
Herbicide DCMU [(3-(3, 4-dichlorophenyl)-1, 1-dimethyl urea)] kills plants due to stoppage of
(a)Photophosphorylation
(b)Rubisco activity
(c)Electron transport
(d)${ O }_{ 2 }$-evolution
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: It is a very specific and sensitive inhibitor of photosynthesis. It interrupts the photosynthetic electron transport chain in photosynthesis and thus reduces the ability of the plant to turn light energy into chemical energy. It does not inhibit photolysis and dehydrogenase.
Complete answer:
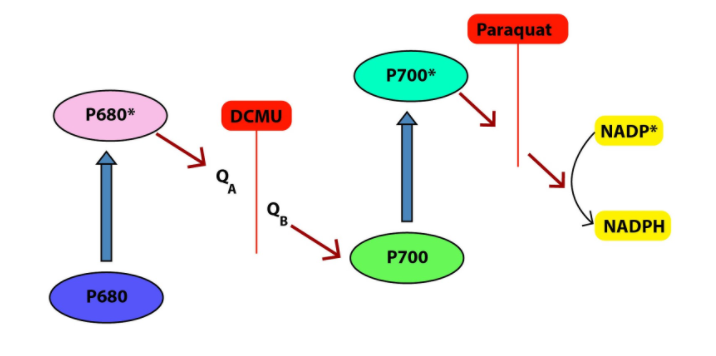
DCMU (Dichlorophenyl dimethyl urea) is an herbicide that kills the weeds by inhibiting ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ fixations as it is a strong inhibitor of photosystem II (P 680). DCMU acts by blocking electron flow at the guanine acceptors of PS II, by competing for the binding site of plastoquinone. DCMU is a plant that works on the stoppage of oxygen evolution in plants. Excess of oxygen in plants leads to the toxicity by oxygen that causes severe tissue damage.
Additional Information: One of the most important factors determining herbicide fate in the environment is its solubility in water. Water-soluble herbicides generally have low adsorption capacities and are consequently more mobile in the environment and more available for microbial metabolism and other degradation processes. The herbicides’ chemical structure dictates how the herbicide will degrade in soil. Some herbicides are rapidly decomposed by microorganisms if the right populations are present and if soil conditions are favorable for their growth.
So, the correct answer is ‘${ O }_{ 2 }$- evolution’.
Note: Herbicide symptoms and plant death are initiated by the blockage of high energy electron transfer. Light-harvesting and the production of high energy electrons carry on even though QB is not transferring an electron to cytochrome. These high electrons react with oxygen to form toxic radicals that can react with proteins and membranes making up the chloroplast. Because photosynthesis creates oxygen from water, oxygen is plentiful in the chloroplast. Some toxic oxygen radicals are always produced by normal photosynthesis.
Complete answer:
DCMU (Dichlorophenyl dimethyl urea) is an herbicide that kills the weeds by inhibiting ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ fixations as it is a strong inhibitor of photosystem II (P 680). DCMU acts by blocking electron flow at the guanine acceptors of PS II, by competing for the binding site of plastoquinone. DCMU is a plant that works on the stoppage of oxygen evolution in plants. Excess of oxygen in plants leads to the toxicity by oxygen that causes severe tissue damage.

Additional Information: One of the most important factors determining herbicide fate in the environment is its solubility in water. Water-soluble herbicides generally have low adsorption capacities and are consequently more mobile in the environment and more available for microbial metabolism and other degradation processes. The herbicides’ chemical structure dictates how the herbicide will degrade in soil. Some herbicides are rapidly decomposed by microorganisms if the right populations are present and if soil conditions are favorable for their growth.
So, the correct answer is ‘${ O }_{ 2 }$- evolution’.
Note: Herbicide symptoms and plant death are initiated by the blockage of high energy electron transfer. Light-harvesting and the production of high energy electrons carry on even though QB is not transferring an electron to cytochrome. These high electrons react with oxygen to form toxic radicals that can react with proteins and membranes making up the chloroplast. Because photosynthesis creates oxygen from water, oxygen is plentiful in the chloroplast. Some toxic oxygen radicals are always produced by normal photosynthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




