
Kolbe’s electrolysis of potassium succinate gives \[C{{O}_{2}}\] and ... If true enter1, else enter O.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Generally in Kolbe’s electrolysis dicarboxylic containing molecules first undergo decarboxylation and later dimerization to give alkenes as the product. A radical intermediate is going to form after decarboxylation is going to combine to form an alkene as the product.
Complete step by step answer:
- The structure of the potassium succinate as follows.
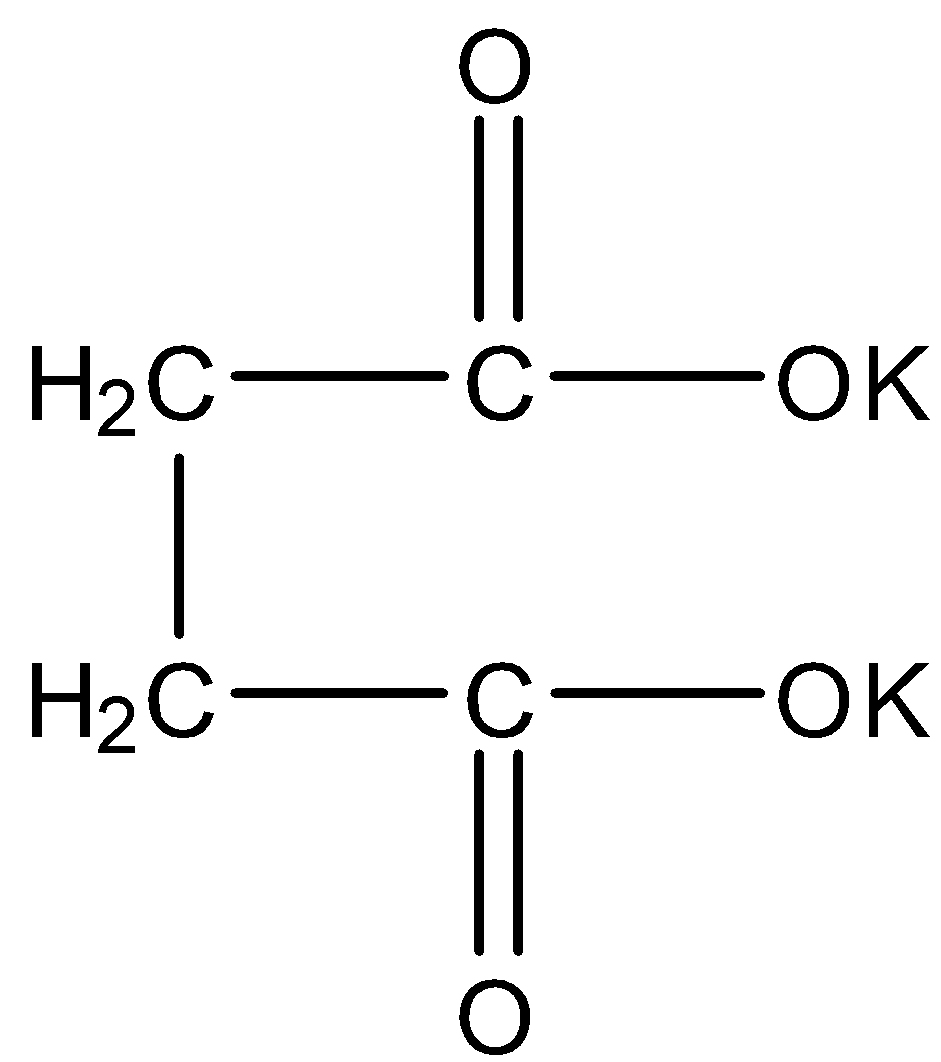
- In Kolbe’s electrolysis results the formation of symmetrical hydrocarbons.
- The Kolbe’s electrolysis of the potassium succinate is as follows.
