
Inorganic benzene is:
A. ${ B }_{ 3 }{ N }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 12 }$
B. ${ B }_{ 3 }{ N }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 6 }$
C. ${ (BN) }_{ 6 }$
D. ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 6 }{ Cl }_{ 6 }$
Answer
611.1k+ views
Hint: You can try by drawing the structures of each compound and then compare this with organic benzene to reach the correct answer. The question itself is saying inorganic, that means this compound will not be having carbon in its structure. Now try to find the correct answer.
Complete answer:
Borazine is called “inorganic benzene” because the compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. The other similarities are it is a colourless liquid with aromatic smell.
Borazine is said to be aromatic because the number of pi electrons obeys (4n+2) rule and the B-N bond lengths are all equal.
We can discuss some properties of borazine -
1. Borazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ${ B }_{ 3 }{ N }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 6 }$. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. Like benzene, borazine is a colorless liquid.
2. Borazine is isostructural with benzene. The six B-N bonds have a length of 1.436 $A$. The carbon–carbon bond in benzene is shorter as the length is 1.397 $A$. The boron–nitrogen bond length is between that of the boron–nitrogen single bond with 0.151 nm and the boron–nitrogen double bond which is 0.131 nm. This suggests partial delocalisation of nitrogen lone-pair electrons.
3. The electronegativity of boron (2.04) compared to that of nitrogen (3.04) and also the electron deficiency on the boron atom and the lone pair on nitrogen favor alternative mesomer structures for Borazine.
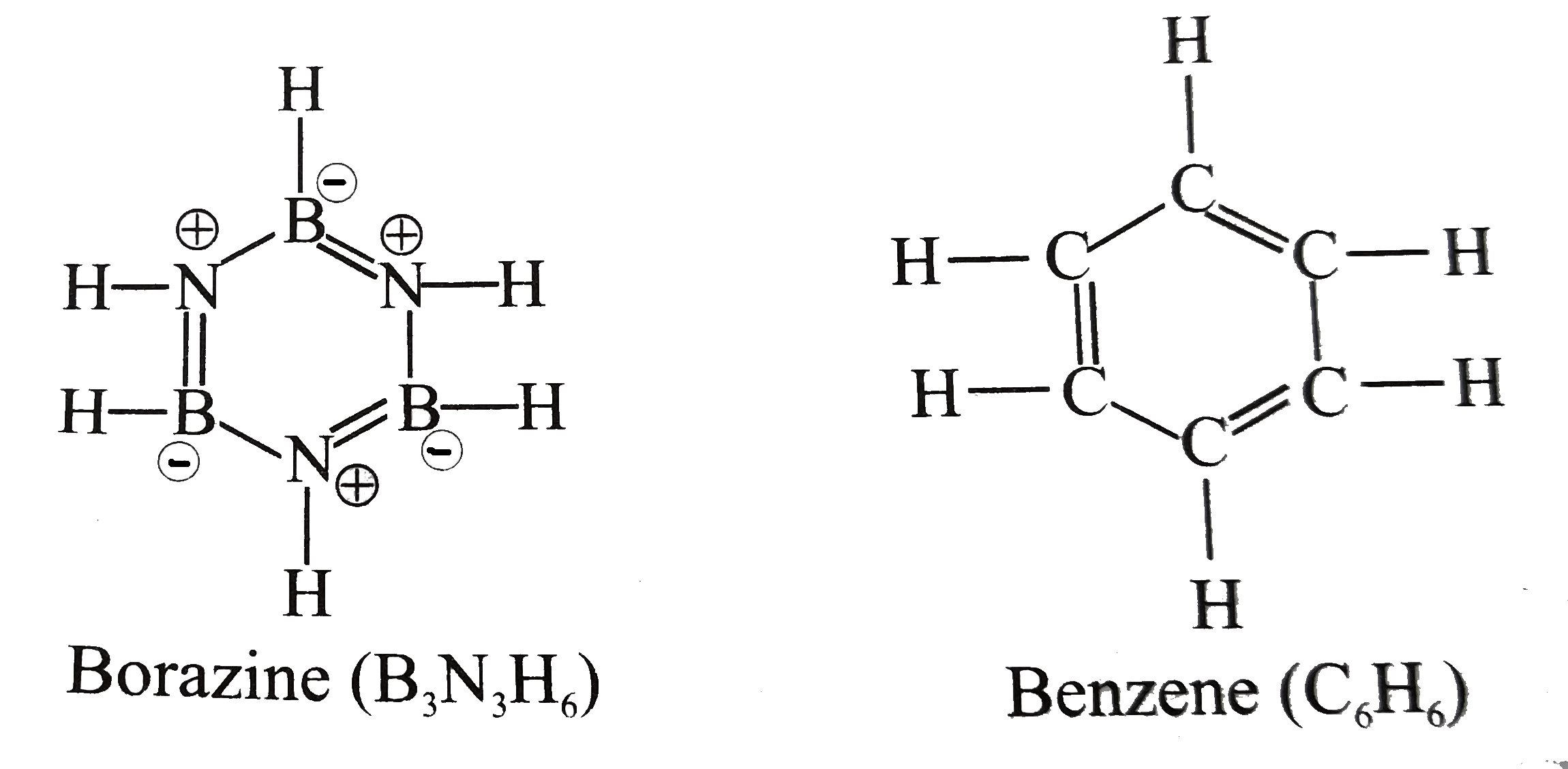
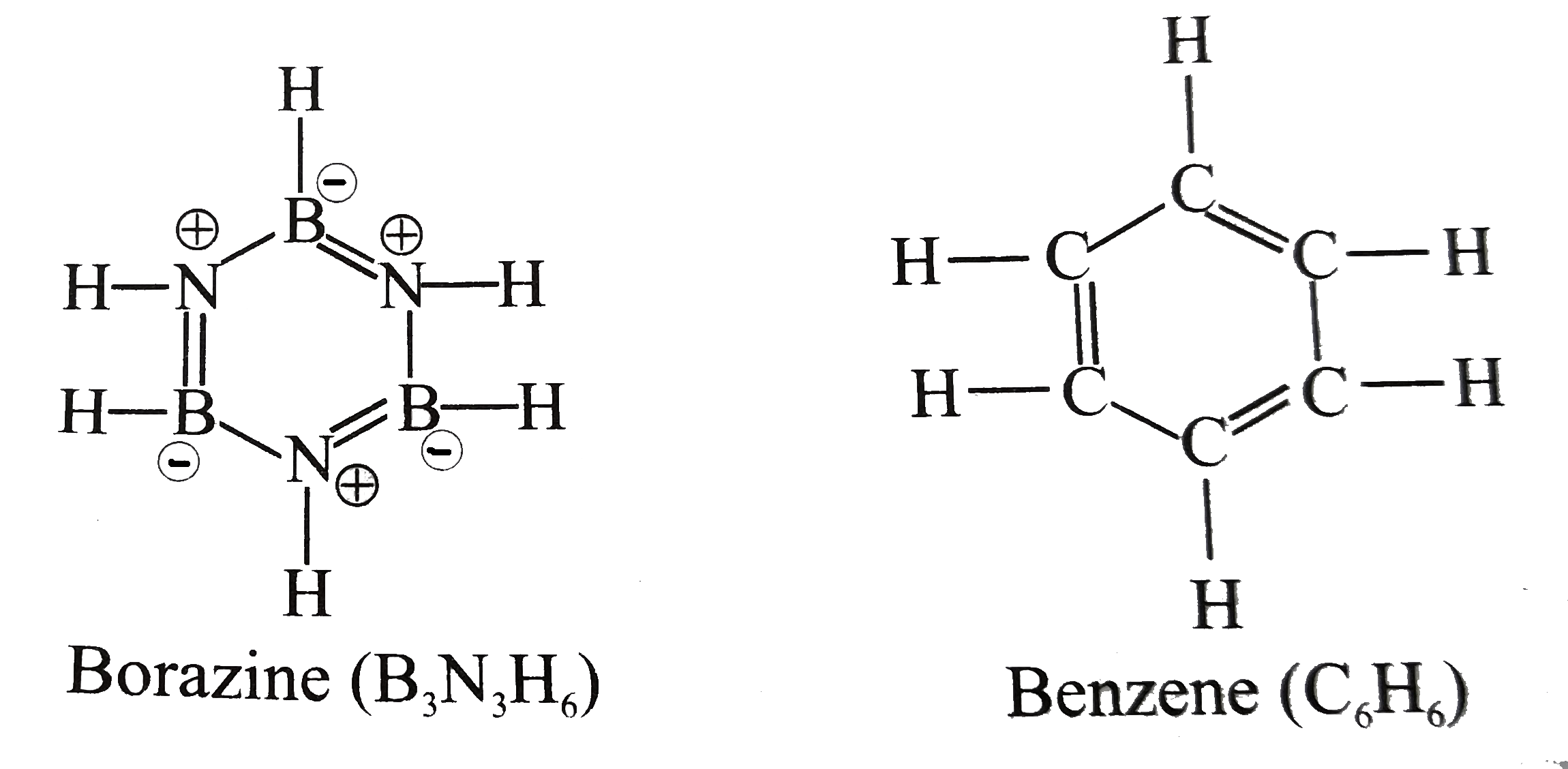
Henceforth, we can conclude that the option B is the correct answer.
Note: We can also identify compounds present in other options too - BN - Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice.
