
Life cycle of gymnosperms is
A. Haplontic
B. Haplodiplontic
C. Diplontic
D. Diplohaplontic
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: Gymnosperms are plants that are flowerless and grow cones and seeds. As gymnosperm seeds are not encased inside an ovary, the word gymnosperm literally means "naked seed."
Complete Answer:
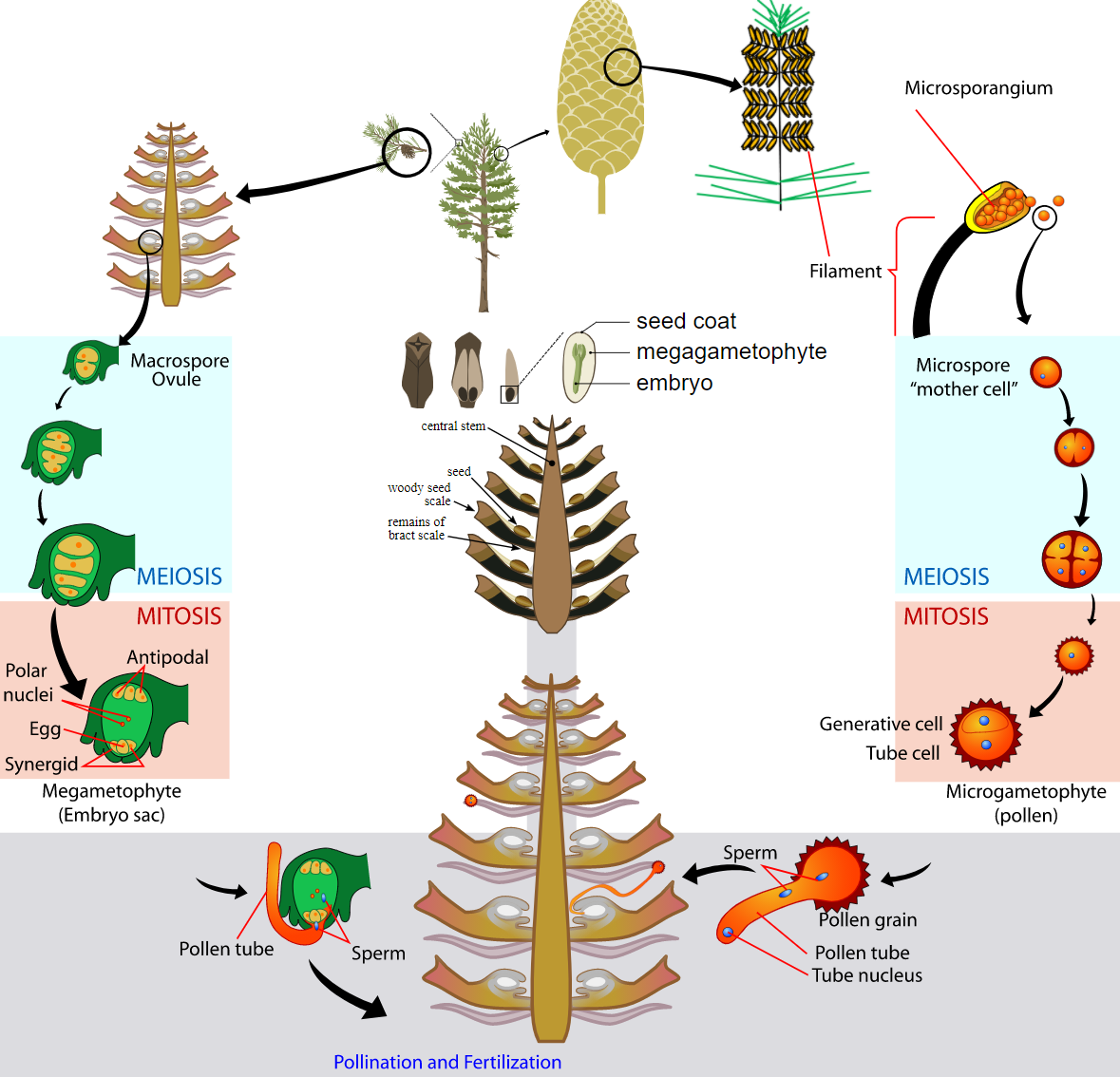
Gymnosperms are vascular plants which, in cones, produce seeds. Conifers, such as pine and spruce trees, are examples. The life cycle of the gymnosperm has a dominant generation of sporophytes. Both gametophytes grow on the sporophyte parent plant and the new sporophytes of the next generation.
On a mature sporophyte plant, cones form. Male spores grow within male cones into male gametophytes. Each male gametophyte is made up of many cells that are enclosed within a pollen grain. Female spores grow into female gametophytes within women's cones. Within an ovule, each female gametophyte produces an egg.
