
When methane is heated with oxygen in the presence of $ M{o_2}{O_3} $ catalyst, the organic product obtained is:
A: methanal
B: ethanol acid
C: methanol
D: ethanol
E: $ 2 - methylpropan - 2 - ol $
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint :As we know that Methane is basically a highly stable compound. Thus, a high amount of activation energy is needed to break the $ C - H $ bond or to oxidize the molecule. Hence, a higher temperature (usually around $ 500k $ ) of catalyst is required for the oxidation of methane in comparison to longer chain hydrocarbons.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know that Heating of methane with oxygen in the presence of $ M{o_2}{O_3} $ catalysts is an oxidation reaction. so, heating is done in order to activate the catalyst i.e. Molybdenum oxide ( $ M{o_2}{O_3} $ ). The process is generally known as the catalytic oxidation of methane. We can show the chemical equation for the process as written below:
$ C{H_4} + {O_2}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{M{o_2}{O_3}}}HCHO + {H_2}O $
The mechanism of the reaction can be depicted as follows:
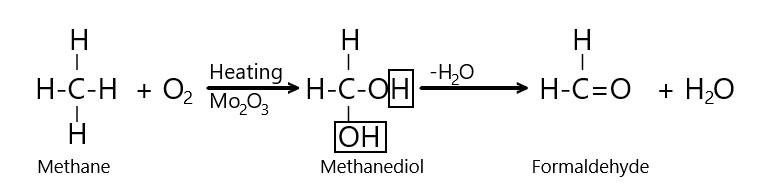
Thus, it is clear from the reaction mechanism that combustion of methane in the presence of Molybdenum oxide results into the production of formaldehyde or methanal (i.e. $ HCHO $ ) and water.
Hence, the correct answer is Option A i.e. methanal.
Additional Information:
Similar to the aforementioned reaction, if we replace the catalyst with another one, a different product will be formed. For instance, if a mixture of methane and oxygen is made to react in the presence of copper tubes at a temperature of $ \;523K $ and $ 100{\text{ }}atm $ pressure, methyl alcohol or methanol is produced instead of methanal. The reaction is depicted below:
$ C{H_4} + {O_2}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{Cu}}C{H_2}OH + {H_2}O $
Methanol can also be oxidized to methanal in the presence of oxidizing agents such as acidified potassium dichromate.
Note :
Always remember that when combustion of methane takes place the product which is generally formed is always an aldehyde. Hence, heating of methane results in the formation of Formaldehyde and water.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know that Heating of methane with oxygen in the presence of $ M{o_2}{O_3} $ catalysts is an oxidation reaction. so, heating is done in order to activate the catalyst i.e. Molybdenum oxide ( $ M{o_2}{O_3} $ ). The process is generally known as the catalytic oxidation of methane. We can show the chemical equation for the process as written below:
$ C{H_4} + {O_2}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{M{o_2}{O_3}}}HCHO + {H_2}O $
The mechanism of the reaction can be depicted as follows:

Thus, it is clear from the reaction mechanism that combustion of methane in the presence of Molybdenum oxide results into the production of formaldehyde or methanal (i.e. $ HCHO $ ) and water.
Hence, the correct answer is Option A i.e. methanal.
Additional Information:
Similar to the aforementioned reaction, if we replace the catalyst with another one, a different product will be formed. For instance, if a mixture of methane and oxygen is made to react in the presence of copper tubes at a temperature of $ \;523K $ and $ 100{\text{ }}atm $ pressure, methyl alcohol or methanol is produced instead of methanal. The reaction is depicted below:
$ C{H_4} + {O_2}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{Cu}}C{H_2}OH + {H_2}O $
Methanol can also be oxidized to methanal in the presence of oxidizing agents such as acidified potassium dichromate.
Note :
Always remember that when combustion of methane takes place the product which is generally formed is always an aldehyde. Hence, heating of methane results in the formation of Formaldehyde and water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




