
Name the process of asexual reproduction shown by Yeast. What type of living being is Yeast? What is its commercial importance?
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Yeast reproduces asexually by giving rise to a small outgrowth on the parent cell called bud.
Complete Answer:
Yeast, scientifically called the Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is quite an interesting organism when it comes to its structure, reproduction and usage. Let us figure out the details asked about Yeast in the question.
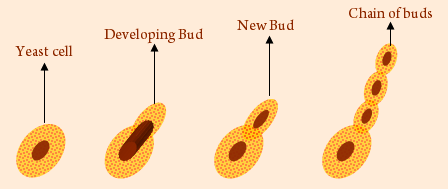
Yeast is a unicellular organism. It shown asexual reproduction, wherein, only a single parent cell in involved in giving rise to a number of offspring. In Yeast, the asexual reproduction occurs through the process of budding as follows:
1) A small outgrowth appears on one side of the parent Yeast cell.
2) It gets filled with cytoplasm and daughter nuclei formed as a result of mitosis of parent nuclei.
3) This small outgrowth is called a bud.
4) It grows and detaches to develop as a new Yeast cell.
5) Sometimes, the buds may remain attached to the parent cell and can form their own buds.
Yeast, as we already saw, is a unicellular, eukaryotic organism that performs heterotrophic nutrition. It is classified under the Kingdom Fungi. It is the only organism in Kingdom Fungi which is unicellular are performs asexual reproduction through budding.
Yeast is used commercially to give us products that we consume in our breakfasts. Let us summarise the commercial uses of Yeast:
a) It is used in making bakery products like cakes, bread, etc.
b) It is used in preparation of alcoholic beverages like beer and wine.
c) It is also added for flavour in non-alcoholic drinks.
d) It is used in the production of biofuel because it converts sugars into ethanol.
e) Its cells are processed to make extracts to be used in food products.
Note: Budding is also seen in multicellular organisms like Hydra, Corals, etc. It is a common mode of asexual reproduction in organisms with simple body organization.
Complete Answer:
Yeast, scientifically called the Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is quite an interesting organism when it comes to its structure, reproduction and usage. Let us figure out the details asked about Yeast in the question.
Yeast is a unicellular organism. It shown asexual reproduction, wherein, only a single parent cell in involved in giving rise to a number of offspring. In Yeast, the asexual reproduction occurs through the process of budding as follows:
1) A small outgrowth appears on one side of the parent Yeast cell.
2) It gets filled with cytoplasm and daughter nuclei formed as a result of mitosis of parent nuclei.
3) This small outgrowth is called a bud.
4) It grows and detaches to develop as a new Yeast cell.
5) Sometimes, the buds may remain attached to the parent cell and can form their own buds.

Yeast, as we already saw, is a unicellular, eukaryotic organism that performs heterotrophic nutrition. It is classified under the Kingdom Fungi. It is the only organism in Kingdom Fungi which is unicellular are performs asexual reproduction through budding.
Yeast is used commercially to give us products that we consume in our breakfasts. Let us summarise the commercial uses of Yeast:
a) It is used in making bakery products like cakes, bread, etc.
b) It is used in preparation of alcoholic beverages like beer and wine.
c) It is also added for flavour in non-alcoholic drinks.
d) It is used in the production of biofuel because it converts sugars into ethanol.
e) Its cells are processed to make extracts to be used in food products.
Note: Budding is also seen in multicellular organisms like Hydra, Corals, etc. It is a common mode of asexual reproduction in organisms with simple body organization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