${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 6 }{ Cl }_{ 6 }$ - Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH), this structure has nine stereoisomers (eight diastereomers, one of which has two enantiomers), which differ by the stereochemistry of the individual chlorine substituents on the cyclohexane.
Complete answer:
Borazine is called “inorganic benzene” because the compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. The other similarities are it is a colourless liquid with aromatic smell.
Borazine is said to be aromatic because the number of pi electrons obeys (4n+2) rule and the B-N bond lengths are all equal.
We can discuss some properties of borazine -
1. Borazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ${ B }_{ 3 }{ N }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 6 }$. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. Like benzene, borazine is a colorless liquid.
2. Borazine is isostructural with benzene. The six B-N bonds have a length of 1.436 $A$. The carbon–carbon bond in benzene is shorter as the length is 1.397 $A$. The boron–nitrogen bond length is between that of the boron–nitrogen single bond with 0.151 nm and the boron–nitrogen double bond which is 0.131 nm. This suggests partial delocalisation of nitrogen lone-pair electrons.
3. The electronegativity of boron (2.04) compared to that of nitrogen (3.04) and also the electron deficiency on the boron atom and the lone pair on nitrogen favor alternative mesomer structures for Borazine.


Henceforth, we can conclude that the option B is the correct answer.
Note: We can also identify compounds present in other options too - BN - Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice.
${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 6 }{ Cl }_{ 6 }$ - Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH), this structure has nine stereoisomers (eight diastereomers, one of which has two enantiomers), which differ by the stereochemistry of the individual chlorine substituents on the cyclohexane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




