
IUPAC name of the below compound is:
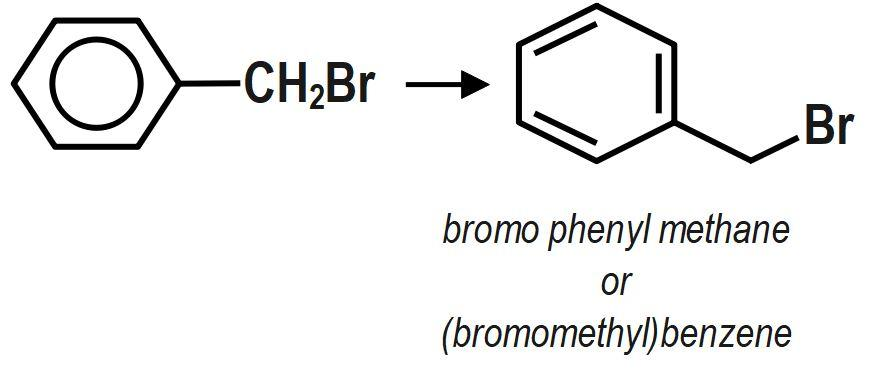
A.Bromo phenyl methane.
B.Phenyl methyl bromide.
C.Benzyl bromide.
D.Benzyl bromide.

Answer
512.1k+ views
Hint: We know that first try and identify the functional group present in the compound, then find the longest carbon chain present in the compound followed by out the substituent groups on the main chain and then using the suffix or prefix of functional group, you can name the compound by IUPAC method.
Complete answer:
In order to give compounds a name, we must follow certain rules. When we want to name organic compounds, we should follow the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature (naming scheme). We will try to know about the norms of IUPAC, that we should follow in naming organic compounds by answering the above question. A set of rules has been formulated by IUPAC for a systematic approach for the nomenclature of organic compounds which has been revised from time to time.
If organic compounds contain one principal functional group then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having that functional group is selected. Functional groups are specific substituents in the molecules which are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
As per IUPAC rules, the first thing is to select the longest continuous chain. Then this chain is numbered and the numbering should begin from the end which is close to the substituent groups. Each substituent group has a certain assigned name whose numbering depends on the position of the carbon it has been attached to. These groups are generally arranged alphabetically. The IUPAC name of the given compound is bromo phenyl methane. Phenyl group acts as a substituent and the parent compound is bromomethane. It can also be written as (bromomethyl) benzene.
 Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
Remember that Isomers are classified as structural (constitutional) and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers are further classified as chain isomers, position isomers and functional group isomers. Position isomers are also structural or constitutional isomers with the same functional group and same carbon skeleton but differing in position of the same functional group on or inside the carbon chain.
Complete answer:
In order to give compounds a name, we must follow certain rules. When we want to name organic compounds, we should follow the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature (naming scheme). We will try to know about the norms of IUPAC, that we should follow in naming organic compounds by answering the above question. A set of rules has been formulated by IUPAC for a systematic approach for the nomenclature of organic compounds which has been revised from time to time.
If organic compounds contain one principal functional group then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having that functional group is selected. Functional groups are specific substituents in the molecules which are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
As per IUPAC rules, the first thing is to select the longest continuous chain. Then this chain is numbered and the numbering should begin from the end which is close to the substituent groups. Each substituent group has a certain assigned name whose numbering depends on the position of the carbon it has been attached to. These groups are generally arranged alphabetically. The IUPAC name of the given compound is bromo phenyl methane. Phenyl group acts as a substituent and the parent compound is bromomethane. It can also be written as (bromomethyl) benzene.

Note:
Remember that Isomers are classified as structural (constitutional) and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers are further classified as chain isomers, position isomers and functional group isomers. Position isomers are also structural or constitutional isomers with the same functional group and same carbon skeleton but differing in position of the same functional group on or inside the carbon chain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




