
In the equation $P.E. = \dfrac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_{\circ}} \dfrac{Ze(-e)}{r}$, should we take (-e) or (e) value?
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Potential energy is a quantity which defines the stability of the system. If it is less, the system is stable and if it is more, the system is unstable. P.E. can be positive, negative or zero. A positive potential energy is when two charges/bodies repel each other due to their nature whereas negative potential energy signifies that there is attraction between two bodies.
Formula used:
$P.E. = \dfrac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_{\circ}} \dfrac{Zq_1q_2}{r}$
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that two charges with opposite signs attract each other, that means the system is stable as the two charges don’t want to get separated, rather want to become a single body. Whereas two charges with the same sign of charge always repel each other. This suggests that the system is unstable and the charges want to get separated. In physics and chemistry, we follow the basic rule that all systems want to get stable. This can be explained by following graph:
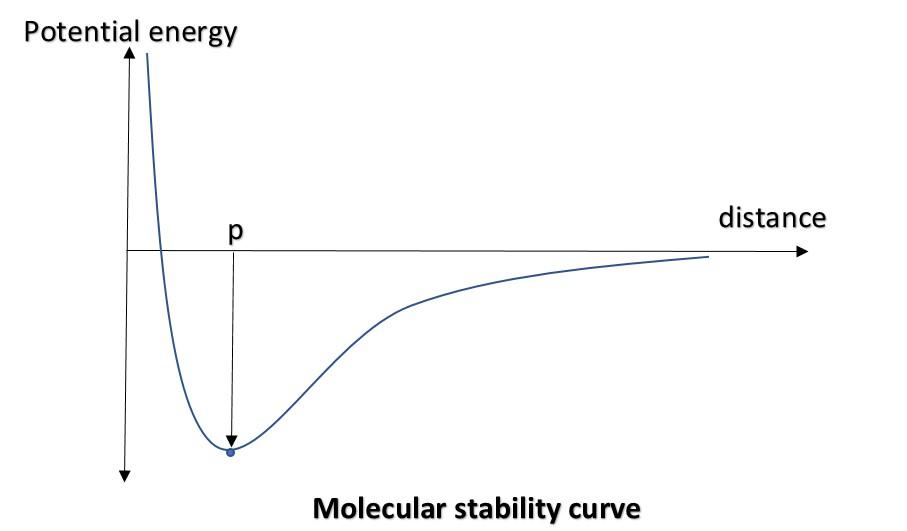
Figure shows a graph between P.E. of a system (for example: two charges with opposite sign). When the distance is sufficiently large, the potential energy between the two is less, but the system is stable due to attraction (negative potential energy). As the distance decreases, the potential energy gets more decreased (it decreases due to sign, but its magnitude will increase which represents more stability in the negative side). There is a point (p) at which P.E. is minimum. After which, the system goes into a state of interatomic and nuclear interactions, decreasing the stability, which can be identified by the curve, continuously going up if we move from right to left.
Hence, we take the sign of charges too.
Note:
The graph is just shown to show the significance of negative potential energy and stability. Laws of nature says, like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. This can be understood by means of their potential energy. For a system to be stable, its potential energy should be as low as possible, preferably negative.
Formula used:
$P.E. = \dfrac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_{\circ}} \dfrac{Zq_1q_2}{r}$
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that two charges with opposite signs attract each other, that means the system is stable as the two charges don’t want to get separated, rather want to become a single body. Whereas two charges with the same sign of charge always repel each other. This suggests that the system is unstable and the charges want to get separated. In physics and chemistry, we follow the basic rule that all systems want to get stable. This can be explained by following graph:

Figure shows a graph between P.E. of a system (for example: two charges with opposite sign). When the distance is sufficiently large, the potential energy between the two is less, but the system is stable due to attraction (negative potential energy). As the distance decreases, the potential energy gets more decreased (it decreases due to sign, but its magnitude will increase which represents more stability in the negative side). There is a point (p) at which P.E. is minimum. After which, the system goes into a state of interatomic and nuclear interactions, decreasing the stability, which can be identified by the curve, continuously going up if we move from right to left.
Hence, we take the sign of charges too.
Note:
The graph is just shown to show the significance of negative potential energy and stability. Laws of nature says, like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. This can be understood by means of their potential energy. For a system to be stable, its potential energy should be as low as possible, preferably negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




