
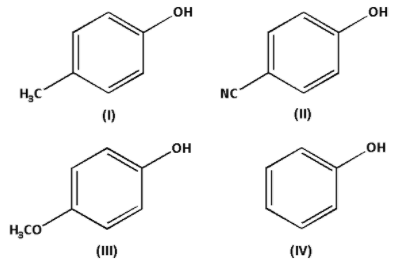
Increasing order of acidic strength of given compounds is:

Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know that if an electron withdrawing group is attached to the benzene ring then the compound is less acidic. And if an electron donating group is attached to the benzene ring then the compound is more acidic.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given four compounds which contain phenol groups with some different functional groups attached to them. We know that acid is a substance which easily donates a hydrogen ion $\left( {{{\text{H}}^ + }} \right)$. When the hydrogen ion is removed from the acid an acid corresponding to conjugate base is obtained. An acid having a stable conjugate base is a strong acid. Thus, the more stable the conjugate base, the stronger is the acid. When a hydrogen ion is removed from an acid the conjugate base gains a negative charge.
When an electron donating group is attached the electron density on the conjugate base increases. As a result the conjugate base becomes more stable and the compound becomes more acidic.
When an electron withdrawing group is attached the electron density on the conjugate base decreases. As a result the conjugate base becomes less stable and the compound becomes less acidic.
Thus, an electron donating group increases the acidic strength while an electron withdrawing group decreases the acidic strength.
-In compound (I), an electron donating methyl $\left( { - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ group is attached. Thus, the compound (I) is more acidic.
-In compound (II), an electron withdrawing cyano $\left( { - {\text{CN}}} \right)$ group is attached. Thus, the compound (II) is less acidic.
-In compound (III), an electron donating methoxy $\left( { - {\text{OC}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ group is attached. Thus, the compound (III) is more acidic.
But methoxy $\left( { - {\text{OC}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ group is more electron donating than methyl $\left( { - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ group. Thus, compound (III) is more acidic than compound (I).
In compound (IV), neither electron donating group nor electron withdrawing group is attached. Thus, the compound (IV) is more acidic than compound (II) but less acidic than compound (I) and compound (III)
Thus, the increasing order of acidic strength is (III) > (I) > (IV) > (II).
Note: Remember that while deciding the acidic strength we have to check the stability of the conjugate base. If an electron withdrawing group is attached to the benzene ring then the compound is less acidic. And if an electron donating group is attached to the benzene ring then the compound is more acidic.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given four compounds which contain phenol groups with some different functional groups attached to them. We know that acid is a substance which easily donates a hydrogen ion $\left( {{{\text{H}}^ + }} \right)$. When the hydrogen ion is removed from the acid an acid corresponding to conjugate base is obtained. An acid having a stable conjugate base is a strong acid. Thus, the more stable the conjugate base, the stronger is the acid. When a hydrogen ion is removed from an acid the conjugate base gains a negative charge.
When an electron donating group is attached the electron density on the conjugate base increases. As a result the conjugate base becomes more stable and the compound becomes more acidic.
When an electron withdrawing group is attached the electron density on the conjugate base decreases. As a result the conjugate base becomes less stable and the compound becomes less acidic.
Thus, an electron donating group increases the acidic strength while an electron withdrawing group decreases the acidic strength.
-In compound (I), an electron donating methyl $\left( { - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ group is attached. Thus, the compound (I) is more acidic.
-In compound (II), an electron withdrawing cyano $\left( { - {\text{CN}}} \right)$ group is attached. Thus, the compound (II) is less acidic.
-In compound (III), an electron donating methoxy $\left( { - {\text{OC}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ group is attached. Thus, the compound (III) is more acidic.
But methoxy $\left( { - {\text{OC}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ group is more electron donating than methyl $\left( { - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ group. Thus, compound (III) is more acidic than compound (I).
In compound (IV), neither electron donating group nor electron withdrawing group is attached. Thus, the compound (IV) is more acidic than compound (II) but less acidic than compound (I) and compound (III)
Thus, the increasing order of acidic strength is (III) > (I) > (IV) > (II).
Note: Remember that while deciding the acidic strength we have to check the stability of the conjugate base. If an electron withdrawing group is attached to the benzene ring then the compound is less acidic. And if an electron donating group is attached to the benzene ring then the compound is more acidic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




