
What is meant by the term Artificial propagation of plants?
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Some plants are grown for commercial purposes in a large number by using various methods.As the word artificial suggests, these are the methods done manually for the propagation of different plants.
Complete answer:
The regeneration or formation of a new individual from any vegetative part of the body is called vegetative propagation or vegetative reproduction.
Several methods of vegetative propagation are man-made and are developed by plant growers and horticulturists for commercially producing crops and they are called artificial propagation methods. In the given procedure, a portion is removed from the plant body and then it is grown separately. Some of the processes are given below:
Cutting - a small piece of any plant organ (stem, root, or leaf) is used for propagation and it is known as cutting. The most common type of cutting used is stem cutting when it comes to artificial propagation. Some of the common examples are Grapes and sugarcanes. Leaf cuttings are used to propagate many plants. Some of the main plants are Begonia and Bryophyllum. Root cuttings are used to propagate Cistron and Tamarind. When such cuttings are planted adventitious roots are grown.
Layering- in this method of artificially propagating plants, the roots are artificially induced on the stem branches while the stem is still attached to the parent plant for propagation. There are 2 common types of layering:
-> Mound layering - in this technique the lower branch of the stem is bent and covered in such a way that the tip of the branch remains above the ground and the roots are grown from the stem. The roots seen here are adventitious roots. Used for strawberries and jasmine propagation.
-> Air layering - it is employed in the plants where the branches are thick with no scope of bending. In this method, a part of the stem is girdled or silt at an upward angle and covered with moist cotton or moss. To prevent drying it is covered with polythene. This portion where the plant is wrapped is called Gootee. The roots appear after some time and then this branch is cut and grown separately. This is used in the propagation of litchi and many citrus fruits like oranges and lemons.
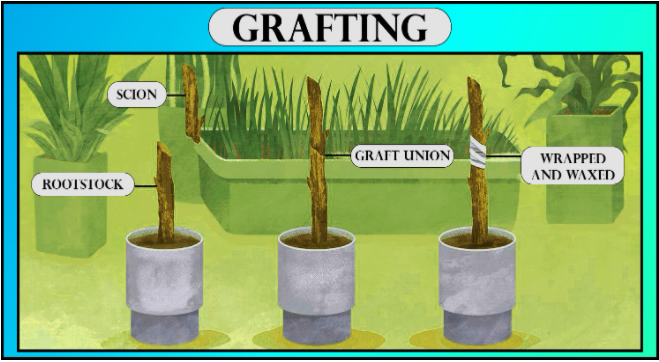
Grafting- a new variety produced by joining parts of 2 different plants and the method is called grafting. The plant root which is rooted is known as the stock and it is joined to the part of the shoot from another plant which is superior and known as the scion. The plant which is more resistant to disease and is more efficient in water absorption is used as the rootstock. Stem cutting from a superior quality plant is then used, scion.
-Both ends of the stock and scion which are the grafting ends are being cut obliquely and then these are placed over one another in a way that the cambia come in contact. The pieces are firmly held in place by tape or rubber tube. This results in the formation of new vascular tissues.
-This technique is used a lot for commercially viable plants like rose, mango, apple, and pear.
Micropropagation- this method includes the propagation of plants by culturing cells, tissues, and organs which is known as tissue culture. The tiny pieces of plant organs or tissues are grown in a suitable nutrient medium that is needed by the plant. In the initial stages, an undifferentiated mass of cells is formed which is called callus and it then leads to the formation of new plantlets. These plantlets are then transferred to separate pots or nursery beds to obtain a large variety of plants.
Note:
>Tissue culture technique was first thought of by Haberlandt (1902) and Hanning (1908) but successful attempts were made by White in the case of tomato root.
>Grafting is usually done between the related varieties or species.
>Micropropagation is often used for quick multiplication of plants.
Complete answer:
The regeneration or formation of a new individual from any vegetative part of the body is called vegetative propagation or vegetative reproduction.
Several methods of vegetative propagation are man-made and are developed by plant growers and horticulturists for commercially producing crops and they are called artificial propagation methods. In the given procedure, a portion is removed from the plant body and then it is grown separately. Some of the processes are given below:
Cutting - a small piece of any plant organ (stem, root, or leaf) is used for propagation and it is known as cutting. The most common type of cutting used is stem cutting when it comes to artificial propagation. Some of the common examples are Grapes and sugarcanes. Leaf cuttings are used to propagate many plants. Some of the main plants are Begonia and Bryophyllum. Root cuttings are used to propagate Cistron and Tamarind. When such cuttings are planted adventitious roots are grown.
Layering- in this method of artificially propagating plants, the roots are artificially induced on the stem branches while the stem is still attached to the parent plant for propagation. There are 2 common types of layering:
-> Mound layering - in this technique the lower branch of the stem is bent and covered in such a way that the tip of the branch remains above the ground and the roots are grown from the stem. The roots seen here are adventitious roots. Used for strawberries and jasmine propagation.
-> Air layering - it is employed in the plants where the branches are thick with no scope of bending. In this method, a part of the stem is girdled or silt at an upward angle and covered with moist cotton or moss. To prevent drying it is covered with polythene. This portion where the plant is wrapped is called Gootee. The roots appear after some time and then this branch is cut and grown separately. This is used in the propagation of litchi and many citrus fruits like oranges and lemons.
Grafting- a new variety produced by joining parts of 2 different plants and the method is called grafting. The plant root which is rooted is known as the stock and it is joined to the part of the shoot from another plant which is superior and known as the scion. The plant which is more resistant to disease and is more efficient in water absorption is used as the rootstock. Stem cutting from a superior quality plant is then used, scion.
-Both ends of the stock and scion which are the grafting ends are being cut obliquely and then these are placed over one another in a way that the cambia come in contact. The pieces are firmly held in place by tape or rubber tube. This results in the formation of new vascular tissues.
-This technique is used a lot for commercially viable plants like rose, mango, apple, and pear.
Micropropagation- this method includes the propagation of plants by culturing cells, tissues, and organs which is known as tissue culture. The tiny pieces of plant organs or tissues are grown in a suitable nutrient medium that is needed by the plant. In the initial stages, an undifferentiated mass of cells is formed which is called callus and it then leads to the formation of new plantlets. These plantlets are then transferred to separate pots or nursery beds to obtain a large variety of plants.
Note:
>Tissue culture technique was first thought of by Haberlandt (1902) and Hanning (1908) but successful attempts were made by White in the case of tomato root.
>Grafting is usually done between the related varieties or species.
>Micropropagation is often used for quick multiplication of plants.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




