
In the reaction the structure of product T is
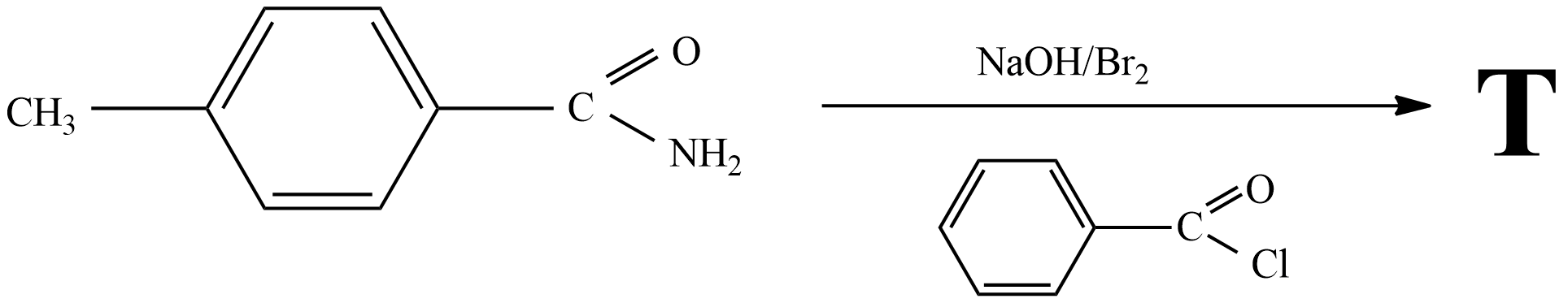


Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The molecules that contain nitrogen atoms attached to the carbon atom of a carbonyl group are amides and the remaining two bonds on the nitrogen atom are connected to hydrogen atoms is a simple amide. Common nomenclature of amides used to class-specific suffix-amide. The characteristic reaction of covalent amides is converted to amines and acids by hydrolysis.
Complete step by step answer:
Chemical properties of amides:
(i) Amides are less basic than the respective nitrogen amine, due to the delocalization of lone pairs of the nitrogen.
(ii) N-H bonds in amide are more acidic than amine N-H bonds because the lone pair of conjugate base is more stable due to its resonance delocalization.
(iii) Hoffmann Bromamide reaction:
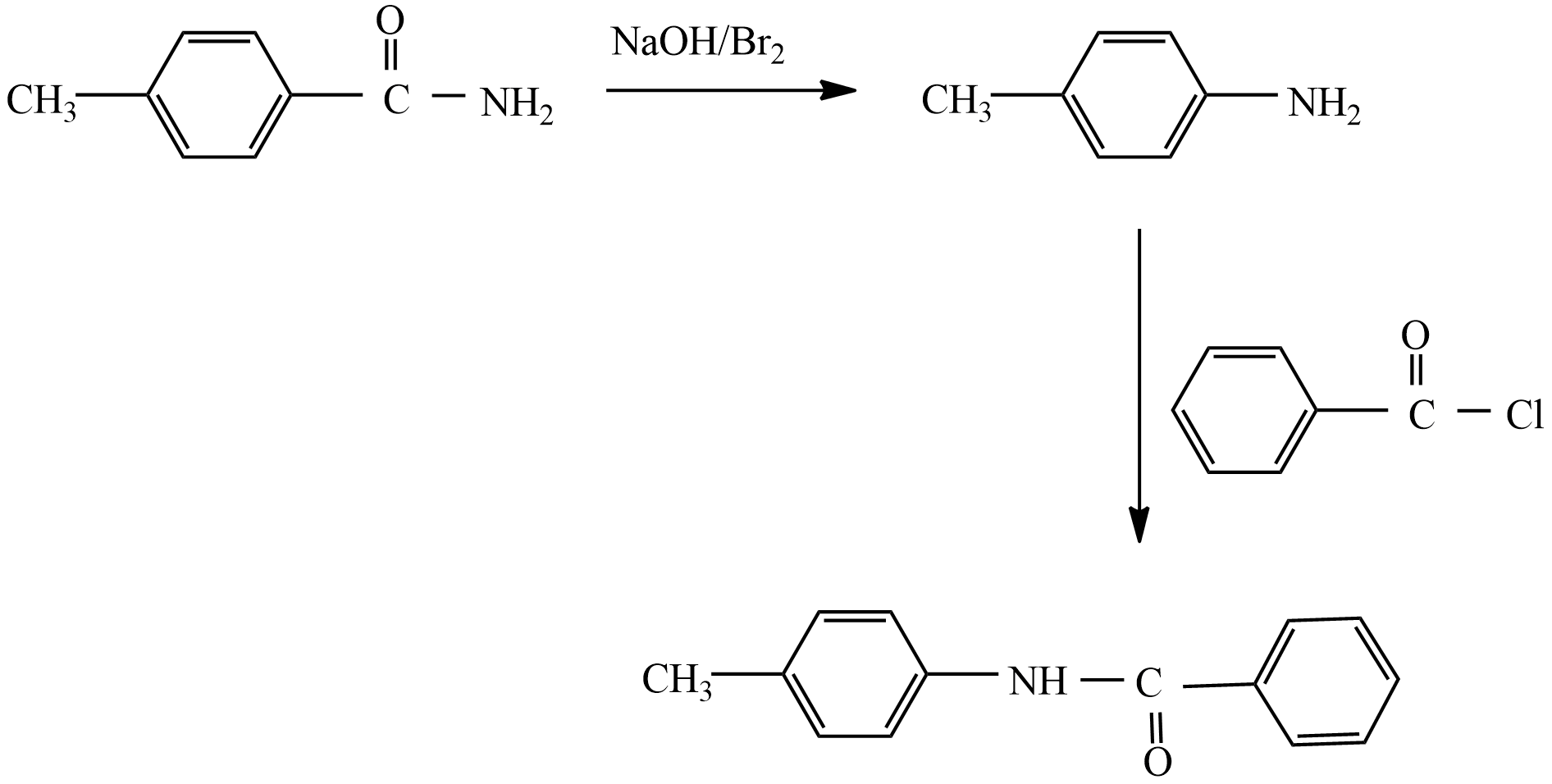
When an aromatic amide or aliphatic amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, then the degradation of amide takes place leading to the formation of primary amine. This reaction is also known as Hoffmann Bromamide degradation reaction, because in this reaction involves the degradation of amide.
