
How is carbocation formed?
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: As we know that carbocation is an organic compound, or we can say an intermediate that is formed as a result of loss of two valence electrons, basically shared electrons from a carbon atom that is already having four bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
- As we know that carbocation carries a positive charge and three bonds instead of four bonds. It is found that carbocation is formed mainly by one of the two mechanisms, that are:
- By heterolytic bond cleavage, basically by the loss of a leaving group. And we can see that this results in the ionization of a carbon atom that is attached to it.
- By addition of pi electrons: It is found that carbocation is formed by the addition of pi electrons to an electrophile. As we know that one of these two carbon atoms involved in the pi bond will have three bonds instead of four and has the positive charge.
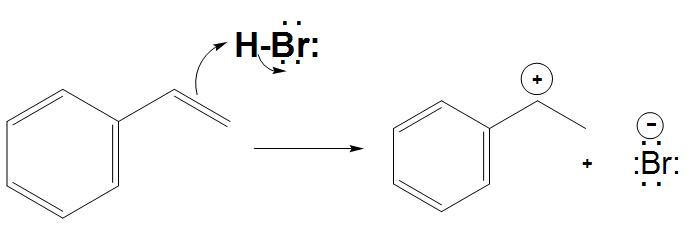
- Hence, we can say that the positively charged carbon atom is hybridised and is having trigonal planar geometry.
- It is found that the p-orbital which is not utilised is empty and is having positive charge, and also represents the orbital available to accept the electrons.
Note: - We should not get confused in the terms carbocation and carbanion. As carbocation carries a positive charge and is an electron deficient species. Whereas, carbanion is negatively charged and is an electron rich species.
Complete step by step answer:
- As we know that carbocation carries a positive charge and three bonds instead of four bonds. It is found that carbocation is formed mainly by one of the two mechanisms, that are:
- By heterolytic bond cleavage, basically by the loss of a leaving group. And we can see that this results in the ionization of a carbon atom that is attached to it.
- By addition of pi electrons: It is found that carbocation is formed by the addition of pi electrons to an electrophile. As we know that one of these two carbon atoms involved in the pi bond will have three bonds instead of four and has the positive charge.

- Hence, we can say that the positively charged carbon atom is hybridised and is having trigonal planar geometry.
- It is found that the p-orbital which is not utilised is empty and is having positive charge, and also represents the orbital available to accept the electrons.
Note: - We should not get confused in the terms carbocation and carbanion. As carbocation carries a positive charge and is an electron deficient species. Whereas, carbanion is negatively charged and is an electron rich species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




