
What is the hybridization of benzylic carbonium in the following structure :
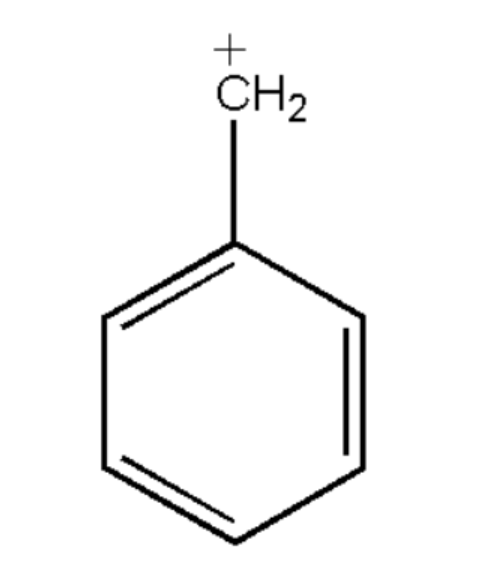
$a.{\text{ sp}}$
$b.{\text{ s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$
$c.{\text{ s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$
$d.{\text{ s}}{{\text{p}}^3}d$

Answer
505.8k+ views
Hint: Hybridization is the mixing of two orbitals of the same energy levels to give new degenerate orbitals. The carbonium ion is one which has a positive charge on it. Maximum hybridization of a carbon is $s{p^3}$. A carbon forming four sigma bonds with another atom has $s{p^3}$ hybridization.
Complete answer:
Hybridization is the redistribution of energy of orbitals of the atoms to produce new orbitals which have equivalent energy. When two orbitals are combined to form a new orbital or hybrid orbital in a molecule, this process is called hybridization. Generally we can predict the hybridisation of the element by knowing the number of sigma bonds it makes within the molecule.
For example, carbon has four valence electrons in its outermost orbit. Then it can form four sigma bonds. Also we can write its electronic configuration as: $1{s^2}{\text{ , 2}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ , 2}}{{\text{p}}^2}$$1{s^2}{\text{ , 2}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ , 2}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. Therefore we can see that there are only two electrons present in the p-subshell. Also during the hybridization the same atomic orbital takes part. Therefore, the s and p orbital take part to form four sigma bonds. One s and three orbitals take part in hybridization. Similarly, we can in the carbonium ion carbon form only three sigma bonds. So here the one s and two p orbital takes part in hybridization.
Therefore the hybridization of carbonium ions in the given figure is: $s{p^2}$. So, option (b) is correct.
Note:
When atomic orbits combine during the mixing, the electrons are in an excited state. Therefore we have one electron in the s orbital and two electrons in the p orbital for carbonium ions. Thus, overlapping takes off one s and two p orbital, which gives hybridization as $s{p^2}$.
Complete answer:
Hybridization is the redistribution of energy of orbitals of the atoms to produce new orbitals which have equivalent energy. When two orbitals are combined to form a new orbital or hybrid orbital in a molecule, this process is called hybridization. Generally we can predict the hybridisation of the element by knowing the number of sigma bonds it makes within the molecule.
For example, carbon has four valence electrons in its outermost orbit. Then it can form four sigma bonds. Also we can write its electronic configuration as: $1{s^2}{\text{ , 2}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ , 2}}{{\text{p}}^2}$$1{s^2}{\text{ , 2}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ , 2}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. Therefore we can see that there are only two electrons present in the p-subshell. Also during the hybridization the same atomic orbital takes part. Therefore, the s and p orbital take part to form four sigma bonds. One s and three orbitals take part in hybridization. Similarly, we can in the carbonium ion carbon form only three sigma bonds. So here the one s and two p orbital takes part in hybridization.
Therefore the hybridization of carbonium ions in the given figure is: $s{p^2}$. So, option (b) is correct.
Note:
When atomic orbits combine during the mixing, the electrons are in an excited state. Therefore we have one electron in the s orbital and two electrons in the p orbital for carbonium ions. Thus, overlapping takes off one s and two p orbital, which gives hybridization as $s{p^2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




