
In presence of a concentration of oxygen, RuBP carboxylase converts RuBP to
(a) Malic acid and PEP
(b) PGA and PEP
(c) PGA and malic acid
(d) PGA and phosphoglycolate
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: RuBP carboxylase is an enzyme necessary for the first step of carbon fixation in plants where carbon dioxide from air is taken and converted into glucose. They are produced during the Calvin cycle as a three-carbon compound and two-carbon compound.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the presence of oxygen the RuBP carboxylase converts the RuBP into PGA and phosphoglycolate.
- This occurs with the help of the enzyme RuBisCo (Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase).
- The RuBisCo enzyme helps in binding the oxygen molecules to the RuBP (Ribulose bi-phosphate) and then breaks the RuBP into two parts forming a three-carbon compound called PGA (Phosphoglyceraldehyde), and a two-carbon compound forming a phosphoglycolate.
${ RuBP }+{ Oxygen+{ RuBisCo\rightarrow { PGA(C3) }+{ Phosphoglycolate(C2) } } }$
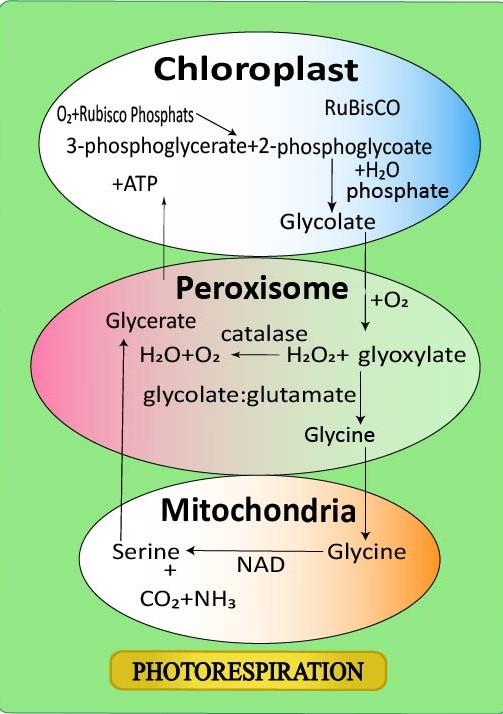
So, the correct answer is ‘PGA and phosphoglycolate’.
Additional information:
- RuBisCo is the important enzyme that is used in the process of fixation of the carbon and converts the carbon molecules into energy-rich glucose molecules.
- RuBP carboxylase/RuBisCo is considered to be the most abundant enzyme on the planet.
- Carbon dioxide is generally fixed to RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate) by the enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase or RuBP carboxylase or RuBisCO. RuBisCO has a relatively low affinity for carbon and fixes oxygen to RuBP during photorespiration.
- The enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or PEP carboxylase fixes the carbon dioxide to RuBP. PEP carboxylase has a higher affinity for carbon.
Note: RuBisCo has the dual capacity to react with both ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and${ O }_{ 2 }$. At high temperature, the concentration of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ decreases and the specificity factor of RuBisCo also decreases. And the plants start undergoing photorespiration where RuBisCo reacts with ${ O }_{ 2 }$ to release ${ CO }_{ 2 }$. ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants have evolved to escape photorespiration by concentrating ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ in bundle sheath cells which is the site of carboxylation for ${ C }_{ 3 }$ cycle. This is done to keep the concentration high enough in bundle sheath for RuBisCo to bind ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ rather than ${ O }_{ 2 }$.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the presence of oxygen the RuBP carboxylase converts the RuBP into PGA and phosphoglycolate.
- This occurs with the help of the enzyme RuBisCo (Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase).
- The RuBisCo enzyme helps in binding the oxygen molecules to the RuBP (Ribulose bi-phosphate) and then breaks the RuBP into two parts forming a three-carbon compound called PGA (Phosphoglyceraldehyde), and a two-carbon compound forming a phosphoglycolate.
${ RuBP }+{ Oxygen+{ RuBisCo\rightarrow { PGA(C3) }+{ Phosphoglycolate(C2) } } }$

So, the correct answer is ‘PGA and phosphoglycolate’.
Additional information:
- RuBisCo is the important enzyme that is used in the process of fixation of the carbon and converts the carbon molecules into energy-rich glucose molecules.
- RuBP carboxylase/RuBisCo is considered to be the most abundant enzyme on the planet.
- Carbon dioxide is generally fixed to RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate) by the enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase or RuBP carboxylase or RuBisCO. RuBisCO has a relatively low affinity for carbon and fixes oxygen to RuBP during photorespiration.
- The enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or PEP carboxylase fixes the carbon dioxide to RuBP. PEP carboxylase has a higher affinity for carbon.
Note: RuBisCo has the dual capacity to react with both ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ and${ O }_{ 2 }$. At high temperature, the concentration of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ decreases and the specificity factor of RuBisCo also decreases. And the plants start undergoing photorespiration where RuBisCo reacts with ${ O }_{ 2 }$ to release ${ CO }_{ 2 }$. ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants have evolved to escape photorespiration by concentrating ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ in bundle sheath cells which is the site of carboxylation for ${ C }_{ 3 }$ cycle. This is done to keep the concentration high enough in bundle sheath for RuBisCo to bind ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ rather than ${ O }_{ 2 }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




