
Inverted omega-shaped arrangement of vascular bundles is found in
A. Cycas leaflet
B. Cycas rachis
C. Cycas stem
D. Cycas root
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: Vascular bundles are present in the vascular plants for the transport of water and nutrients to and from the plants. Omega is a Greek symbol that is represented as \[\Omega \] and therefore, inverted omega will be represented as an inverted form of $\Omega $.
Complete answer:
Option (A) is incorrect. In the Cycas leaflet, vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral, and open. The arrangement of vascular bundles is not inverted omega-shaped.
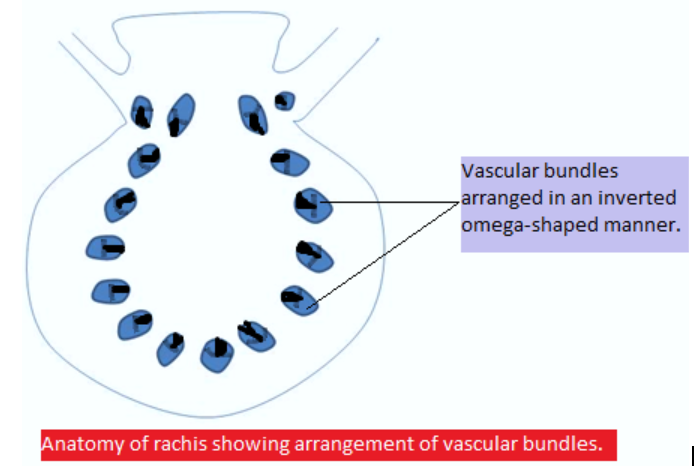
Option (B) is correct. The rachis is mostly found in compound leaves where many leaves are attached to this single large structure which forms the main axis for the joining of leaves. In Cycas rachis, vascular bundles are arranged in an inverted omega-shaped manner. When the vascular bundles are arranged at the base of the rachis in endarch condition, at the center in pseudo mesarch condition, and at the tip of the rachis in exarch condition then this type of arrangement of vascular bundles is called inverted omega-shaped arrangement of vascular bundles.
Option (C) is incorrect. The vascular bundles are arranged in the form of rings in the stem of Cycas. The stem of Cycas shows polyxylic condition i.e., the number of vascular rings is variable from 2-14.
Option (D) is incorrect. Inverted omega-shaped vascular bundle arrangements are not present in the Cycas root. In young roots, the arrangement of vascular bundles is radial which means that xylem and phloem are present on different radii.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: Cycas is a gymnosperm that contains pinnately compound leaves that are arranged on a long axis called a rachis. This plant contains vascular bundles that are arranged radially in the root, in the form of rings in the stem and inverted omega-shaped arrangement in the rachis.
Complete answer:
Option (A) is incorrect. In the Cycas leaflet, vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral, and open. The arrangement of vascular bundles is not inverted omega-shaped.
Option (B) is correct. The rachis is mostly found in compound leaves where many leaves are attached to this single large structure which forms the main axis for the joining of leaves. In Cycas rachis, vascular bundles are arranged in an inverted omega-shaped manner. When the vascular bundles are arranged at the base of the rachis in endarch condition, at the center in pseudo mesarch condition, and at the tip of the rachis in exarch condition then this type of arrangement of vascular bundles is called inverted omega-shaped arrangement of vascular bundles.

Option (C) is incorrect. The vascular bundles are arranged in the form of rings in the stem of Cycas. The stem of Cycas shows polyxylic condition i.e., the number of vascular rings is variable from 2-14.
Option (D) is incorrect. Inverted omega-shaped vascular bundle arrangements are not present in the Cycas root. In young roots, the arrangement of vascular bundles is radial which means that xylem and phloem are present on different radii.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: Cycas is a gymnosperm that contains pinnately compound leaves that are arranged on a long axis called a rachis. This plant contains vascular bundles that are arranged radially in the root, in the form of rings in the stem and inverted omega-shaped arrangement in the rachis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




