
In an AC circuit $R=0\Omega $, ${{X}_{L}}=8\Omega $ & ${{X}_{C}}=6\Omega $ phase difference between voltage and current is :
A) ${{11}^{0}}$
B) ${{90}^{0}}$
C) ${{37}^{0}}$
D) ${{12}^{0}}$
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: The phase difference between voltage and current varies for RC and RC circuit. In resistors the phase difference between voltage and current are in phase. In RC the current leads the voltage and in the RC Current lags the voltage in the inductor we consider current whereas in capacitor we consider voltage.
Complete step-by-step solution:
when the capacitor or inductor are present in an AC circuit. The current and the voltage cannot peak at the same time the fraction of a period difference between the peaks expressed in degree is said to be the phase difference. In inductive circuits the current lags the voltage and in the capacitive circuit the current leads the voltage . Phasor diagram of $RLC$ circuit .
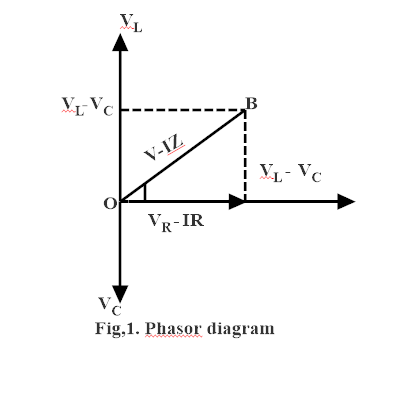
The phasor diagram of the $RLC$ series circuit when the circuit as an inductive circuit means$({{V}_{L}}>{{V}_{C}})$ is shown below and if $({{V}_{L}}<{{V}_{C}})$ the circuit will behave as a capacitive circuit
$V=\sqrt{{{V}_{R}}^{2}+{{({{V}_{L}}-{{V}_{C}})}^{2}}}$
$\phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{{{V}_{L}}-{{V}_{C}}}{{{V}_{R}}}$
$impedance(z)=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{({{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}})}^{2}}}$
$phase angle(\phi )={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}}}{R}$ $\cdots \cdots (1)$
Power in $RLC$ series circuit is given by
$P=VI\cos \varphi $
Power factor is given by
$\cos \varphi =\dfrac{{{V}_{R}}}{V}$
In the question they have given the values of $R=0\Omega $ ${{X}_{L}}=8\Omega $ & ${{X}_{C}}=6\Omega $
Substitute in formula (1)
On substituting
$\phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{(8-6)}{0}$
$\phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{2}{0}$
$\phi =90$
So option B is correct.
Note: In a pure ohmic resistance, the current and voltage are both in phase as there is no phase difference between them. The current flows through the resistance is directly proportional to the voltage across it with this linear relationship in an AC circuit being called impedance and the indian standard frequency is 50Hz.
Complete step-by-step solution:
when the capacitor or inductor are present in an AC circuit. The current and the voltage cannot peak at the same time the fraction of a period difference between the peaks expressed in degree is said to be the phase difference. In inductive circuits the current lags the voltage and in the capacitive circuit the current leads the voltage . Phasor diagram of $RLC$ circuit .

The phasor diagram of the $RLC$ series circuit when the circuit as an inductive circuit means$({{V}_{L}}>{{V}_{C}})$ is shown below and if $({{V}_{L}}<{{V}_{C}})$ the circuit will behave as a capacitive circuit
$V=\sqrt{{{V}_{R}}^{2}+{{({{V}_{L}}-{{V}_{C}})}^{2}}}$
$\phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{{{V}_{L}}-{{V}_{C}}}{{{V}_{R}}}$
$impedance(z)=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{({{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}})}^{2}}}$
$phase angle(\phi )={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{{{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}}}{R}$ $\cdots \cdots (1)$
Power in $RLC$ series circuit is given by
$P=VI\cos \varphi $
Power factor is given by
$\cos \varphi =\dfrac{{{V}_{R}}}{V}$
In the question they have given the values of $R=0\Omega $ ${{X}_{L}}=8\Omega $ & ${{X}_{C}}=6\Omega $
Substitute in formula (1)
On substituting
$\phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{(8-6)}{0}$
$\phi ={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{2}{0}$
$\phi =90$
So option B is correct.
Note: In a pure ohmic resistance, the current and voltage are both in phase as there is no phase difference between them. The current flows through the resistance is directly proportional to the voltage across it with this linear relationship in an AC circuit being called impedance and the indian standard frequency is 50Hz.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




