
Indicate the correct sequence during spermatogenesis.
A. Spermatozoa $ \to $ spermatogonia $ \to $ spermatid $ \to $ spermatocyte.
B. Spermatogonia $ \to $ spermatocyte $ \to $ spermatid $ \to $ spermatozoa.
C. Spermatid $ \to $ spermatocyte $ \to $ spermatozoa $ \to $ spermatogonia.
D. Spermatocyte $ \to $ spermatozoa $ \to $ spermatid $ \to $ spermatogonia.
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: The word spermatogenesis has been derived from two words, the Greek word sperma which means ‘the seed or germ’, and the other word genesis which means ‘birth’ or ‘origin’ or ‘creation’. Hence, it is the process of the formation of mature sperm cells.
Complete answer:
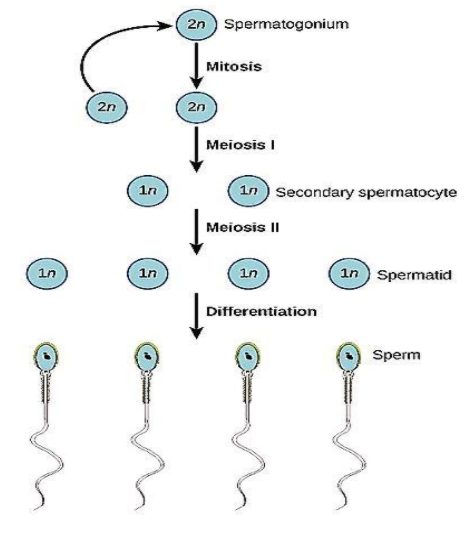
Spermatogenesis is a form of gametogenesis that takes place in the seminiferous tubule of the male testis and is known to produce mature sperm cells known as spermatozoa from undifferentiated male germ cells. This process involves a series of stages:
Spermatocytogenesis is that stage in which through mitotic cell division, the spermatogonia give rise to primary spermatocytes. These primary spermatocytes (having ‘2n’ number of chromosomes) undergo meiosis I and produce secondary spermatocytes (having ‘n’ number of chromosomes).
Spermatidogenesis is the stage which involves the formation of spermatids (haploid sperm cells) from the secondary spermatocytes by the process of meiosis II.
Spermiogenesis is the stage during which the spermatids transform into spermatozoa (mature sperm cells) by the process of differentiation.
Stages of spermatogenesis.
Therefore, the sequence of spermatogenesis is-
Spermatogonia $ \to $ spermatocyte $ \to $ spermatid $ \to $ spermatozoa
Options (A), (C), and (D) do not represent the correct sequence of spermatogenesis. Therefore, these options are incorrect.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: The spermatogenesis process starts with the diploid spermatogonium. This spermatogonia is an undifferentiated stem cell that undergoes mitosis to produce primary spermatocytes. Each primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I to give rise to two haploid secondary spermatocytes. Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis II to give rise to four haploid spermatids (i.e., two spermatids from each secondary spermatocyte). These spermatids then develop into mature sperm cells called spermatozoa.
Complete answer:
Spermatogenesis is a form of gametogenesis that takes place in the seminiferous tubule of the male testis and is known to produce mature sperm cells known as spermatozoa from undifferentiated male germ cells. This process involves a series of stages:
Spermatocytogenesis is that stage in which through mitotic cell division, the spermatogonia give rise to primary spermatocytes. These primary spermatocytes (having ‘2n’ number of chromosomes) undergo meiosis I and produce secondary spermatocytes (having ‘n’ number of chromosomes).
Spermatidogenesis is the stage which involves the formation of spermatids (haploid sperm cells) from the secondary spermatocytes by the process of meiosis II.
Spermiogenesis is the stage during which the spermatids transform into spermatozoa (mature sperm cells) by the process of differentiation.
Stages of spermatogenesis.
Therefore, the sequence of spermatogenesis is-
Spermatogonia $ \to $ spermatocyte $ \to $ spermatid $ \to $ spermatozoa
Options (A), (C), and (D) do not represent the correct sequence of spermatogenesis. Therefore, these options are incorrect.

Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: The spermatogenesis process starts with the diploid spermatogonium. This spermatogonia is an undifferentiated stem cell that undergoes mitosis to produce primary spermatocytes. Each primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I to give rise to two haploid secondary spermatocytes. Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis II to give rise to four haploid spermatids (i.e., two spermatids from each secondary spermatocyte). These spermatids then develop into mature sperm cells called spermatozoa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