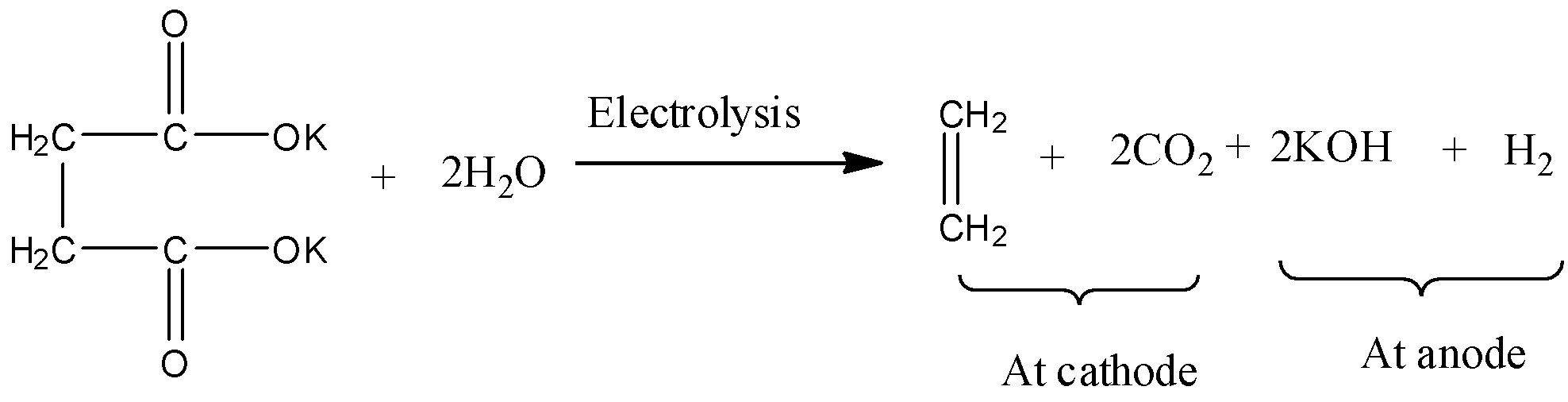
- Potassium succinate undergoes decarboxylation and forms carbon dioxide (\[C{{O}_{2}}\]) and alkene (ethylene-\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}\]) at cathode and potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas forms at anode.
- Therefore Kolbe’s electrolysis of potassium succinate gives \[C{{O}_{2}}\] and \[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}\]
- The given statement is correct so we have to enter 1.
Additional information:
- Kolbe’s electrolysis is used to prepare most useful hydrocarbons.
- This type of electrolysis is modified and done by using liquid ammonia.
- In Kolbe’s electrolysis free radicals are going to form at anode, after formation of free radicals at anode they undergo dimerization and form alkenes as the product.
- Kolbe’ electrolysis used to prepare low molecular weight polymers and in the preparation of polystyrene.
Note: If any organic molecule has two carboxylic acids on side by side carbon they are unstable and will give alkene as the product always to get stabilization. The number of carbon dioxide molecules liberated in Kolbe’s electrolysis is nothing but the number of carboxylic acid functional groups present in the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
- The structure of the potassium succinate as follows.

- In Kolbe’s electrolysis results the formation of symmetrical hydrocarbons.
- The Kolbe’s electrolysis of the potassium succinate is as follows.

- Potassium succinate undergoes decarboxylation and forms carbon dioxide (\[C{{O}_{2}}\]) and alkene (ethylene-\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}\]) at cathode and potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas forms at anode.
- Therefore Kolbe’s electrolysis of potassium succinate gives \[C{{O}_{2}}\] and \[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}\]
- The given statement is correct so we have to enter 1.
Additional information:
- Kolbe’s electrolysis is used to prepare most useful hydrocarbons.
- This type of electrolysis is modified and done by using liquid ammonia.
- In Kolbe’s electrolysis free radicals are going to form at anode, after formation of free radicals at anode they undergo dimerization and form alkenes as the product.
- Kolbe’ electrolysis used to prepare low molecular weight polymers and in the preparation of polystyrene.
Note: If any organic molecule has two carboxylic acids on side by side carbon they are unstable and will give alkene as the product always to get stabilization. The number of carbon dioxide molecules liberated in Kolbe’s electrolysis is nothing but the number of carboxylic acid functional groups present in the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




