
In an inverting amplifier, what must be the phase difference between input and output voltages?
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Amplifier is a device which is used to increase the amplitude of electric signals. Amplifier which inverts the input voltage is known as an inverting amplifier.
The inversion in phase is due to the feedback being negative in value. Negative feedback occurs when a part of output voltage is connected to inverting input of op-amp.
Complete answer:
Amplifier is an electronic device which increases one or more of the input signal’s parameters, voltage, current, or power.
An inverting amplifier is that amplifier in which the output is 180 degrees out of phase with the input. A non-inverting amplifier is that in which the output is in phase with the input.
Therefore, for an amplifier to be inverting there must be a phase difference of ${{180}^{{}^\circ }}$ between input and output voltages.
Additional Information:
An ideal Operational Amplifier or op-amp has following characteristics:
1. It has infinite input impedance.
2. It has zero output impedance
3. It has infinite bandwidth
4. It has infinite open loop gain
Therefore, we apply a resistance between the negative terminal of the op-amp and the output terminal. This resistance is called negative feedback resistance and is denoted by R with subscript f i.e. ${{R}_{f}}$
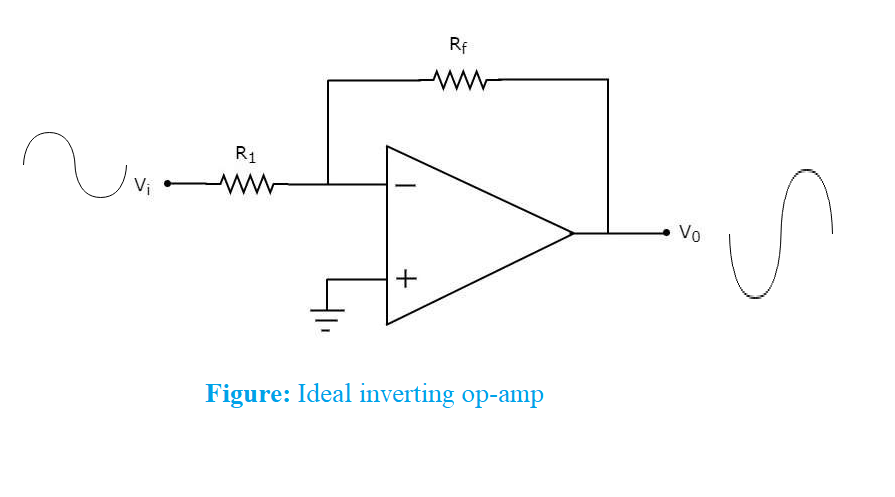
An op-amp, with configuration shown below, behaves as an inverting amplifier.
Note:
Inverting amplifier has a phase difference of ${{180}^{{}^\circ }}$ between input and output voltage.
Non-inverting amplifier, as the name suggests, does not invert the phase of the input signal.
Output voltage ${{V}_{o}}$ of an inverting amplifier is ${{V}_{o}}=-\dfrac{{{R}_{f}}}{{{R}_{1}}}{{V}_{i}}$, where ${{R}_{f}}$, ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{V}_{i}}$ are as shown in figure.
The inversion in phase is due to the feedback being negative in value. Negative feedback occurs when a part of output voltage is connected to inverting input of op-amp.
Complete answer:
Amplifier is an electronic device which increases one or more of the input signal’s parameters, voltage, current, or power.
An inverting amplifier is that amplifier in which the output is 180 degrees out of phase with the input. A non-inverting amplifier is that in which the output is in phase with the input.
Therefore, for an amplifier to be inverting there must be a phase difference of ${{180}^{{}^\circ }}$ between input and output voltages.
Additional Information:
An ideal Operational Amplifier or op-amp has following characteristics:
1. It has infinite input impedance.
2. It has zero output impedance
3. It has infinite bandwidth
4. It has infinite open loop gain
Therefore, we apply a resistance between the negative terminal of the op-amp and the output terminal. This resistance is called negative feedback resistance and is denoted by R with subscript f i.e. ${{R}_{f}}$
An op-amp, with configuration shown below, behaves as an inverting amplifier.

Note:
Inverting amplifier has a phase difference of ${{180}^{{}^\circ }}$ between input and output voltage.
Non-inverting amplifier, as the name suggests, does not invert the phase of the input signal.
Output voltage ${{V}_{o}}$ of an inverting amplifier is ${{V}_{o}}=-\dfrac{{{R}_{f}}}{{{R}_{1}}}{{V}_{i}}$, where ${{R}_{f}}$, ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{V}_{i}}$ are as shown in figure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




