
What is the internal reflection of light? What are two essential conditions for total internal reflection to take place?
Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint: It is an application of refraction of light; in this phenomenon light gets totally reflected back into the same medium when light passes from denser medium to rarer medium. This is the only phenomenon of refraction in which reflection properties are obeyed. Total internal reflection is obeyed in optical fiber also.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Since we know that in refraction, when light passes from rarer medium to denser medium then light bends towards the normal and when light passes from denser medium to rarer medium then it bends away from normal.
Since when the ray of light passes from denser to rarer medium it bends away from the normal and as the angle of incidence in denser medium increases, the angle of refraction in the rarer medium also increases.
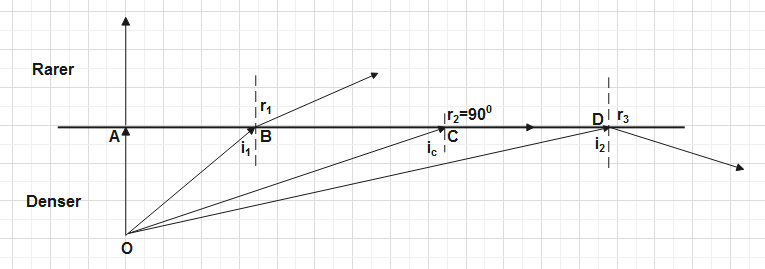
As shown in the figure as angle of incidence increases the angle of refraction also increases.
\[\because {{i}_{1}}<{{i}_{c}}<{{i}_{2}}\]
\[\therefore {{r}_{1}}<{{r}_{2}}<{{r}_{3}}\]
When light falls on point A then it directs without any deviation as it passes along the normal.
When light falls on point B at angle of incidence \[{{i}_{1}}\]then it bends away from normal with angle of refraction\[{{r}_{1}}\].
When light falls on point C at angle of incidence \[{{i}_{2}}\] then it will along the interface at angle of refraction of \[{{90}^{0}}\].At this certain angle of incidence, when angle of refraction becomes \[{{90}^{0}}\]then this angle of incidence is called critical angle \[{{i}_{c}}\].
When light falls on point D then angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle then refracted light ray comes back into the same medium after reflection from the interface. This phenomenon is called Total internal reflection (TIR).
Essential Condition of Total internal Reflection to occur: -
1. Ray of light always passes from denser medium to rarer medium.
2. Angle of incidence should always be greater than the critical angle.
Note: Optical fibre also follows the phenomenon of TIR. When the light is incident on one end of the fibre at a small angle, the light passes inside, undergoes repeated total internal reflections along the fibre and finally comes out. The angle of incidence is always larger than the critical angle of the core material with respect to its cladding. Even if the fibre is bent, the light can easily travel along the fibre.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Since we know that in refraction, when light passes from rarer medium to denser medium then light bends towards the normal and when light passes from denser medium to rarer medium then it bends away from normal.
Since when the ray of light passes from denser to rarer medium it bends away from the normal and as the angle of incidence in denser medium increases, the angle of refraction in the rarer medium also increases.
As shown in the figure as angle of incidence increases the angle of refraction also increases.
\[\because {{i}_{1}}<{{i}_{c}}<{{i}_{2}}\]
\[\therefore {{r}_{1}}<{{r}_{2}}<{{r}_{3}}\]
When light falls on point A then it directs without any deviation as it passes along the normal.
When light falls on point B at angle of incidence \[{{i}_{1}}\]then it bends away from normal with angle of refraction\[{{r}_{1}}\].
When light falls on point C at angle of incidence \[{{i}_{2}}\] then it will along the interface at angle of refraction of \[{{90}^{0}}\].At this certain angle of incidence, when angle of refraction becomes \[{{90}^{0}}\]then this angle of incidence is called critical angle \[{{i}_{c}}\].
When light falls on point D then angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle then refracted light ray comes back into the same medium after reflection from the interface. This phenomenon is called Total internal reflection (TIR).

Essential Condition of Total internal Reflection to occur: -
1. Ray of light always passes from denser medium to rarer medium.
2. Angle of incidence should always be greater than the critical angle.
Note: Optical fibre also follows the phenomenon of TIR. When the light is incident on one end of the fibre at a small angle, the light passes inside, undergoes repeated total internal reflections along the fibre and finally comes out. The angle of incidence is always larger than the critical angle of the core material with respect to its cladding. Even if the fibre is bent, the light can easily travel along the fibre.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




