
Mention the functions of each component of a nuclear reactor?
Answer
537.3k+ views
Hint: Nuclear reactor is the place where the nuclear chain reactions take place that produce energy by fission. The main purpose of a nuclear reactor is to generate and control the amount of energy released and this can be achieved by using a device that can absorb neutrons so that the nuclear chain reaction, nuclear fission and fusion, taking place within the reactor core can be slowed down.
Complete answer:
Nuclear fission is described as the process where the nucleus of a heavy atom splits into fragments of lighter nuclei. This process gives out a huge amount of energy. One of the ways to achieve this process is to bombard the nucleus of heavy atoms with neutrinos. Along with producing energy, the reaction also produces some neutrons. These neutrons can later be used to split other atoms further in the reaction.
The kinetic energy produced during the process of fission reaction is converted into thermal energy. The resulting fission products undergo extreme deceleration, where the KE is converted to heat. The heat produced by the process is transferred to a coolant which can be used directly or indirectly by converting into steam. The steam can be used to operate turbines, thereby converting the thermal energy into mechanical energy.
A nuclear reactor is an essential part of a nuclear power plant. It is the place where the nuclear chain reactions take place that produce energy by fission. The heat thus produced can be used to produce electricity. The main purpose of a nuclear reactor is to contain and control the amount of energy released. Uranium and Plutonium are used as the nuclear fuel in the reactors. The heat produced by nuclear reactions is used to convert the water into steam, which can be further converted into carbon-free electricity by the help of turbines.
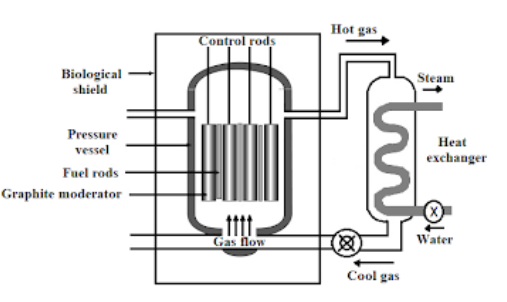
Main Components of a Nuclear Reactor:
1.The Core: It contains all the fuel for reaction and generates the heat required for energy production.
2.Control rod: It is used in nuclear reactors to control the fission rate of nuclear fuel, that is, Uranium or Plutonium.
3.The Coolant: It passes through the core; it absorbs the heat and transfer it into turbines
4.The Turbine: It transfers energy into the mechanical form.
5.The Cooling Tower: It eliminates the excess heat that is not converted or transferred by the reactor.
6.The Containment: It is the enveloping structure that separated the nuclear reactor from the surrounding environment.
Control rods are loaded into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted specifically in order to control the rate of the nuclear chain reaction, which results in the controlled thermal power output of the nuclear reactor, the rate of steam production, and the electrical power output generation of the nuclear power station. The number of control rods inserted into the core, and the distance to which they are inserted, strongly affect the reactivity of the reactor.
Note:
Control rods are the steering tools of the fission rate in reactors. They have the capability to absorb neutrons; these neutrons can be used to split other atoms further in the reaction, so that the nuclear chain reaction taking place within the reactor core can be slowed down in order to get the controlled amount of energy.
Complete answer:
Nuclear fission is described as the process where the nucleus of a heavy atom splits into fragments of lighter nuclei. This process gives out a huge amount of energy. One of the ways to achieve this process is to bombard the nucleus of heavy atoms with neutrinos. Along with producing energy, the reaction also produces some neutrons. These neutrons can later be used to split other atoms further in the reaction.
The kinetic energy produced during the process of fission reaction is converted into thermal energy. The resulting fission products undergo extreme deceleration, where the KE is converted to heat. The heat produced by the process is transferred to a coolant which can be used directly or indirectly by converting into steam. The steam can be used to operate turbines, thereby converting the thermal energy into mechanical energy.
A nuclear reactor is an essential part of a nuclear power plant. It is the place where the nuclear chain reactions take place that produce energy by fission. The heat thus produced can be used to produce electricity. The main purpose of a nuclear reactor is to contain and control the amount of energy released. Uranium and Plutonium are used as the nuclear fuel in the reactors. The heat produced by nuclear reactions is used to convert the water into steam, which can be further converted into carbon-free electricity by the help of turbines.

Main Components of a Nuclear Reactor:
1.The Core: It contains all the fuel for reaction and generates the heat required for energy production.
2.Control rod: It is used in nuclear reactors to control the fission rate of nuclear fuel, that is, Uranium or Plutonium.
3.The Coolant: It passes through the core; it absorbs the heat and transfer it into turbines
4.The Turbine: It transfers energy into the mechanical form.
5.The Cooling Tower: It eliminates the excess heat that is not converted or transferred by the reactor.
6.The Containment: It is the enveloping structure that separated the nuclear reactor from the surrounding environment.
Control rods are loaded into the core of a nuclear reactor and adjusted specifically in order to control the rate of the nuclear chain reaction, which results in the controlled thermal power output of the nuclear reactor, the rate of steam production, and the electrical power output generation of the nuclear power station. The number of control rods inserted into the core, and the distance to which they are inserted, strongly affect the reactivity of the reactor.
Note:
Control rods are the steering tools of the fission rate in reactors. They have the capability to absorb neutrons; these neutrons can be used to split other atoms further in the reaction, so that the nuclear chain reaction taking place within the reactor core can be slowed down in order to get the controlled amount of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




