
How do multiple alleles affect the number of phenotypes?
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: Multiple allelism can be defined as a condition in which a gene has three or more alleles. Therefore, the term multiple alleles refer to the existence of three or more alleles for a single gene.
Complete answer:
A probable coding sequence of a gene is an allele. The presence of genes for unique characteristics is a common myth or flawed terminology. Genes regulate distinct characteristics of an organism.
Depending on the trait's particular pattern of inheritance, having more than 1 or 2 alleles for a trait will significantly increase the number of phenotypes.
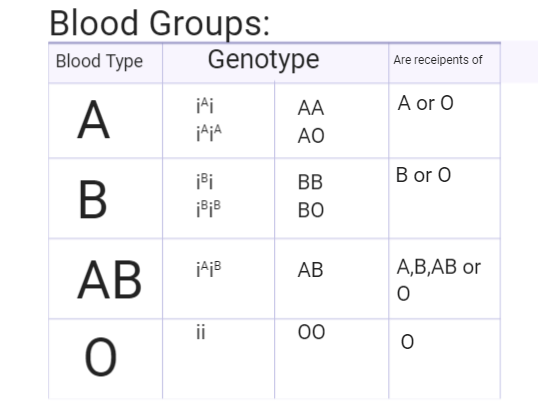
For instance, 3 alleles regulate the human blood type (just referring to the ABO blood groups here): \[A\], \[B\], and \[O\]. Both \[A\] and \[B\] dominate \[O\], but they are co-dominant with each other. On the surface of red blood cells, the letters refer to two unique carbohydrate molecules. Individuals may have carbohydrates \[A\] (type A blood), carbohydrates \[B\] (type B blood), carbohydrates \[A\] and \[B\] (type AB blood), or carbohydrates B (type B blood), or carbohydrates \[A\] and \[B\] (type AB blood) (blood type O).
So, while there may be two individuals with different alleles, like one is \[AA\] and one is \[AO\], both of them will have the same phenotype, which is type A blood. There are four phenotypes here in particular. Again, however, depending on the trait's inheritance pattern, the exact number of phenotypes can vary, whether it is Mendelian, incomplete dominance, codominance, polygenic, etc.
Note:
Coat color in cats is also an example of multiple allelism: Breeding has occurred for thousands of years in domestic cats, selecting for numerous and varied coat colors. With long hair, short hair and no hair, cats can be seen. There are genes that code for whether a cat is going to have fur or not. For this gene, there are several alleles, some that produce hairless cats, and some that produce hairy cats. The length of hair is regulated by another gene. Long-haired cats have two recessive alleles, whereas short hair is formed by a dominant allele.
Complete answer:
A probable coding sequence of a gene is an allele. The presence of genes for unique characteristics is a common myth or flawed terminology. Genes regulate distinct characteristics of an organism.
Depending on the trait's particular pattern of inheritance, having more than 1 or 2 alleles for a trait will significantly increase the number of phenotypes.
For instance, 3 alleles regulate the human blood type (just referring to the ABO blood groups here): \[A\], \[B\], and \[O\]. Both \[A\] and \[B\] dominate \[O\], but they are co-dominant with each other. On the surface of red blood cells, the letters refer to two unique carbohydrate molecules. Individuals may have carbohydrates \[A\] (type A blood), carbohydrates \[B\] (type B blood), carbohydrates \[A\] and \[B\] (type AB blood), or carbohydrates B (type B blood), or carbohydrates \[A\] and \[B\] (type AB blood) (blood type O).
So, while there may be two individuals with different alleles, like one is \[AA\] and one is \[AO\], both of them will have the same phenotype, which is type A blood. There are four phenotypes here in particular. Again, however, depending on the trait's inheritance pattern, the exact number of phenotypes can vary, whether it is Mendelian, incomplete dominance, codominance, polygenic, etc.

Note:
Coat color in cats is also an example of multiple allelism: Breeding has occurred for thousands of years in domestic cats, selecting for numerous and varied coat colors. With long hair, short hair and no hair, cats can be seen. There are genes that code for whether a cat is going to have fur or not. For this gene, there are several alleles, some that produce hairless cats, and some that produce hairy cats. The length of hair is regulated by another gene. Long-haired cats have two recessive alleles, whereas short hair is formed by a dominant allele.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




