
Identify the product ‘C’ in the following reaction:
\[Aniline\xrightarrow[pyridine]{{{(C{{H}_{3}}CO)}_{2}}O}A\xrightarrow[C{{H}_{3}}COOH]{B{{r}_{2}}}B\xrightarrow{{{H}^{+}}/O{{H}^{-}}}C\]
A. acetanilide
B. p-bromoacetanilide
C. p-bromoaniline
D. o-bromoaniline
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Consider and work out the reaction in 3 stages till you get ‘C’. Formulate the product when an aromatic compound reacts with an acid anhydride. Then the product has to react with bromine in the presence of acetic acid. This product will then be hydrolyzed.
Complete answer:
First, let us consider the reaction:
\[Aniline\xrightarrow[pyridine]{{{(C{{H}_{3}}COO)}_{2}}O}A\]
The lone pair on the nitrogen of the aniline attacks one of the carbonyl carbons of the acetic anhydride. The bond that this carbonyl carbon has formed with $O$ will break and oxygen will now have a minus charge. This oxygen will then take the acidic proton from the aniline-acetic acid intermediate complex and the products acetanilide and acetic acid will be formed.
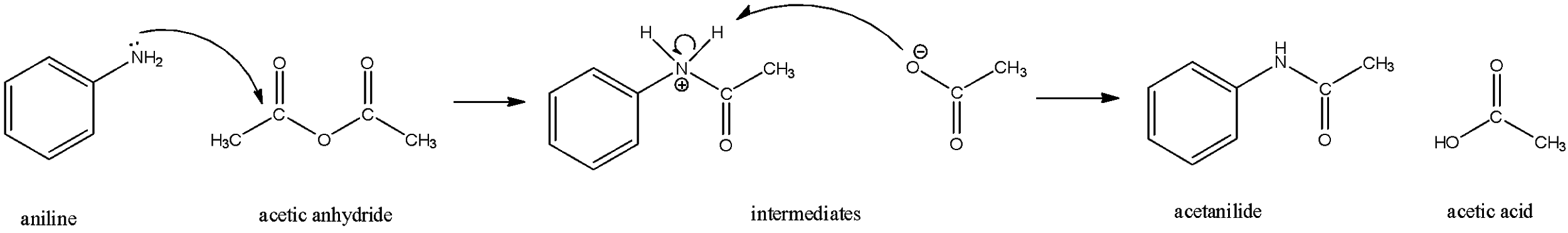
Thus, ‘A’ is acetanilide.
Now that acetanilide is formed, it will react with bromine in the presence of acetic acid.
\[\text{Acetanilide}\xrightarrow[C{{H}_{3}}COOH]{B{{r}_{2}}}B\]
Since acetanilide is an electron withdrawing group, it is ortho-para directing. The bromine will get attached to the para position since the functional group of acetanilide is too bulky for it to attach at the ortho position.
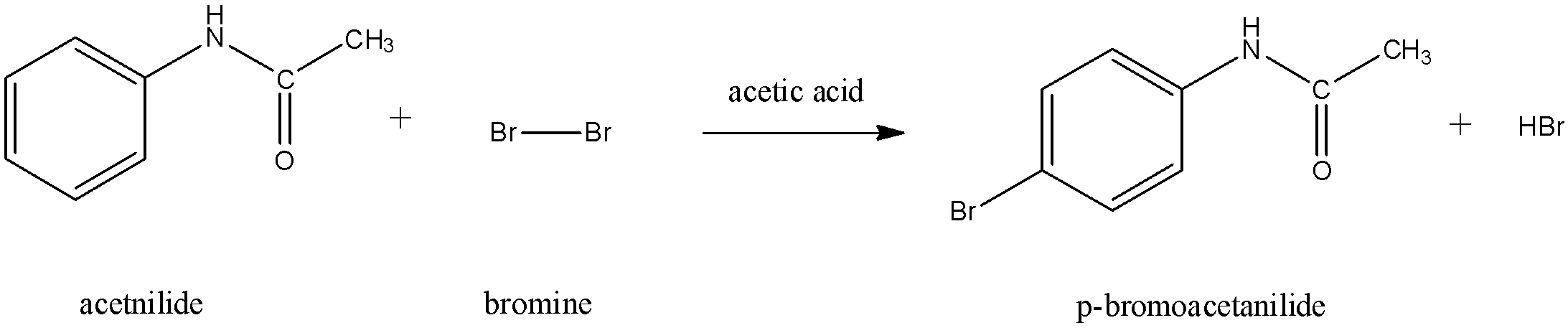
Thus, ‘B’ is p-bromoacetanilide.
Now we carry out hydrolysis of p-bromoacetanilide.
The $O{{H}^{-}}$ will attach itself to the carbonyl carbon and the ${{H}^{+}}$ ion will get attached to the nitrogen.
