
In reaction between phenol and bromine water, the equivalent weight of phenol is obtained by dividing the molecular weight of phenol by:
A.3
B.4
C.5
D.6
Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint: To calculate the equivalent weight of phenol we need to write the reaction of phenol with bromine. The number of atoms of bromine required for the reaction with phenol gives a number of equivalents to be divided with.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Bromine water is basically bromine gas dissolved in water. When phenol reacts with bromine water then 3 moles of bromine reacts with one mole of phenol to form one mole of tri-substituted phenol and 3 moles of hydrogen bromide. The reaction is as follow:
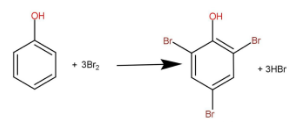
One molecule of bromine contains 2 atoms of bromines, so the number of atoms that are getting reacted are 6. So we have to divide the molecular mass of phenol with 6 to obtain the equivalent mass.
Additional information: Equivalent weight is the mass of 1 equivalent, which means it is the mass of a given substance that reacts with or combines with or displaces a fixed quantity of another substance. Equivalent weight is the ratio of molecular weight to the n factor, which is also known as valency. The definition of n-factor changes according to the type of compound. For example, in an acid n-factor is the number of protons it gives, for a salt the total number of ions it gives.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: The n-factor in the above reaction is 6. The molecular mass of phenol is 94 and hence its equivalent weight will be \[15.6{\text{ g e}}{{\text{q}}^ - }\]. The equivalent mass will change if n factor changes for some other reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Bromine water is basically bromine gas dissolved in water. When phenol reacts with bromine water then 3 moles of bromine reacts with one mole of phenol to form one mole of tri-substituted phenol and 3 moles of hydrogen bromide. The reaction is as follow:

One molecule of bromine contains 2 atoms of bromines, so the number of atoms that are getting reacted are 6. So we have to divide the molecular mass of phenol with 6 to obtain the equivalent mass.
Additional information: Equivalent weight is the mass of 1 equivalent, which means it is the mass of a given substance that reacts with or combines with or displaces a fixed quantity of another substance. Equivalent weight is the ratio of molecular weight to the n factor, which is also known as valency. The definition of n-factor changes according to the type of compound. For example, in an acid n-factor is the number of protons it gives, for a salt the total number of ions it gives.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: The n-factor in the above reaction is 6. The molecular mass of phenol is 94 and hence its equivalent weight will be \[15.6{\text{ g e}}{{\text{q}}^ - }\]. The equivalent mass will change if n factor changes for some other reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




