
Name the product formed when phenol is treated with acidified solution of $N{{a}_{2}}C{{r}_ {2}} {{O}_ {7}} $. Give an equation.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Sodium dichromate is the inorganic compound with the formula$N{{a}_{2}}C{{r}_ {2}} {{O}_ {7}} $. Usually, however, the salt is handled as its dihydrate $N{{a}_{2}}C{{r}_ {2}} {{O}_{7}}.2{{H}_ {2}} O$. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via conversion to sodium dichromate and virtually all compounds and materials based on chromium are prepared from this salt.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been provided with phenol,
Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula ${{C}_ {6}} {{H}_ {5}} OH$. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group $\left(-{{C}_ {6}} {{H}_ {6}} \right) $ bonded to a hydroxyl group (−OH). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.
If we treat phenol with acidified solution of $N{{a}_{2}}C{{r}_ {2}} {{O}_ {7}} $,
The product formed when phenol is treated with acidified solution of $N{{a}_{2}}C{{r}_ {2}} {{O}_ {7}} $ is benzoquinone a conjugated diketone. It is an oxidation reaction.
Oxidation is any chemical reaction that involves the moving of electrons. When iron reacts with oxygen it forms a chemical called rust because it has been oxidized (the iron has lost some electrons) and the oxygen has been reduced (the oxygen has gained some electrons).
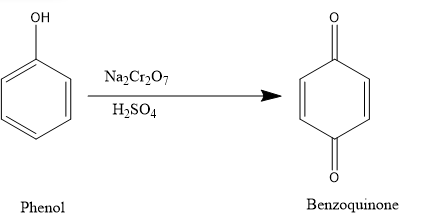
1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula ${{C}_ {6}} {{H}_ {4}} {{O}_ {2}} $. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odour, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde.
Note: The double bonds in aromatic compounds are less likely to participate in additional reactions than those found in typical alkenes. Instead, cyclic aromatic compounds undergo electrophilic substitution reactions (reactions in which the ring acts as a nucleophile to a suitable electrophile).
Complete step by step solution:
We have been provided with phenol,
Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula ${{C}_ {6}} {{H}_ {5}} OH$. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group $\left(-{{C}_ {6}} {{H}_ {6}} \right) $ bonded to a hydroxyl group (−OH). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.
If we treat phenol with acidified solution of $N{{a}_{2}}C{{r}_ {2}} {{O}_ {7}} $,
The product formed when phenol is treated with acidified solution of $N{{a}_{2}}C{{r}_ {2}} {{O}_ {7}} $ is benzoquinone a conjugated diketone. It is an oxidation reaction.
Oxidation is any chemical reaction that involves the moving of electrons. When iron reacts with oxygen it forms a chemical called rust because it has been oxidized (the iron has lost some electrons) and the oxygen has been reduced (the oxygen has gained some electrons).

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula ${{C}_ {6}} {{H}_ {4}} {{O}_ {2}} $. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odour, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde.
Note: The double bonds in aromatic compounds are less likely to participate in additional reactions than those found in typical alkenes. Instead, cyclic aromatic compounds undergo electrophilic substitution reactions (reactions in which the ring acts as a nucleophile to a suitable electrophile).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




