
In phenol, electrophilic substitution takes place at
(A) m-position
(B) o-position
(C) p-position
(D) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: In the phenol molecule, a hydroxyl group is attached to the benzene ring. A chemical reaction in which the functional group attached to a compound is replaced by an electrophile is called an electrophilic substitution reaction. Due to rich electron density, phenols are highly prone to electrophilic substitution reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
- As we know, Phenols are those aromatic compounds which have a hydroxyl group (OH) directly attached to the benzene ring. The OH group is attached to $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid carbon of the aromatic ring and the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group has two lone pairs of electrons.
- A chemical reaction in which the functional group attached to a compound is replaced by an electrophile (electron loving group) is known as an electrophilic substitution reaction. The displaced functional group will be usually a hydrogen atom.
- Generally the electrophilic substitution reactions proceed via a three-step mechanism which involves the steps such as generation of electrophile, formation of a carbocation intermediate and removal of a proto from the intermediate.
- As we mentioned, due to rich electron density Phenols are highly prone to electrophilic substitution reactions. The hydroxyl group (OH) which is attached to the aromatic ring (benzene) in phenol enables the effective delocalization of the charge in the aromatic ring and thus it stabilizes the arenium ion through resonance. The resonance structures of phenol is given below
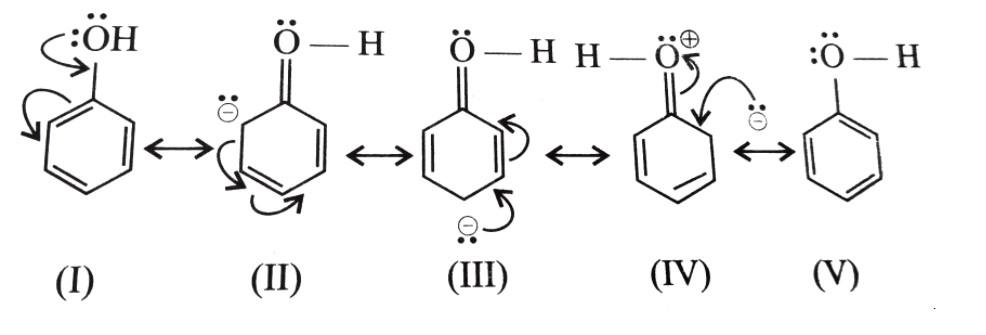
- As we can see, the electron density at ortho and para positions in phenol will be greater than the electron density at Meta position. This means that the hydroxyl group (−OH) is an ortho-para directing group towards an electron loving species or an electrophile. Therefore, the Electrophilic substitution reaction in phenol takes place at ortho and para position.
Thus the answer is option (D) Both (b) and (C)
Note: Also, keep in mind that the OH group is an electron donating group and it can activate the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution at ortho and para positions. The main examples for the Electrophilic substitution reaction of phenols include the nitration of phenols, halogenation of phenols, Kolbe’s reaction, Riemer-Tiemann reaction etc.
Complete step by step solution:
- As we know, Phenols are those aromatic compounds which have a hydroxyl group (OH) directly attached to the benzene ring. The OH group is attached to $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid carbon of the aromatic ring and the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group has two lone pairs of electrons.
- A chemical reaction in which the functional group attached to a compound is replaced by an electrophile (electron loving group) is known as an electrophilic substitution reaction. The displaced functional group will be usually a hydrogen atom.
- Generally the electrophilic substitution reactions proceed via a three-step mechanism which involves the steps such as generation of electrophile, formation of a carbocation intermediate and removal of a proto from the intermediate.
- As we mentioned, due to rich electron density Phenols are highly prone to electrophilic substitution reactions. The hydroxyl group (OH) which is attached to the aromatic ring (benzene) in phenol enables the effective delocalization of the charge in the aromatic ring and thus it stabilizes the arenium ion through resonance. The resonance structures of phenol is given below

- As we can see, the electron density at ortho and para positions in phenol will be greater than the electron density at Meta position. This means that the hydroxyl group (−OH) is an ortho-para directing group towards an electron loving species or an electrophile. Therefore, the Electrophilic substitution reaction in phenol takes place at ortho and para position.
Thus the answer is option (D) Both (b) and (C)
Note: Also, keep in mind that the OH group is an electron donating group and it can activate the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution at ortho and para positions. The main examples for the Electrophilic substitution reaction of phenols include the nitration of phenols, halogenation of phenols, Kolbe’s reaction, Riemer-Tiemann reaction etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




