
In the cross YYRR × yyrr, the number of green coloured seeds in ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation is __________.
(a) $8/16$
(b) $6/16$
(c) $4/16$
(d) $2/16$
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: A dihybrid cross is a cross in which the parents differ from each other with respect to two pairs of alleles or contrasting characters. The phenotypic ratio of the dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1.
Complete answer:
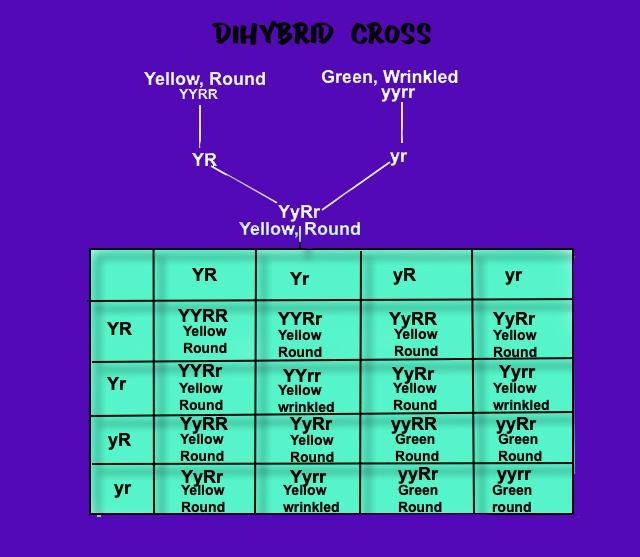
Here in a dihybrid cross, a plant with yellow color round seeds (YYRR) is crossed to green color wrinkled (yyrr) seeds. In the ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation, plants with yellow color wrinkled seeds (YyRr) are formed. When ${ F }_{ 1 }$ plant is subjected to self-pollination, in the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation 9 plants are Yellow round (1YYRR, 2YYRr, 2YyRR, 4YyRr), 3 plants are yellow wrinkled (1YYrr, 2Yyrr), 3 plants are green round (1yyRR, 2yyRr) and 1 plant is green wrinkled (1yyrr) are formed phenotypically.
Additional Information:
- The procedure adopted was similar to that of monohybrid crosses. At first, true-breeding pure line varieties were produced by repeated self-fertilization.
- Then two such varieties are crossed to raise the ${ F }_{ 1 }$hybrid generation. The ${ F }_{ 1 }$ hybrids were then interbred to raise the F2 generation.
- The selfing of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ hybrids produced a mixed ${ F }_{ 2 }$ progeny with four phenotypic combinations in the ratio 9:3:3:1. In addition to parental combinations, two new phenotypic combinations appeared in ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generations. They can be called recombinants.
So, the correct option is ‘$4/16$ ’.
Note:
- On the basis of his findings from a dihybrid cross, Mendel formulated the Principle of Independent Assortment.
- Later on, Correns developed this as the law of independent Assortment, which is now regarded as the second Mendelian law of heredity.
- It states that the factors for different pairs of contrasting characters behave as independent units and so their distribution in the gametes and also in succeeding generations is independent of each other. So as given, the alleles assort independently in random combinations.
Complete answer:
Here in a dihybrid cross, a plant with yellow color round seeds (YYRR) is crossed to green color wrinkled (yyrr) seeds. In the ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation, plants with yellow color wrinkled seeds (YyRr) are formed. When ${ F }_{ 1 }$ plant is subjected to self-pollination, in the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation 9 plants are Yellow round (1YYRR, 2YYRr, 2YyRR, 4YyRr), 3 plants are yellow wrinkled (1YYrr, 2Yyrr), 3 plants are green round (1yyRR, 2yyRr) and 1 plant is green wrinkled (1yyrr) are formed phenotypically.
Additional Information:
- The procedure adopted was similar to that of monohybrid crosses. At first, true-breeding pure line varieties were produced by repeated self-fertilization.

- Then two such varieties are crossed to raise the ${ F }_{ 1 }$hybrid generation. The ${ F }_{ 1 }$ hybrids were then interbred to raise the F2 generation.
- The selfing of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ hybrids produced a mixed ${ F }_{ 2 }$ progeny with four phenotypic combinations in the ratio 9:3:3:1. In addition to parental combinations, two new phenotypic combinations appeared in ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generations. They can be called recombinants.
So, the correct option is ‘$4/16$ ’.
Note:
- On the basis of his findings from a dihybrid cross, Mendel formulated the Principle of Independent Assortment.
- Later on, Correns developed this as the law of independent Assortment, which is now regarded as the second Mendelian law of heredity.
- It states that the factors for different pairs of contrasting characters behave as independent units and so their distribution in the gametes and also in succeeding generations is independent of each other. So as given, the alleles assort independently in random combinations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