When pollen is moved from a male cone to a female cone, pollination occurs. If sperm then moves so that fertilisation will occur from the pollen to an egg, a diploid zygote results. Inside a seed, the zygote grows into an embryo that emerges from the ovule within the female cone. It can grow into a mature sporophyte tree if the seed germinates, which repeats the cycle.
The diploid sporophyte in the diplontic life cycle is the dominant autonomous photosynthetic process of the plant body. Gametes reflect the haploid process only. In gametic meiosis, the zygote divides mitotically to produce a multicellular diploid individual, instead of dividing meiotically immediately to produce haploid cells. To produce haploid cells or gametes, cells from the diploid individuals then undergo meiosis.
As in many leaves, haploid cells can divide again (by mitosis) to form more haploid cells, but the haploid phase is not the predominant phase of the life cycle. Mitosis occurs only in the diploid process in most graduates, i.e. gametes typically develop rapidly and fuse to create diploid zygotes. The diploid is the primary plant body (sporophyte 2n). Both seed-bearing plants, gymnosperms, and angiosperms are examples.
The haploid cell process is prevalent in the haplontic life cycle. The meiosis of the zygotic produces haploid spores. In order to generate more haplons, these things will then break mitotically. Male and female gametes will give rise to these haplontic. The 2n state of the nucleus is present only in the zygote in the haplontic life cycle and this state is very short lived.
The diploid process of the organism ends and develops multiple haploid cells.
To shape either larger, multicellular individuals, or more haploid cells, these cells divide mitotically. To become a zygote, two opposite forms of gametes (e.g., male and female) from these individuals or cells fuse. The primary body of vegetative plants is haploid. Examples include mushrooms, green algae and several protozoa. Both the diploid (2n) and haploid (1n) stages are multicellular in the haplodiplontic period.
The correct Answer is option C, Diplontic.
Note: Gymnosperms are a group of plants that produce seeds inside an ovary or fruit that are not enclosed. The seeds are exposed to the air and are directly fertilised by pollination.
Complete Answer:
Gymnosperms are vascular plants which, in cones, produce seeds. Conifers, such as pine and spruce trees, are examples. The life cycle of the gymnosperm has a dominant generation of sporophytes. Both gametophytes grow on the sporophyte parent plant and the new sporophytes of the next generation.
On a mature sporophyte plant, cones form. Male spores grow within male cones into male gametophytes. Each male gametophyte is made up of many cells that are enclosed within a pollen grain. Female spores grow into female gametophytes within women's cones. Within an ovule, each female gametophyte produces an egg.
When pollen is moved from a male cone to a female cone, pollination occurs. If sperm then moves so that fertilisation will occur from the pollen to an egg, a diploid zygote results. Inside a seed, the zygote grows into an embryo that emerges from the ovule within the female cone. It can grow into a mature sporophyte tree if the seed germinates, which repeats the cycle.
The diploid sporophyte in the diplontic life cycle is the dominant autonomous photosynthetic process of the plant body. Gametes reflect the haploid process only. In gametic meiosis, the zygote divides mitotically to produce a multicellular diploid individual, instead of dividing meiotically immediately to produce haploid cells. To produce haploid cells or gametes, cells from the diploid individuals then undergo meiosis.
As in many leaves, haploid cells can divide again (by mitosis) to form more haploid cells, but the haploid phase is not the predominant phase of the life cycle. Mitosis occurs only in the diploid process in most graduates, i.e. gametes typically develop rapidly and fuse to create diploid zygotes. The diploid is the primary plant body (sporophyte 2n). Both seed-bearing plants, gymnosperms, and angiosperms are examples.
The haploid cell process is prevalent in the haplontic life cycle. The meiosis of the zygotic produces haploid spores. In order to generate more haplons, these things will then break mitotically. Male and female gametes will give rise to these haplontic. The 2n state of the nucleus is present only in the zygote in the haplontic life cycle and this state is very short lived.
The diploid process of the organism ends and develops multiple haploid cells.
To shape either larger, multicellular individuals, or more haploid cells, these cells divide mitotically. To become a zygote, two opposite forms of gametes (e.g., male and female) from these individuals or cells fuse. The primary body of vegetative plants is haploid. Examples include mushrooms, green algae and several protozoa. Both the diploid (2n) and haploid (1n) stages are multicellular in the haplodiplontic period.
The correct Answer is option C, Diplontic.

Note: Gymnosperms are a group of plants that produce seeds inside an ovary or fruit that are not enclosed. The seeds are exposed to the air and are directly fertilised by pollination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




