
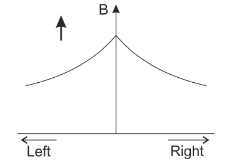
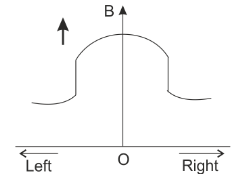
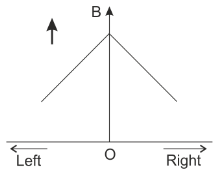
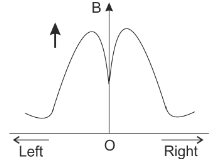
In an experiment using tangent galvanometer, the magnetic induction is measured at various points on the axis of a current carrying circular coil on both sides of the center O of the coil. The variation of magnetic field along the axis is best represented in the curve:
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
552.9k+ views
Hint: In a current carrying coil the electric current creates a magnetic field which is more concentrated in the center of the coil than outside the loop. According to Biot-Savart’s law, the magnetic field at a point due to an element of a conductor carrying current is,
-Directly proportional to the strength of the current.
-Directly proportional to the length of the element.
-Directly proportional to the Sine of the angle between the element and the line joining the element to the point.
-Inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the element and the point.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume that the radius of the coil be R.
Then the magnetic field at distance r on the axis of coil is given by,
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I{R^2}}}{{2{{({r^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}$
Now when $r > > R$
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I{R^2}}}{{2{r^3}}}$
Since radius of the coil and current are constant we can say that,
$B \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r^3}}}......(1)$
Now at the center of the coil we have,
$r = R$
Hence, the expression for magnetic field becomes
$
B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I{r^2}}}{{{r^3}}} \\
\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{r} \\ $
Since, current is constant Therefore, we have
$B \propto \dfrac{1}{r}......(2)$
From (1) and (2) we can observe that the plot for magnetic field due to current carrying coil is
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
B& \propto &{\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\dfrac{1}{{{r^3}}}}&{r > > R} \\
{\dfrac{1}{r}}&{r = R}
\end{array}} \right\}}
\end{array}\]
It is clear from the above equations that option B is the correct representation.
Note:When a current flows in a wire, it creates a circular magnetic field around the wire. This magnetic field can deflect the needle of a magnetic compass. The strength of a magnetic field is directly proportional to the current flowing. Therefore, if an alternating current is flowing, a magnetic field around the conductor will be produced, that is in phase with the alternating current.
-Directly proportional to the strength of the current.
-Directly proportional to the length of the element.
-Directly proportional to the Sine of the angle between the element and the line joining the element to the point.
-Inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the element and the point.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume that the radius of the coil be R.
Then the magnetic field at distance r on the axis of coil is given by,
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I{R^2}}}{{2{{({r^2} + {R^2})}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}$
Now when $r > > R$
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I{R^2}}}{{2{r^3}}}$
Since radius of the coil and current are constant we can say that,
$B \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r^3}}}......(1)$
Now at the center of the coil we have,
$r = R$
Hence, the expression for magnetic field becomes
$
B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I{r^2}}}{{{r^3}}} \\
\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{r} \\ $
Since, current is constant Therefore, we have
$B \propto \dfrac{1}{r}......(2)$
From (1) and (2) we can observe that the plot for magnetic field due to current carrying coil is
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
B& \propto &{\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\dfrac{1}{{{r^3}}}}&{r > > R} \\
{\dfrac{1}{r}}&{r = R}
\end{array}} \right\}}
\end{array}\]
It is clear from the above equations that option B is the correct representation.
Note:When a current flows in a wire, it creates a circular magnetic field around the wire. This magnetic field can deflect the needle of a magnetic compass. The strength of a magnetic field is directly proportional to the current flowing. Therefore, if an alternating current is flowing, a magnetic field around the conductor will be produced, that is in phase with the alternating current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




