{d}_{2}AtL}{8}}{\dfrac {{d}_{1}At+{d}_{2}At}{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {X}_{CM}= \dfrac {2}{8} . (\dfrac {{d}_{1}AtL+ 3{d}_{2}AtL}{{d}_{1}At+ {d}_{2}At})$
$\Rightarrow {X}_{CM}= \dfrac {2AtL}{8At} .\dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {X}_{CM}= \dfrac {L}{4} .\dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}}$
Hence, the perpendicular distance of mass from AB is $\dfrac {L}{4} .\dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}}$.
So, the correct answer is option B i.e. $ \dfrac {{d}_{1}+3{d}_{2}}{{d}_{1}+{d}_{2}} \times \dfrac {L}{4}$
Note:
Students must understand that if they do not substitute the value of volume in terms of area and thickness, still they will get the same answer as the term At gets cancelled any way. So, if they don’t write that step, the length of the solution gets reduced. Students must try to solve a given problem in a shorter method, this will save their time and they can go to the next question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




