
Name the largest bacterium species.
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: Bacteria are single-celled unicellular organisms and are classified under the domain Prokaryote because they lack membrane-bound organelles like those found in eukaryotes. Although they are all microscopic organisms and cannot be seen with naked eyes that can be found in various environments in nature, bacteria widely vary in size, shape, and arrangement.
Complete answer:
Bacteria are present in the environment in the range of 0.2 and 2.0\[\mu \]m- the average size of most bacteria. Research studies have shown their size to play an important role in survival over time. Due to their small size, bacteria can be used to exploit and can survive in various microenvironments.
The bacterial include such environments as the vertical gradients in intertidal marine sediments in which various types of bacteria have been found because they can thrive in harsh habitats
The small size of bacteria is also beneficial for parasitism and oligotrophy. Bacteria can continue relying on a range of hosts (large and small) for their nutrition.
There are Some of the smallest bacteria present in the environment called microorganisms known as nanobacterium.
They are featured due to reason by their slow growth under aerobic conditions as well as being Gram-negative in nature.
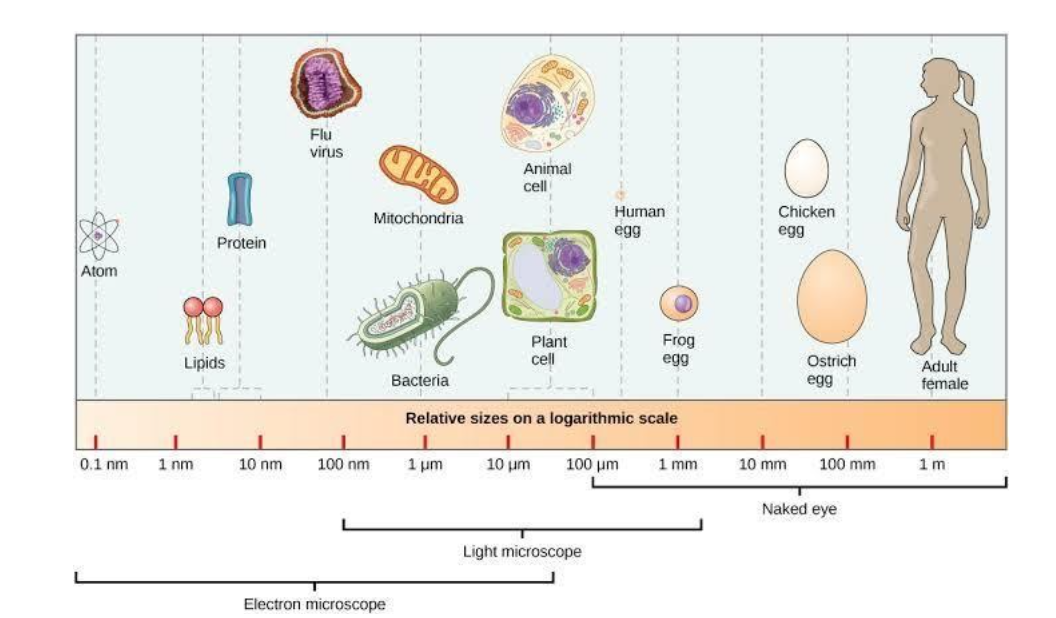
Although they have been present in sizes that range between 0.2 and 0.5\[\mu \]m (200 to 500 nanometres) there have been studies where some were found to filter through 0.1\[\mu \]m filters. Some bacteria have large sizes that they are able to see with the naked eye.
For example, the Schaudinn bütschlii have sizes that measure between 4 and 5\[\mu \]m in diameter and are considered to be large bacteria.
Thiomargarita namibiensis are able to grow to be as large as 0.75mm in diameter. This helps to make them some of the largest bacteria ever.
So, the largest bacterium species is Thiomargarita namibiensis.
Note:
Pelagibacter ubique the smallest known free-living bacteria, having a length of 370 to 890 nm and an average cell diameter of 120 to 200 nm. They also have the smallest free-living bacterium genome:
1.3Mbp, 1354 protein genes, 35 RNA genes.
Complete answer:
Bacteria are present in the environment in the range of 0.2 and 2.0\[\mu \]m- the average size of most bacteria. Research studies have shown their size to play an important role in survival over time. Due to their small size, bacteria can be used to exploit and can survive in various microenvironments.
The bacterial include such environments as the vertical gradients in intertidal marine sediments in which various types of bacteria have been found because they can thrive in harsh habitats
The small size of bacteria is also beneficial for parasitism and oligotrophy. Bacteria can continue relying on a range of hosts (large and small) for their nutrition.
There are Some of the smallest bacteria present in the environment called microorganisms known as nanobacterium.
They are featured due to reason by their slow growth under aerobic conditions as well as being Gram-negative in nature.

Although they have been present in sizes that range between 0.2 and 0.5\[\mu \]m (200 to 500 nanometres) there have been studies where some were found to filter through 0.1\[\mu \]m filters. Some bacteria have large sizes that they are able to see with the naked eye.
For example, the Schaudinn bütschlii have sizes that measure between 4 and 5\[\mu \]m in diameter and are considered to be large bacteria.
Thiomargarita namibiensis are able to grow to be as large as 0.75mm in diameter. This helps to make them some of the largest bacteria ever.
So, the largest bacterium species is Thiomargarita namibiensis.
Note:
Pelagibacter ubique the smallest known free-living bacteria, having a length of 370 to 890 nm and an average cell diameter of 120 to 200 nm. They also have the smallest free-living bacterium genome:
1.3Mbp, 1354 protein genes, 35 RNA genes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




