
In a Claisen condensation reaction (when an ester is treated with a strong base):
(A)A proton is removed from the $\alpha - $ carbon to form a resonance stabilised carbanion of the ester.
(B)Carbanion acts as a nucleophile in a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction with another ester molecule.
(C)A new $C - C$ bond is formed.
(D)All of the above statements are correct.
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: When ester is treated with a strong base, it results in the formation of $\beta - $ Keto esters or a $\beta - $ diketone. In products, carbon atoms are more than the starting $1$ molecule of reactant. In claisen condensation, the one ester is made to react with another ester or with any carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know esters are organic compounds having the general formula $R - C - O - R'$ which is derived from a carboxylic acid. Esters are usually sweet smelling compounds and are considered as high quality solvents. Esters are polar compounds but less polar than alcohols. Esters are volatile compounds. Esters are responsible for sweetness in many fruits such as apples, pears, bananas and strawberries.
When ester is reacted in the presence of a strong base, it results in the formation of $\beta - $ keto esters or a $\beta - $ diketone and the process is known as claisen condensation. It is named after Rainer Ludwig Claisen who first introduced this reaction in $1887.$ For this reaction, one of the reagents should have an $\alpha - $ proton and be able to undergo deprotonation to form a carbanion.
The carbanion acts as a nucleophile in nucleophilic substitution reaction with another ester molecule which leads to the formation of a new $C - C$ bond.
The reaction of claisen condensation occur as
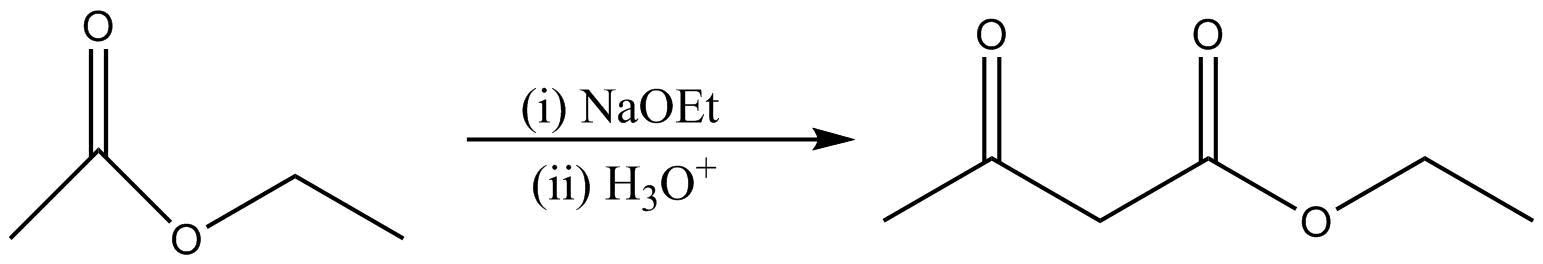
Here the two molecules of reactant should be taken in order to carry out the claisen condensation.