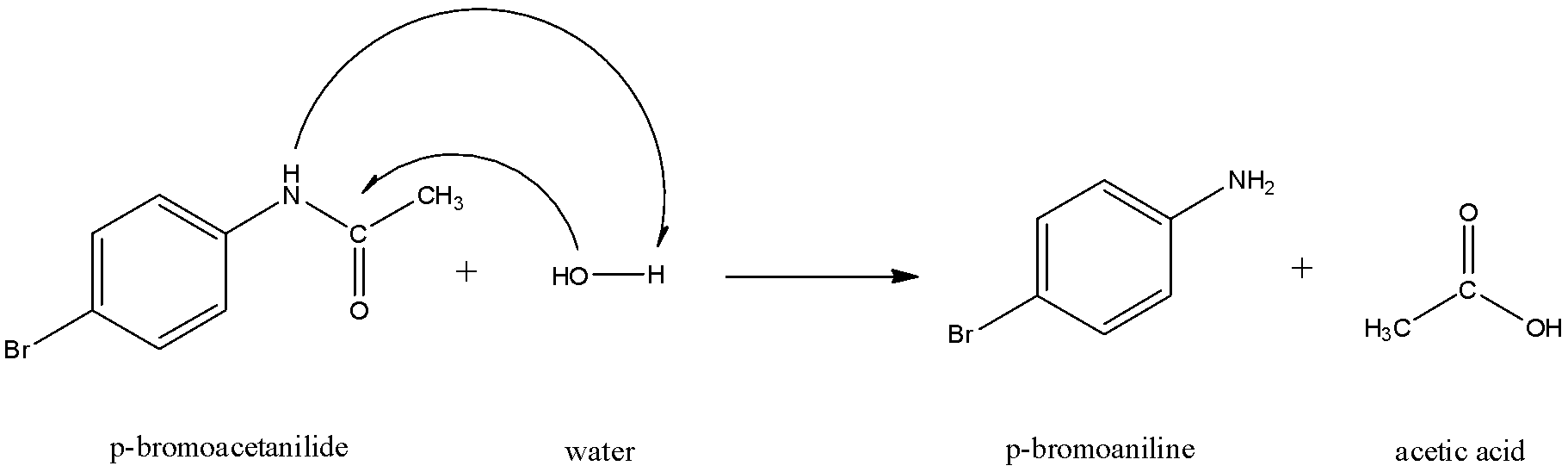
Thus, ‘C’ is p-bromoaniline
Hence, the answer is ‘C. p-bromoaniline’
Note: Remember that acetanilide has an ortho-para directing functional group and therefore o-bromoaniline may also be formed if certain reagents are added during the bromination process of acetanilide.
Complete answer:
First, let us consider the reaction:
\[Aniline\xrightarrow[pyridine]{{{(C{{H}_{3}}COO)}_{2}}O}A\]
The lone pair on the nitrogen of the aniline attacks one of the carbonyl carbons of the acetic anhydride. The bond that this carbonyl carbon has formed with $O$ will break and oxygen will now have a minus charge. This oxygen will then take the acidic proton from the aniline-acetic acid intermediate complex and the products acetanilide and acetic acid will be formed.

Thus, ‘A’ is acetanilide.
Now that acetanilide is formed, it will react with bromine in the presence of acetic acid.
\[\text{Acetanilide}\xrightarrow[C{{H}_{3}}COOH]{B{{r}_{2}}}B\]
Since acetanilide is an electron withdrawing group, it is ortho-para directing. The bromine will get attached to the para position since the functional group of acetanilide is too bulky for it to attach at the ortho position.

Thus, ‘B’ is p-bromoacetanilide.
Now we carry out hydrolysis of p-bromoacetanilide.
The $O{{H}^{-}}$ will attach itself to the carbonyl carbon and the ${{H}^{+}}$ ion will get attached to the nitrogen.

Thus, ‘C’ is p-bromoaniline
Hence, the answer is ‘C. p-bromoaniline’
Note: Remember that acetanilide has an ortho-para directing functional group and therefore o-bromoaniline may also be formed if certain reagents are added during the bromination process of acetanilide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




