
Micropropagation is
(a) Raising of plants from a small tissue in culture
(b) Multiplication of small plants
(c) Propagation of small parts of organisms
(d) Indefinite maintenance of an organ or tissue
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Propagation means taking a part from an organism and growing it in an artificially created environment. The asexual method of reproduction is commonly employed in Micropropagation. It is also known as the tissue culture technique.
Complete answer:
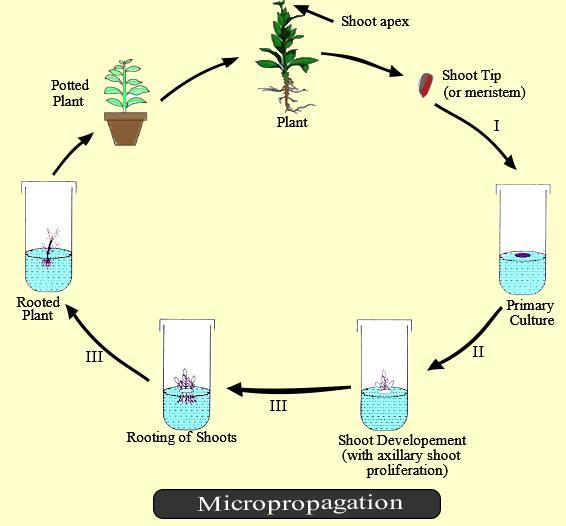
Micropropagation is the multiplication of small plants. It is the propagation of plants by growing plantlets in tissue culture up to a certain stage of development and then planting them out. Only the vegetative parts of the plants are used in tissue culture techniques. Another means of asexual reproduction is by multiplying their genetic replicas of plants called clonal propagation, here the plants can be populated from a single individual through asexual means by cloning (duplicating) their cells.
Steps in Micropropagation:
- The stock plant is selected and grown under controlled conditions.
- The explants (part) are established in a suitable culture medium by isolating the explant, sterilization of the explant, and washing.
- Rapid multiplication of shoots or somatic embryo formation in the culture medium.
- The shoot is transferred to a culture medium for the development of roots. The shoots also can be transferred directly to the soil for the root development.
- The plantlet is now established in the soil and is transferred to a greenhouse under controlled conditions of temperature, humidity, and light. Here, the plant continues to grow.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Raising of plants from a small tissue in culture.’
Note: In the artificial propagation of specific plants via multiplication of vegetative parts, do not generate functional seeds as seen in figs, grapes, bananas, etc. In potato, apple and many other ornamental plants successful application of clonal propagation has been observed.
Complete answer:
Micropropagation is the multiplication of small plants. It is the propagation of plants by growing plantlets in tissue culture up to a certain stage of development and then planting them out. Only the vegetative parts of the plants are used in tissue culture techniques. Another means of asexual reproduction is by multiplying their genetic replicas of plants called clonal propagation, here the plants can be populated from a single individual through asexual means by cloning (duplicating) their cells.
Steps in Micropropagation:
- The stock plant is selected and grown under controlled conditions.
- The explants (part) are established in a suitable culture medium by isolating the explant, sterilization of the explant, and washing.
- Rapid multiplication of shoots or somatic embryo formation in the culture medium.
- The shoot is transferred to a culture medium for the development of roots. The shoots also can be transferred directly to the soil for the root development.
- The plantlet is now established in the soil and is transferred to a greenhouse under controlled conditions of temperature, humidity, and light. Here, the plant continues to grow.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Raising of plants from a small tissue in culture.’
Note: In the artificial propagation of specific plants via multiplication of vegetative parts, do not generate functional seeds as seen in figs, grapes, bananas, etc. In potato, apple and many other ornamental plants successful application of clonal propagation has been observed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




