
In the same flowers, the stamens and pistil reach maturity at the same time known as
(a) Porogamy
(b) Mesogamy
(c) Siphonogamy
(d) Homogamy
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: The stamen and pistil reach maturity at the same time so that the plants can undergo self-pollination. Orchids, peas are examples of autogamous plants (i.e.,) the plants that undergo self-pollination.
Complete answer:
The method by which the stamens and pistils of the same flower reach the stage of maturity at the same time to undergo autogamy is known as homogamy. Autogamy is also called self-fertilization/self-pollination where the male and the female gamete from the same plants will undergo fusion. Since these plants undergo self-pollination, genetic diversity will be very less.
Additional information
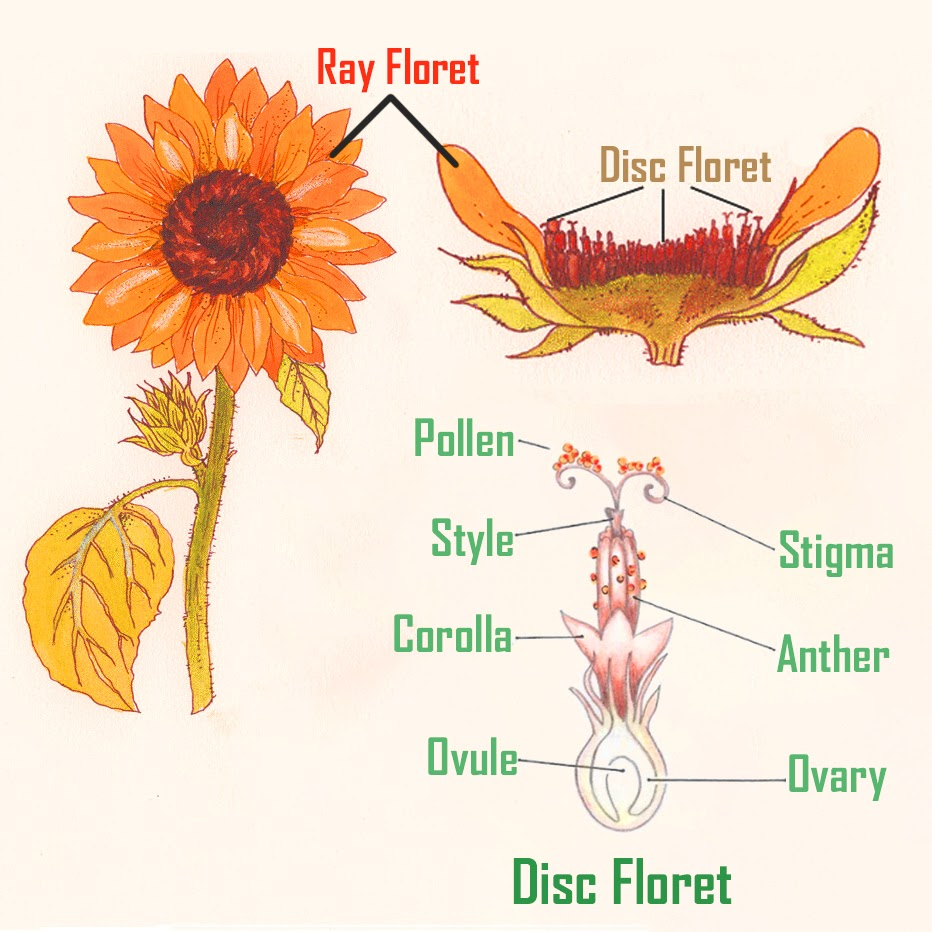
-The maturation of both the male and female reproductive organs at the same time is also called simultaneous or synchronous hermaphroditism. Many flowers seem homogamous but some of these may not be strictly functionally homogamous, as male and female reproduction in some plants may not overlap fully. It is generally observed in the case of the Sunflower.
-In contrast, the process of entry of a pollen tube through the micropyle end is called Porogamy. Mesogamy refers to the entry of the pollen tubes through integuments. The development of the pollen tube to make the entry of pollen grains into eggs is known as siphonogamy.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Homogamy’.
Note:
Inbreeding is Homogamy. The process of production of offspring by mating the animals or organisms that are genetically closely related. But the main drawback of inbreeding is that the recessive diseases affect the offspring and also they will lack genetic variation. The main aim of inbreeding is to maintain the characteristics of the ancestors or within the population in a herd.
Complete answer:
The method by which the stamens and pistils of the same flower reach the stage of maturity at the same time to undergo autogamy is known as homogamy. Autogamy is also called self-fertilization/self-pollination where the male and the female gamete from the same plants will undergo fusion. Since these plants undergo self-pollination, genetic diversity will be very less.
Additional information
-The maturation of both the male and female reproductive organs at the same time is also called simultaneous or synchronous hermaphroditism. Many flowers seem homogamous but some of these may not be strictly functionally homogamous, as male and female reproduction in some plants may not overlap fully. It is generally observed in the case of the Sunflower.
-In contrast, the process of entry of a pollen tube through the micropyle end is called Porogamy. Mesogamy refers to the entry of the pollen tubes through integuments. The development of the pollen tube to make the entry of pollen grains into eggs is known as siphonogamy.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Homogamy’.
Note:
Inbreeding is Homogamy. The process of production of offspring by mating the animals or organisms that are genetically closely related. But the main drawback of inbreeding is that the recessive diseases affect the offspring and also they will lack genetic variation. The main aim of inbreeding is to maintain the characteristics of the ancestors or within the population in a herd.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




