
In the leaves, veins are useful for
A. Transport of water and minerals
B. Mechanical support
C. Transport of organic nutrients
D. All of the above
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The veins of a leaf represent the vascular structure of the organ that extends into the leaf via the petiole and provides the transportation of water and nutrients between the leaf and the stem.
Complete answer: The veins play an important role in the maintenance of the status of the water in the leaf and the capacity of photosynthesis.
Veins in leaves are made up of two major tissues – xylem and phloem.
It helps to provide mechanical support to the leaf.
It also helps in the transportation of both water and minerals, where water is transported by xylem tissue and food and organic nutrients are transported by phloem tissue to the other parts of the plant body.
Thus, the correct answer is option D. All of the above.
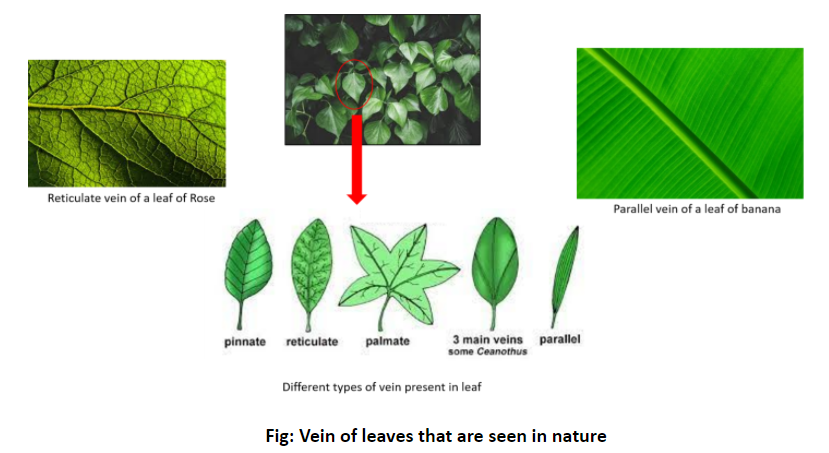
Note: There are two types of veins seen in the angiosperms – parallel and reticulate or net-like structure.
In general, parallel venation is typically seen in monocot plants, for example, banana trees, whereas reticulate veins are more typically seen in the case of eudicots and magnoliids or dicots, for example, Rose, China rose, etc.
Complete answer: The veins play an important role in the maintenance of the status of the water in the leaf and the capacity of photosynthesis.
Veins in leaves are made up of two major tissues – xylem and phloem.
It helps to provide mechanical support to the leaf.
It also helps in the transportation of both water and minerals, where water is transported by xylem tissue and food and organic nutrients are transported by phloem tissue to the other parts of the plant body.

Thus, the correct answer is option D. All of the above.
Note: There are two types of veins seen in the angiosperms – parallel and reticulate or net-like structure.
In general, parallel venation is typically seen in monocot plants, for example, banana trees, whereas reticulate veins are more typically seen in the case of eudicots and magnoliids or dicots, for example, Rose, China rose, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