Mechanism of Reaction:-
Step $1$ :- The strong base leads to removal of $\alpha $ -proton from ester molecule which generates the enolate ion
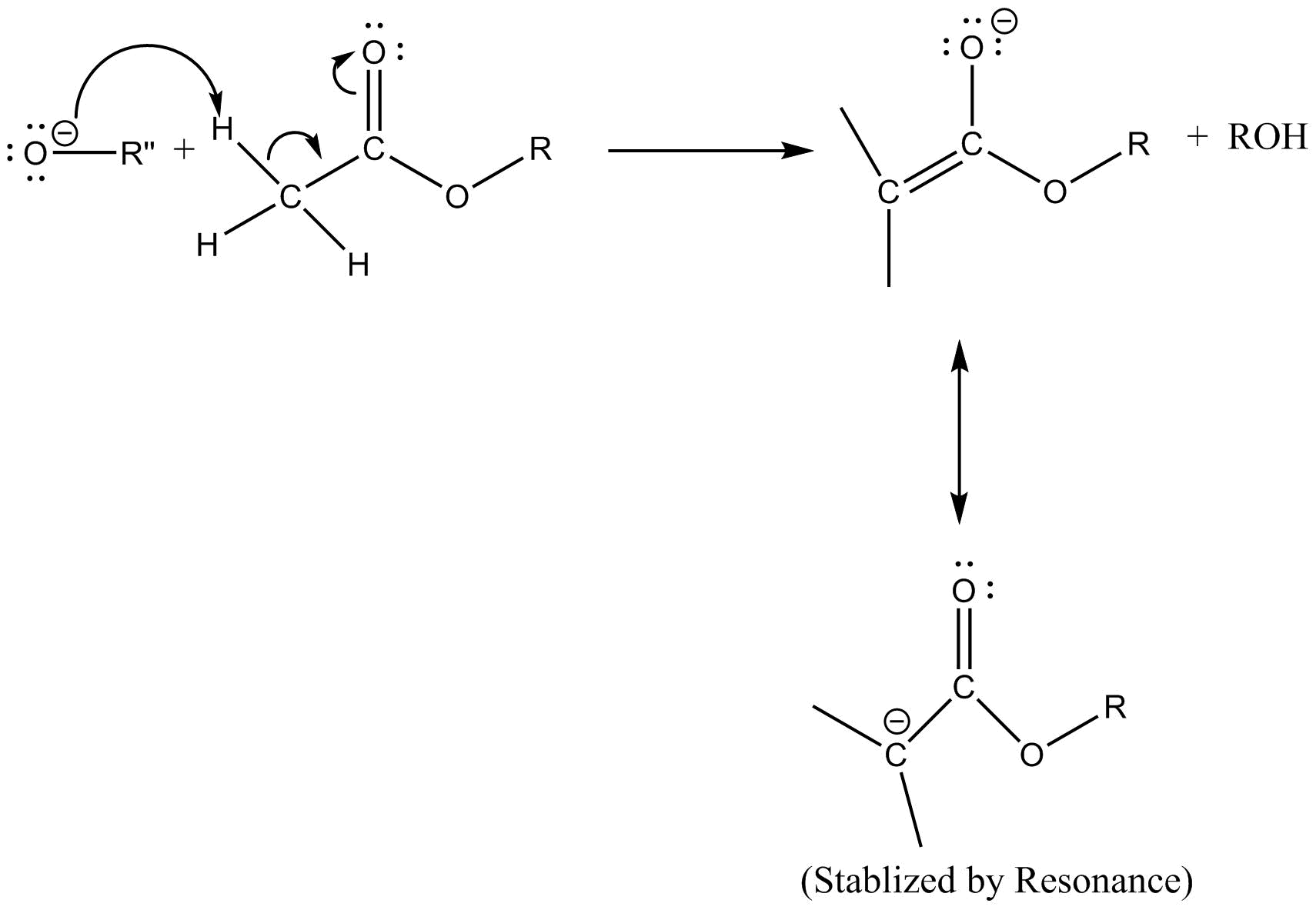
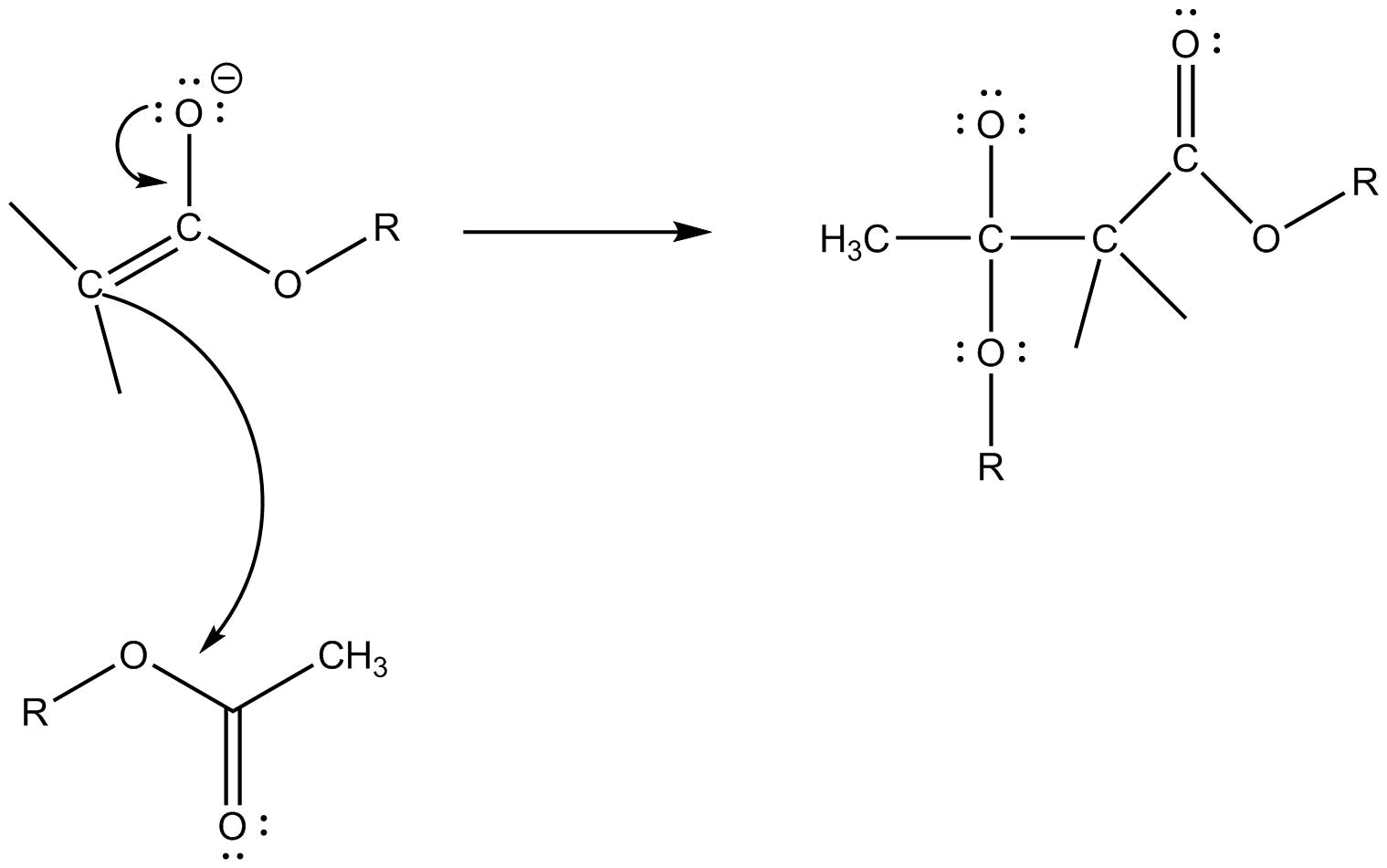
