
In a right-angled triangle, five times the square on the hypotenuse is equal to four times the sum of the squares on the medians drawn from the acute angles. Prove it.

Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: In a right-angled triangle, as the Pythagoras theorems say, ${h^2} = {p^2} + {b^2}$, where h is the hypotenuse of a right-angle triangle, p is the perpendicular and b is the base.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Consider a right angle triangle, $\vartriangle ABC$
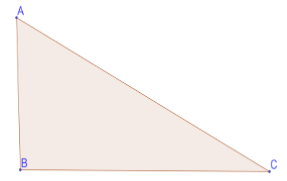
In $\vartriangle ABC$, using Pythagoras theorem, ${h^2} = {p^2} + {b^2}$, where h is the hypotenuse of a right-angle triangle, p is the perpendicular and b is the base.
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Let AB=x and BC=y
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = {x^2} + {y^2}$
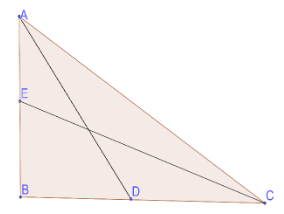
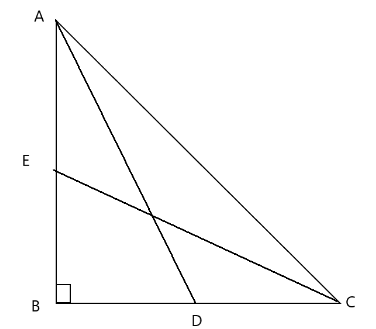
AD and CE are the median drawn from A and B respectively.
Now, further applying Pythagoras theorem in $\vartriangle ABD$, we get
$
A{D^2} = {x^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{y}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow AD = \sqrt {{x^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{y}{2}} \right)}^2}} \\
$
Similarly, In $\vartriangle ECB$,
$
C{E^2} = {y^2} + {(\dfrac{x}{2})^2} \\
\Rightarrow CE = \sqrt {{y^2} + {{(\dfrac{x}{2})}^2}} \\
$
Now, the sum of the squares of the medians is
$
\Rightarrow A{D^2} + C{E^2} = {x^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{y}{2}} \right)^2} + {y^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow A{D^2} + C{E^2} = \dfrac{5}{4}({x^2} + {y^2}) \\
\Rightarrow 4\left( {A{D^2} + C{E^2}} \right) = 5({x^2} + {y^2}) \\
$
As, we know $A{C^2} = {x^2} + {y^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 4(A{D^2} + C{E^2}) = 5A{C^2}$
Hence, five times the square on the hypotenuse is equal to four times the sum of the squares on the medians drawn from the acute angles
Note: The Median joins the vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. The properties of the median are as follows:-
The median divides the triangle into two parts of equal area.
The point of concurrency of medians is called Centroid.
The centroid divides the median in the ratio 2:1 with the larger parts toward the vertex.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Consider a right angle triangle, $\vartriangle ABC$

In $\vartriangle ABC$, using Pythagoras theorem, ${h^2} = {p^2} + {b^2}$, where h is the hypotenuse of a right-angle triangle, p is the perpendicular and b is the base.
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Let AB=x and BC=y
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = {x^2} + {y^2}$

AD and CE are the median drawn from A and B respectively.
Now, further applying Pythagoras theorem in $\vartriangle ABD$, we get
$
A{D^2} = {x^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{y}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow AD = \sqrt {{x^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{y}{2}} \right)}^2}} \\
$
Similarly, In $\vartriangle ECB$,
$
C{E^2} = {y^2} + {(\dfrac{x}{2})^2} \\
\Rightarrow CE = \sqrt {{y^2} + {{(\dfrac{x}{2})}^2}} \\
$
Now, the sum of the squares of the medians is
$
\Rightarrow A{D^2} + C{E^2} = {x^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{y}{2}} \right)^2} + {y^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow A{D^2} + C{E^2} = \dfrac{5}{4}({x^2} + {y^2}) \\
\Rightarrow 4\left( {A{D^2} + C{E^2}} \right) = 5({x^2} + {y^2}) \\
$
As, we know $A{C^2} = {x^2} + {y^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 4(A{D^2} + C{E^2}) = 5A{C^2}$
Hence, five times the square on the hypotenuse is equal to four times the sum of the squares on the medians drawn from the acute angles
Note: The Median joins the vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. The properties of the median are as follows:-
The median divides the triangle into two parts of equal area.
The point of concurrency of medians is called Centroid.
The centroid divides the median in the ratio 2:1 with the larger parts toward the vertex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




