
In the given structure, is enol form of:
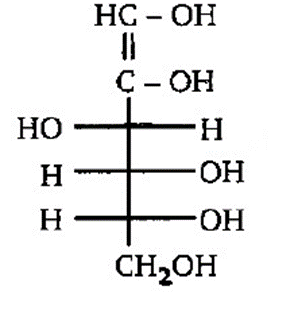
(A) D-glucose
(B) D-mannose
(C) D- fructose
(D) all of these

Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: The structure of the given compound belongs to the carbohydrate fructose(${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$). It’s an example of ketohexose monosaccharide whereas glucose is an aldohexose and mannose is the C-2 epimer of glucose. Hence they are isomers and they undergo tautomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
- Let’s start with the concept of tautomerism. Enols and ketones are isomers. The enols are a combination of a carbonyl ($C=O$) containing group, such as a ketone or aldehyde and an alcohol or hydroxyl ($-OH$) group. The process tautomerism arises from the interconversion between these two forms.
- The isomers ketone and enol are related by a change in the position of the hydrogen and the double bond in the molecule. Thus, the process of tautomerism describes the equilibrium between enol and keto forms interconverted through a change in the position of hydrogen and bonding electrons to produce two isomers.
- The prefix ‘D’ is used in order to refer to the direction that an optical isomer rotates the plane polarized light. An optical isomer is the one with asymmetric groups surrounding a central atom.
- In sugars, the cyclic hemiacetal and linear form exist in equilibrium and in the linear form, they can undergo keto-enol tautomerism. This tautomerism takes place during the interconversion between the ketose and aldose forms.
- Glucose, mannose, and fructose, all belong to the D series and they are easily interconvertible through their keto-enol tautomerism and these relation is represented below,
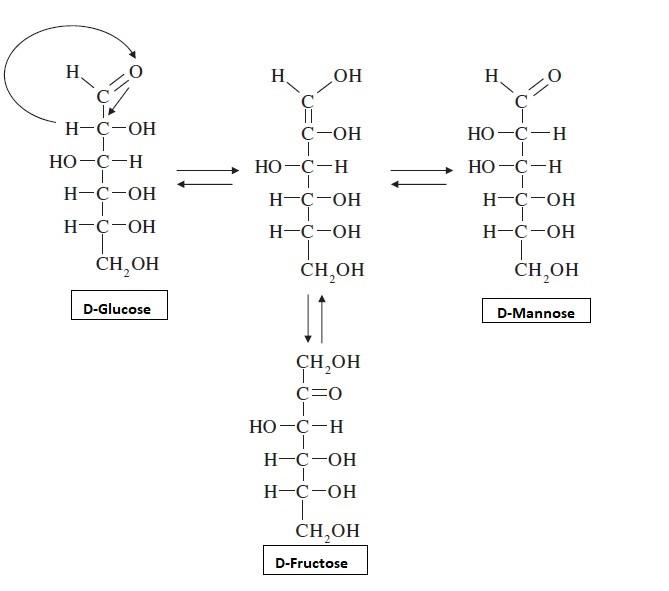
- Thus D-glucose, D-mannose and D- fructose are enol forms of the given compound (fructose).
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: It should be noted that the carbohydrates are generally classified into three categories. They are monosaccharides which are simple sugar molecules like we discussed above, oligosaccharides which are polymers of two to ten sugar molecules and polysaccharides which are polymers of more than ten sugars. Glucose is an example of monosaccharide, sucrose is of oligosaccharide and starch is an example of polysaccharides.
Complete step by step answer:
- Let’s start with the concept of tautomerism. Enols and ketones are isomers. The enols are a combination of a carbonyl ($C=O$) containing group, such as a ketone or aldehyde and an alcohol or hydroxyl ($-OH$) group. The process tautomerism arises from the interconversion between these two forms.
- The isomers ketone and enol are related by a change in the position of the hydrogen and the double bond in the molecule. Thus, the process of tautomerism describes the equilibrium between enol and keto forms interconverted through a change in the position of hydrogen and bonding electrons to produce two isomers.
- The prefix ‘D’ is used in order to refer to the direction that an optical isomer rotates the plane polarized light. An optical isomer is the one with asymmetric groups surrounding a central atom.
- In sugars, the cyclic hemiacetal and linear form exist in equilibrium and in the linear form, they can undergo keto-enol tautomerism. This tautomerism takes place during the interconversion between the ketose and aldose forms.
- Glucose, mannose, and fructose, all belong to the D series and they are easily interconvertible through their keto-enol tautomerism and these relation is represented below,

- Thus D-glucose, D-mannose and D- fructose are enol forms of the given compound (fructose).
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: It should be noted that the carbohydrates are generally classified into three categories. They are monosaccharides which are simple sugar molecules like we discussed above, oligosaccharides which are polymers of two to ten sugar molecules and polysaccharides which are polymers of more than ten sugars. Glucose is an example of monosaccharide, sucrose is of oligosaccharide and starch is an example of polysaccharides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




