
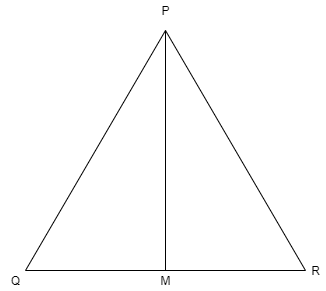
In \[\Delta PQR\] , \[PM\] is the median. If \[PM=26cm\] and \[QR=24cm\] , then find \[P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}\] .

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: We solve this problem by using the cosine rule of a triangle. Cosine rule states that if \[a,b,c\] are the sides of \[\Delta ABC\] then cosine rule for any angle is given as
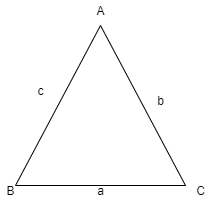
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle A \right)=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{2bc}\] . Similarly for the other two angles.
From the question we apply cosine rule to both the angles present at the point \['M'\] which will be added to zero to get the required result.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that \[PM\] is the median which means \['M'\] is midpoint of \[QR\]
So, we can write \[QM=MR=12cm\]
Let us consider the two angles that are formed by \['M'\] then, we can write
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle PMQ+\angle PMR={{180}^{0}} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle PMQ={{180}^{0}}-\angle PMR \\
\end{align}\]
By applying cosine function on both sides we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=-\cos \left( \angle PMR \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)+\cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=0...equation(i) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us find the two parameters in equation (i)
Let us consider the triangle \[\Delta PMQ\]
We know that cosine rule states that if \[a,b,c\] are the sides of \[\Delta ABC\] then cosine rule for any angle is given as
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle A \right)=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{2bc}\] .
By using this theorem to \[\Delta PMQ\] we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=\dfrac{P{{M}^{2}}+M{{Q}^{2}}-P{{Q}^{2}}}{2.PM.MQ}\]
By substituting the required values in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=\dfrac{{{12}^{2}}+{{26}^{2}}-P{{Q}^{2}}}{2\times 12\times 26} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=\dfrac{144+676-P{{Q}^{2}}}{624} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=\dfrac{820-P{{Q}^{2}}}{624} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us calculate the other part.
Let us consider the triangle \[\Delta PMR\]
By using cosine theorem to \[\Delta PMR\] we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=\dfrac{P{{M}^{2}}+M{{R}^{2}}-P{{R}^{2}}}{2.PM.MR}\]
By substituting the required values in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=\dfrac{{{12}^{2}}+{{26}^{2}}-P{{R}^{2}}}{2\times 12\times 26} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=\dfrac{144+676-P{{R}^{2}}}{624} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=\dfrac{820-P{{R}^{2}}}{624} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by substituting the results we found in equation (i) we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)+\cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{820-P{{Q}^{2}}}{624}+\dfrac{820-P{{R}^{2}}}{624}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=1640 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the value of \[P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}\] is 1640.
Note: We can solve this problem by using the direct result of median that is, if \[PM\] is the median of triangle \[\Delta PQR\] then the direct condition is
\[\Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=2P{{M}^{2}}+\dfrac{Q{{R}^{2}}}{2}\]
By substituting the required values we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=2{{\left( 26 \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{24}^{2}}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=1352+288 \\
& \Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=1640 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the value of \[P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}\] is 1640.

\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle A \right)=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{2bc}\] . Similarly for the other two angles.
From the question we apply cosine rule to both the angles present at the point \['M'\] which will be added to zero to get the required result.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that \[PM\] is the median which means \['M'\] is midpoint of \[QR\]
So, we can write \[QM=MR=12cm\]
Let us consider the two angles that are formed by \['M'\] then, we can write
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle PMQ+\angle PMR={{180}^{0}} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle PMQ={{180}^{0}}-\angle PMR \\
\end{align}\]
By applying cosine function on both sides we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=-\cos \left( \angle PMR \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)+\cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=0...equation(i) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us find the two parameters in equation (i)
Let us consider the triangle \[\Delta PMQ\]
We know that cosine rule states that if \[a,b,c\] are the sides of \[\Delta ABC\] then cosine rule for any angle is given as
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle A \right)=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{2bc}\] .
By using this theorem to \[\Delta PMQ\] we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=\dfrac{P{{M}^{2}}+M{{Q}^{2}}-P{{Q}^{2}}}{2.PM.MQ}\]
By substituting the required values in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=\dfrac{{{12}^{2}}+{{26}^{2}}-P{{Q}^{2}}}{2\times 12\times 26} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=\dfrac{144+676-P{{Q}^{2}}}{624} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)=\dfrac{820-P{{Q}^{2}}}{624} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us calculate the other part.
Let us consider the triangle \[\Delta PMR\]
By using cosine theorem to \[\Delta PMR\] we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=\dfrac{P{{M}^{2}}+M{{R}^{2}}-P{{R}^{2}}}{2.PM.MR}\]
By substituting the required values in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=\dfrac{{{12}^{2}}+{{26}^{2}}-P{{R}^{2}}}{2\times 12\times 26} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=\dfrac{144+676-P{{R}^{2}}}{624} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=\dfrac{820-P{{R}^{2}}}{624} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by substituting the results we found in equation (i) we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \angle PMQ \right)+\cos \left( \angle PMR \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{820-P{{Q}^{2}}}{624}+\dfrac{820-P{{R}^{2}}}{624}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=1640 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the value of \[P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}\] is 1640.
Note: We can solve this problem by using the direct result of median that is, if \[PM\] is the median of triangle \[\Delta PQR\] then the direct condition is
\[\Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=2P{{M}^{2}}+\dfrac{Q{{R}^{2}}}{2}\]
By substituting the required values we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=2{{\left( 26 \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{24}^{2}}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=1352+288 \\
& \Rightarrow P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}=1640 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the value of \[P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}\] is 1640.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




