
Identify the semiconductor devices whose characteristics are given above in the order (a), (b), (c), (d):
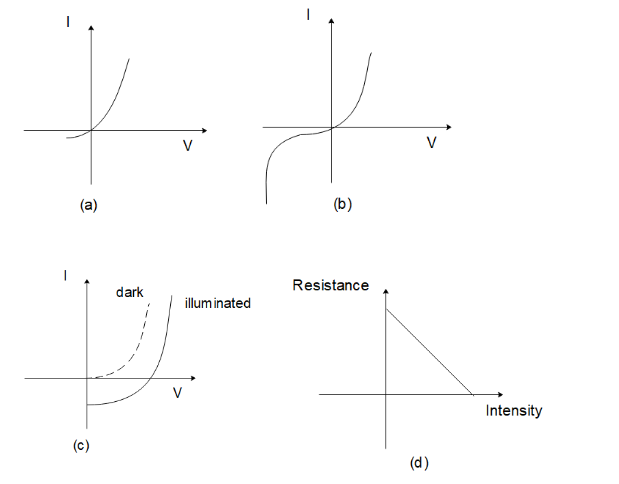
A) Simple diode, Zener diode, Solar cells, Light-dependent resistance
B) Zener diode, Simple diode, Light-dependent resistance, Solar cells
C) Solar cell, Light-dependent resistance, Zener diode, Simple diode,
D) Zener diode, Solar cell, Simple diode, Light-dependent resistance

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint To answer this question we will use the different properties of materials that utilize semiconductors. All the devices mentioned in the options, need a specific kind of semiconductor to work according to their functions.
Complete answer:
The graph given in (A) is that of a simple diode. It can generate current only in forward bias i.e. when the potential applied to the diode is positive. It cannot generate current in reverse bias where the potential is negative.
The graph in (B) corresponds to that of a Zener diode. Zener diode works like a normal diode in forwarding bias. But in reverse bias, it acts as a normal diode only up to a certain negative voltage. Beyond that voltage Zener breakdown occurs and hence they can act as voltage regulators.
The graph in option (C) corresponds to a solar cell that will operate differently in dark and light conditions.
The graph in option (D) is that of a light-dependent resistance. A light-dependent resistance is such a device that increases its resistance based on the amount of light it receives. It is often used as a light sensor due to its property.
Hence the correct choice is option (A).
Note:
To answer such questions, we should know the properties of the devices formed by using different semiconductor appliances. We can get some clues about which graph corresponds to which device e.g., a solar cell will work differently in light and dark conditions, and a light-dependent resistance will have a varying resistance both of which are only presented in one graph individually.
Complete answer:
The graph given in (A) is that of a simple diode. It can generate current only in forward bias i.e. when the potential applied to the diode is positive. It cannot generate current in reverse bias where the potential is negative.
The graph in (B) corresponds to that of a Zener diode. Zener diode works like a normal diode in forwarding bias. But in reverse bias, it acts as a normal diode only up to a certain negative voltage. Beyond that voltage Zener breakdown occurs and hence they can act as voltage regulators.
The graph in option (C) corresponds to a solar cell that will operate differently in dark and light conditions.
The graph in option (D) is that of a light-dependent resistance. A light-dependent resistance is such a device that increases its resistance based on the amount of light it receives. It is often used as a light sensor due to its property.
Hence the correct choice is option (A).
Note:
To answer such questions, we should know the properties of the devices formed by using different semiconductor appliances. We can get some clues about which graph corresponds to which device e.g., a solar cell will work differently in light and dark conditions, and a light-dependent resistance will have a varying resistance both of which are only presented in one graph individually.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




