
In potassium chloride, ionic bond formation takes place between potassium and chloride:
A. True
B. False
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Ionic bonding can be described as the complete transfer of valence electrons between atoms. It is the type of a bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. In case of the ionic bonds, the metal ion loses electrons to become a positively charged cation, whereas the non- metal ion accepts those electrons to become a negatively charged anion.
Complete step by step answer:
Formation of potassium chloride, $KCl$
- A potassium atom has a proton number of $19$ and it’s electron arrangement is of $2.8.8.1$
- A potassium atom has one valence electron in its valence shell.
- During the bond formation, each of the potassium atom loses one electron from its valence shell to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement to achieve the electron arrangement of its closest noble gas i.e Argon (proton number $18$). A positive ion, ${K^ + }$ is formed.
$K(2.8.8.1) \to K(2.8.8) + {e^ - }$
- The electron lost by the potassium atom is transferred to the chlorine atom.
- A chlorine atom has a proton number of $17$ and an electron arrangement of $2.8.7$
- A chlorine atom has seven valence electrons in its valence shell.
- Each chlorine atom gains one electron from a potassium atom into its valence shell to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement to achieve the electron arrangement of its closest noble gas i.e Argon (proton number $18$ ) A negative ion. $C{l^ - }$ is formed. $Cl(2.8.7) + {e^ - } \to C{l^ - }(2.8.8)$
- Figure shows the formation of an ionic bond.
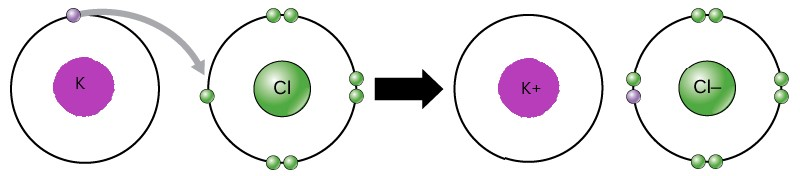
-The oppositely-charged ions formed, ${K^ + }$ and $C{l^ - }$ , are then strongly attracted to each other by strong electrostatic forces in the crystal lattice, called ionic bonds or electrovalent bonds.
-Hence, the ionic compound potassium chloride with the formula $KCl$ is formed.
Therefore, the correct option is (A) .
Note:Apart from ionic bonding, another type of bonding is called the covalent bonding. Covalent bonding is described as the sharing of electrons between atoms. This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of elements close to each other in the periodic table. This bonding occurs primarily between non-metals, although it can also be observed between nonmetals and metals. . Ionic bonds require an electron donor, most likely a metal, and an electron acceptor, usually a non- metal.
-If atoms have similar electronegativity values (the same affinity for electrons), covalent bonds are most likely to occur. Because both atoms have the same affinity for electrons and neither of them has a tendency to donate them, they share electrons in order to achieve an octet configuration and become more stable.
Complete step by step answer:
Formation of potassium chloride, $KCl$
- A potassium atom has a proton number of $19$ and it’s electron arrangement is of $2.8.8.1$
- A potassium atom has one valence electron in its valence shell.
- During the bond formation, each of the potassium atom loses one electron from its valence shell to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement to achieve the electron arrangement of its closest noble gas i.e Argon (proton number $18$). A positive ion, ${K^ + }$ is formed.
$K(2.8.8.1) \to K(2.8.8) + {e^ - }$
- The electron lost by the potassium atom is transferred to the chlorine atom.
- A chlorine atom has a proton number of $17$ and an electron arrangement of $2.8.7$
- A chlorine atom has seven valence electrons in its valence shell.
- Each chlorine atom gains one electron from a potassium atom into its valence shell to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement to achieve the electron arrangement of its closest noble gas i.e Argon (proton number $18$ ) A negative ion. $C{l^ - }$ is formed. $Cl(2.8.7) + {e^ - } \to C{l^ - }(2.8.8)$
- Figure shows the formation of an ionic bond.

-The oppositely-charged ions formed, ${K^ + }$ and $C{l^ - }$ , are then strongly attracted to each other by strong electrostatic forces in the crystal lattice, called ionic bonds or electrovalent bonds.
-Hence, the ionic compound potassium chloride with the formula $KCl$ is formed.
Therefore, the correct option is (A) .
Note:Apart from ionic bonding, another type of bonding is called the covalent bonding. Covalent bonding is described as the sharing of electrons between atoms. This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of elements close to each other in the periodic table. This bonding occurs primarily between non-metals, although it can also be observed between nonmetals and metals. . Ionic bonds require an electron donor, most likely a metal, and an electron acceptor, usually a non- metal.
-If atoms have similar electronegativity values (the same affinity for electrons), covalent bonds are most likely to occur. Because both atoms have the same affinity for electrons and neither of them has a tendency to donate them, they share electrons in order to achieve an octet configuration and become more stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