The general equation is,
$RCON{{H}_{2}}+B{{r}_{2}}+4NaOH\to R-N{{H}_{2}}+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2NaBr+2{{H}_{2}}O$
The important observation in this reaction is the primary formed as the product is less than one carbon atom of the reactant amide.
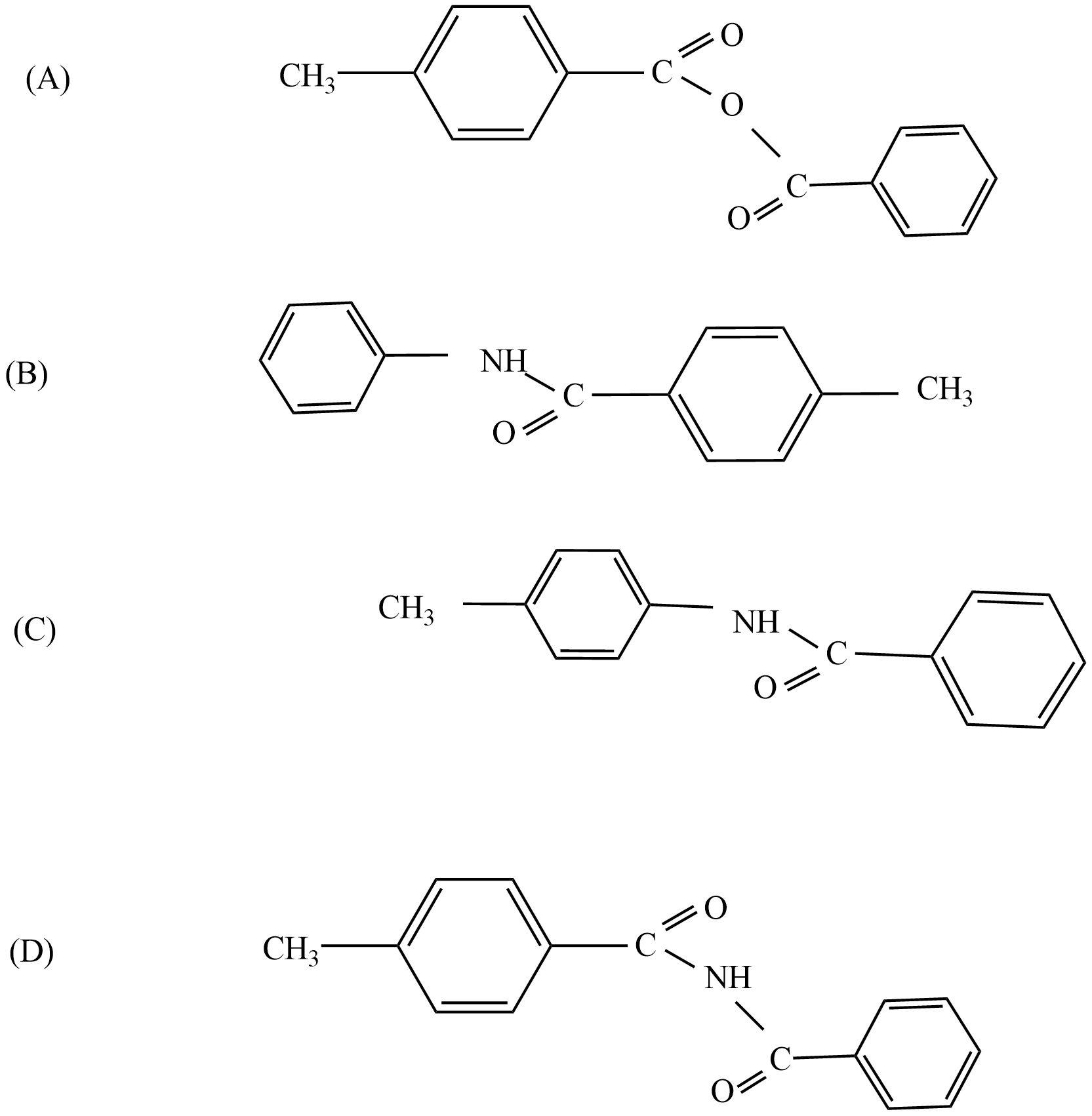
If the given compound involves in this reaction:
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Except for formamide, is liquid and all simple amides are solids. Like esters, amides solutions in water are neutral, either acidic or basic. Generally, these amides are high boiling points and melting points due to hydrogen bonding in amides and solubility in water more because amide molecules can engage hydrogen bonding with water.
Complete step by step answer:
Chemical properties of amides:
(i) Amides are less basic than the respective nitrogen amine, due to the delocalization of lone pairs of the nitrogen.
(ii) N-H bonds in amide are more acidic than amine N-H bonds because the lone pair of conjugate base is more stable due to its resonance delocalization.
(iii) Hoffmann Bromamide reaction:
When an aromatic amide or aliphatic amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, then the degradation of amide takes place leading to the formation of primary amine. This reaction is also known as Hoffmann Bromamide degradation reaction, because in this reaction involves the degradation of amide.
The general equation is,
$RCON{{H}_{2}}+B{{r}_{2}}+4NaOH\to R-N{{H}_{2}}+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+2NaBr+2{{H}_{2}}O$
The important observation in this reaction is the primary formed as the product is less than one carbon atom of the reactant amide.
If the given compound involves in this reaction:

So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Except for formamide, is liquid and all simple amides are solids. Like esters, amides solutions in water are neutral, either acidic or basic. Generally, these amides are high boiling points and melting points due to hydrogen bonding in amides and solubility in water more because amide molecules can engage hydrogen bonding with water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




