
Interfascicular cambium is situated.
(a) Between xylem and phloem
(b) Between vascular bundles
(c) Outside the vascular bundles
(d) Inner side of the vascular bundles
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: During secondary growth, the medullary rays adjacent to the intrafascicular cambium become meristematic tissue and are called interfascicular cambium active cambial ring initiates differentiation of the latest cells; numerous cells are formed towards the center and periphery regions Interfascicular cambium is a secondary meristem.
Complete answer:
The vascular cambium is the meristem that produces secondary xylem and phloem in stems and roots of gymnosperms, woody dicots, and, to a limited extent, some herbaceous dicots. It differentiates from the procambium, the progenitor of the primary xylem and phloem, within vascular bundles. In elongating shoots, the differentiation of the cambium in a vascular bundle starts at the stem base and proceeds acropetally, occurring in a particular stem portion as its elongation ceases. Within a vascular bundle, the procambium and the cambium exist as a developmental continuum. Consequently, the transition from primary xylem to secondary xylem cannot be precisely delimited.
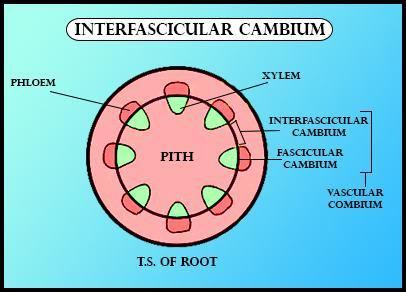
The cambium found within vascular bundles is denoted the fascicular cambium. Subsequently, in the transverse plane, periclinal divisions occur in the interfascicular parenchyma cells located at the edges of the fascicular cambium, and the interfascicular cambium is initiated.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) Between vascular bundles’.
Additional Information: The initiation of the interfascicular cambium progresses laterally until the interfascicular cambia originating from two adjacent vascular bundles connect. Ultimately, a continuous ring of vascular cambium is formed within the stem and, with the production of additional vascular tissue, the fascicular and interfascicular cambia become indistinguishable. In some members of plants, vascular cambium is made from the outer region of the bottom tissues like Dracaena, yucca, Agave, Aloe arborescens, Lomandra, Kingia, Sansevieria, etc. Parenchyma formed towards the surface by the vascular cambium and secondary vascular bundles is formed toward the inner side.
Note: The interfascicular cambium usually does not develop in stems exhibiting little fascicular cambial activity. In such stems, other cells specialized for support are formed. For example, in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Complete answer:
The vascular cambium is the meristem that produces secondary xylem and phloem in stems and roots of gymnosperms, woody dicots, and, to a limited extent, some herbaceous dicots. It differentiates from the procambium, the progenitor of the primary xylem and phloem, within vascular bundles. In elongating shoots, the differentiation of the cambium in a vascular bundle starts at the stem base and proceeds acropetally, occurring in a particular stem portion as its elongation ceases. Within a vascular bundle, the procambium and the cambium exist as a developmental continuum. Consequently, the transition from primary xylem to secondary xylem cannot be precisely delimited.

The cambium found within vascular bundles is denoted the fascicular cambium. Subsequently, in the transverse plane, periclinal divisions occur in the interfascicular parenchyma cells located at the edges of the fascicular cambium, and the interfascicular cambium is initiated.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) Between vascular bundles’.
Additional Information: The initiation of the interfascicular cambium progresses laterally until the interfascicular cambia originating from two adjacent vascular bundles connect. Ultimately, a continuous ring of vascular cambium is formed within the stem and, with the production of additional vascular tissue, the fascicular and interfascicular cambia become indistinguishable. In some members of plants, vascular cambium is made from the outer region of the bottom tissues like Dracaena, yucca, Agave, Aloe arborescens, Lomandra, Kingia, Sansevieria, etc. Parenchyma formed towards the surface by the vascular cambium and secondary vascular bundles is formed toward the inner side.
Note: The interfascicular cambium usually does not develop in stems exhibiting little fascicular cambial activity. In such stems, other cells specialized for support are formed. For example, in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




