
In jaundice, which organ is mainly affected?
(a) Liver
(b) Kidney
(c) Lungs
(d) Brain
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: Jaundice is a clinical condition caused due to disturbed metabolism and the production of the bilirubin.
Complete answer: The liver is the most affected organ by jaundice. Jaundice refers to the yellowing of the skin, soft tissues, and mucus membranes in our body such as the sclera of eyes, nails, palm, etc. due to the abnormal definition of bile pigments (hyperbilirubinemia). The normal level of bilirubin in our blood is 0.2-0.8mg/dl. In jaundice, this level rises to approximately >2 mg/dl.
The bilirubin formed by the liver cannot flow freely in the blood. Instead, it binds with the albumin. This is known as Conjugation. It takes place in the liver or blood.
The normal level of unconjugated bilirubin is 0.2-0.5 and that of conjugated bilirubin is 0.2-0.8.
Jaundice can be divided into three types-
So, the correct answer is ‘Liver'.
Note:
1. Jaundice is not a disease but only a sign of some underlying pathological condition or disease. It can also occur physiologically i.e. in absence of a disease in newborn babies.
2. Latent jaundice- It refers to the condition when the blood bilirubin level is between 0.8-2 mg/dl.
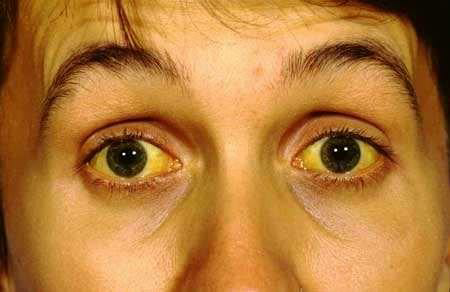
Complete answer: The liver is the most affected organ by jaundice. Jaundice refers to the yellowing of the skin, soft tissues, and mucus membranes in our body such as the sclera of eyes, nails, palm, etc. due to the abnormal definition of bile pigments (hyperbilirubinemia). The normal level of bilirubin in our blood is 0.2-0.8mg/dl. In jaundice, this level rises to approximately >2 mg/dl.
The bilirubin formed by the liver cannot flow freely in the blood. Instead, it binds with the albumin. This is known as Conjugation. It takes place in the liver or blood.
The normal level of unconjugated bilirubin is 0.2-0.5 and that of conjugated bilirubin is 0.2-0.8.
Jaundice can be divided into three types-
| Pre-hepatic or Hemolytic | Intrahepatic or Obstructive | Post-hepatic |
| It is caused due to excessive breakdown of RBCs in conditions like hereditary spherocytosis, malaria, mismatched blood transfusion, etc. | It is caused due to the blockage of the bile duct or common hepatic duct. This results in the diffusion of the bile pigments into the surrounding blood. | It is caused due to certain hepatic diseases such as Gilbert syndrome, hepatocellular cancer, etc. It leads to defect in the conjugation of bile or release of bile |
| Unconjugated bilirubin is mainly found. | The bilirubin is mainly conjugated. | The bilirubin can be conjugated or unconjugated. |
So, the correct answer is ‘Liver'.
Note:
1. Jaundice is not a disease but only a sign of some underlying pathological condition or disease. It can also occur physiologically i.e. in absence of a disease in newborn babies.
2. Latent jaundice- It refers to the condition when the blood bilirubin level is between 0.8-2 mg/dl.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