Step $2$ :- The carbonyl carbon of other molecules of ester attacks gets attacked by nucleophile products in the previous step.
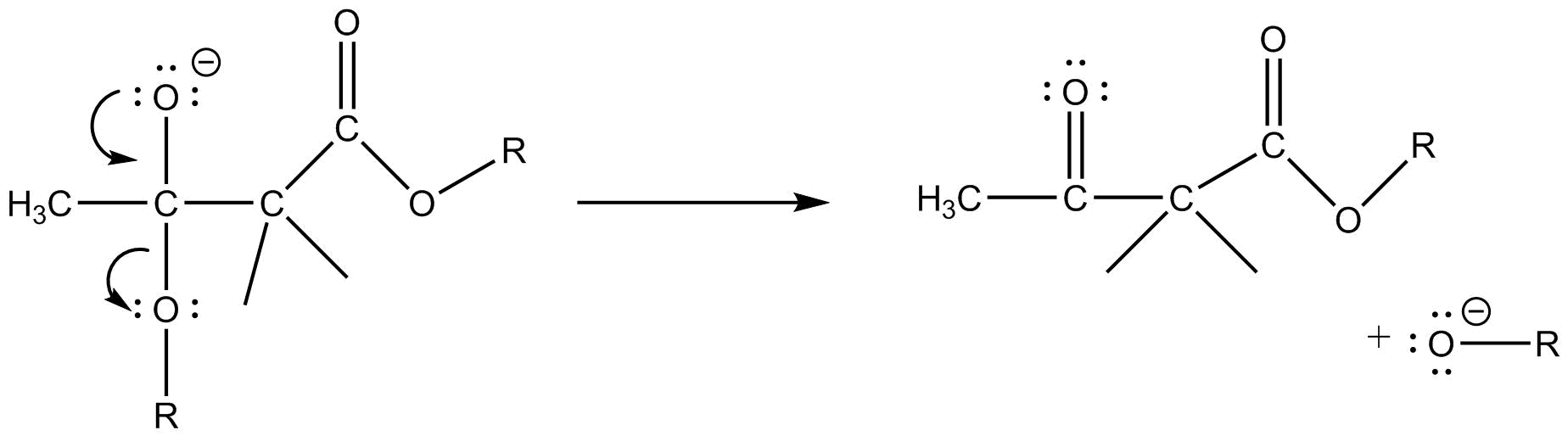
Step $3$ :- Now a dilute acid is added to remove the negative charge present and to get the required product.
