
Miracidium larva occurs in the life history of
(a) Roundworm
(b) Liver fluke
(c) Earthworm
(d) Tapeworm
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: Fasciola hepatica also known as the common liver fluke. It is a parasite of the class phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the liver of various mammals including humans. Fasciolosis is currently classified as a plant trematode infection often acquired through eating the parasites.
Complete answer:
-Compared to other helminths the life cycle is complex and involves a host (human, cattle, etc.), an intermediate host (the mud snail: Galba truncate), and several free-living stages.
- Adult fluke lay eggs in the host that are passed out onto pasture in the feces. At a suitable temperature, a Miracidium develops within the egg, hatches, and migrates in thin films of moisture actively seeking the snail host. Miracidia can only survive for a few hrs outside the snails. Within the snail undergo two further development stages including multiplication eventually becoming infective cercariae which emerge from the snail when the temperature and moisture levels are suitable. The cercariae migrate onto wet herbage encysting as metacercaria the highly resilient infective stage of liver fluke. The young flukes cause tissue damage when they migrate to the liver.
-Thus, the Miracidium larva is a part of the Liver fluke life cycle.
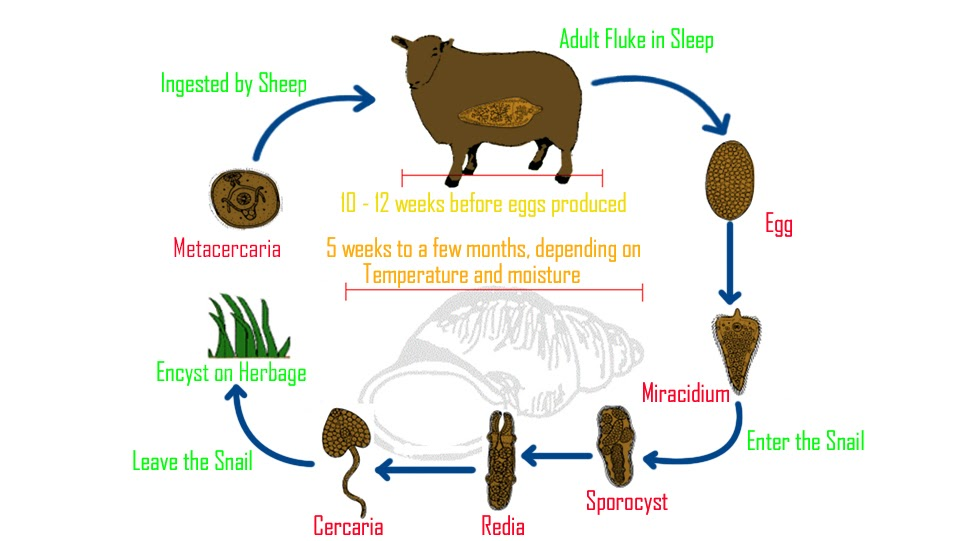 Figure: The Life cycle of Liver flukes
Figure: The Life cycle of Liver flukes
Additional information:
Liver fluke disease is caused by the trematode parasite Fasciola hepatica. The disease can result from the migration of large numbers of immature flukes through the liver or the presence of adult flukes in the bile duct or both. Liver flukes can infect all grazing animals but mainly affects sheep and cattle. It is most pathogenic in sheep.
So, the correct answer is ‘Liver fluke’.
Note:
Miracidia will grow and develop within the intermediate host into a sac-like structure known as sporocyst, either of which may give rise to free-swimming motile cercariae larvae. Miracidium larva is a minute oval and elongates it is covered with 18 to 21 flat ciliated epidermal cells lying in five rin
Complete answer:
-Compared to other helminths the life cycle is complex and involves a host (human, cattle, etc.), an intermediate host (the mud snail: Galba truncate), and several free-living stages.
- Adult fluke lay eggs in the host that are passed out onto pasture in the feces. At a suitable temperature, a Miracidium develops within the egg, hatches, and migrates in thin films of moisture actively seeking the snail host. Miracidia can only survive for a few hrs outside the snails. Within the snail undergo two further development stages including multiplication eventually becoming infective cercariae which emerge from the snail when the temperature and moisture levels are suitable. The cercariae migrate onto wet herbage encysting as metacercaria the highly resilient infective stage of liver fluke. The young flukes cause tissue damage when they migrate to the liver.
-Thus, the Miracidium larva is a part of the Liver fluke life cycle.

Additional information:
Liver fluke disease is caused by the trematode parasite Fasciola hepatica. The disease can result from the migration of large numbers of immature flukes through the liver or the presence of adult flukes in the bile duct or both. Liver flukes can infect all grazing animals but mainly affects sheep and cattle. It is most pathogenic in sheep.
So, the correct answer is ‘Liver fluke’.
Note:
Miracidia will grow and develop within the intermediate host into a sac-like structure known as sporocyst, either of which may give rise to free-swimming motile cercariae larvae. Miracidium larva is a minute oval and elongates it is covered with 18 to 21 flat ciliated epidermal cells lying in five rin
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