Hence the statements in option (A), (B) and (C) are correct. So the correct answer is option (D).
Note:
The base used in the reaction should not interfere with the reaction by undergoing nucleophilic substitution or addition with carbonyl carbon. Moreover the alkoxy group of ester should be a good leaving group.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know esters are organic compounds having the general formula $R - C - O - R'$ which is derived from a carboxylic acid. Esters are usually sweet smelling compounds and are considered as high quality solvents. Esters are polar compounds but less polar than alcohols. Esters are volatile compounds. Esters are responsible for sweetness in many fruits such as apples, pears, bananas and strawberries.
When ester is reacted in the presence of a strong base, it results in the formation of $\beta - $ keto esters or a $\beta - $ diketone and the process is known as claisen condensation. It is named after Rainer Ludwig Claisen who first introduced this reaction in $1887.$ For this reaction, one of the reagents should have an $\alpha - $ proton and be able to undergo deprotonation to form a carbanion.
The carbanion acts as a nucleophile in nucleophilic substitution reaction with another ester molecule which leads to the formation of a new $C - C$ bond.
The reaction of claisen condensation occur as
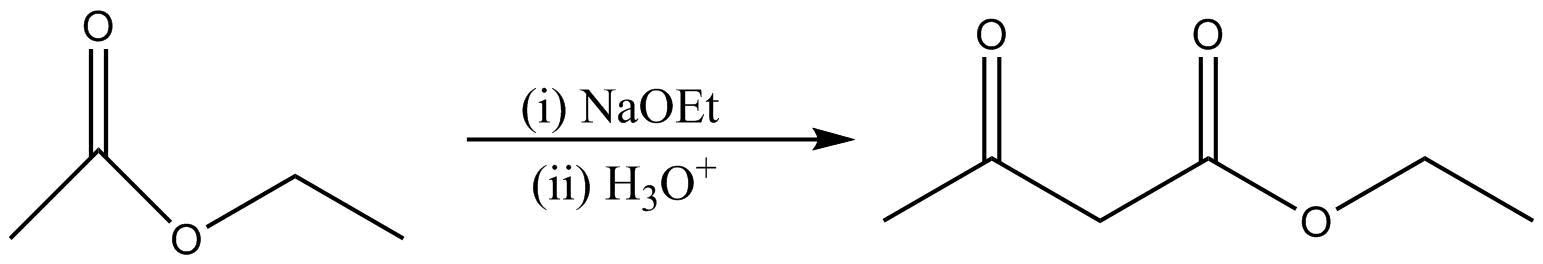
Here the two molecules of reactant should be taken in order to carry out the claisen condensation.
Mechanism of Reaction:-
Step $1$ :- The strong base leads to removal of $\alpha $ -proton from ester molecule which generates the enolate ion

Step $2$ :- The carbonyl carbon of other molecules of ester attacks gets attacked by nucleophile products in the previous step.

Step $3$ :- Now a dilute acid is added to remove the negative charge present and to get the required product.

Hence the statements in option (A), (B) and (C) are correct. So the correct answer is option (D).
Note:
The base used in the reaction should not interfere with the reaction by undergoing nucleophilic substitution or addition with carbonyl carbon. Moreover the alkoxy group of ester should be a good leaving group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




