
Name the types of chromosomes based on the position of the centromere and draw a suitable diagram for each.
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint:
It is a DNA molecule with the genetic material of an organism. The morphological classification of an organism is an important karyotypic feature.
Complete answer:
In the different phases of the cell cycle, the size and shape of chromosomes changes like in interphase, they appear thin, coiled, and thread-like structures. However, in meiotic and mitotic cell division they appear thicker and shorter in length. Every chromosome has a primary constriction known as centromere that contains a disc-shaped structure on its side called kinetochores. The centromere divides the chromosome into two portions called chromosomes arms.
Based on the position of centromere and length of chromosomes arms, the chromosomes are divided into four group-
Metacentric: In this chromosome, the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome and divides it into equal arms. These chromosomes appear as ‘V’ shapes in the metaphase stage of cell division.
Sub-metacentric: This type of chromosome has a centromere nearer to one end of the chromosome that resulted in one shorter arm and one long arm. They appear in ‘L’ shape structure during cell division.
Acrocentric: In this type of chromosome, the centromere is located close to its end which resulted in one extremely short arm and one very long arm. Sat-chromosomes include all acrocentric chromosomes.
Telocentric: In this chromosome, the centromere is located at the proximal end that resulted in only one arm. The chromosomal tips are known as telomeres.
Note:
1. Few chromosomes possess non-staining secondary constrictions at a fixed place that shows a small fragment called the satellite.
2. Amphibians generally show metacentric chromosomes.
3. Most of the human chromosomes are considered as sub-metacentric chromosome
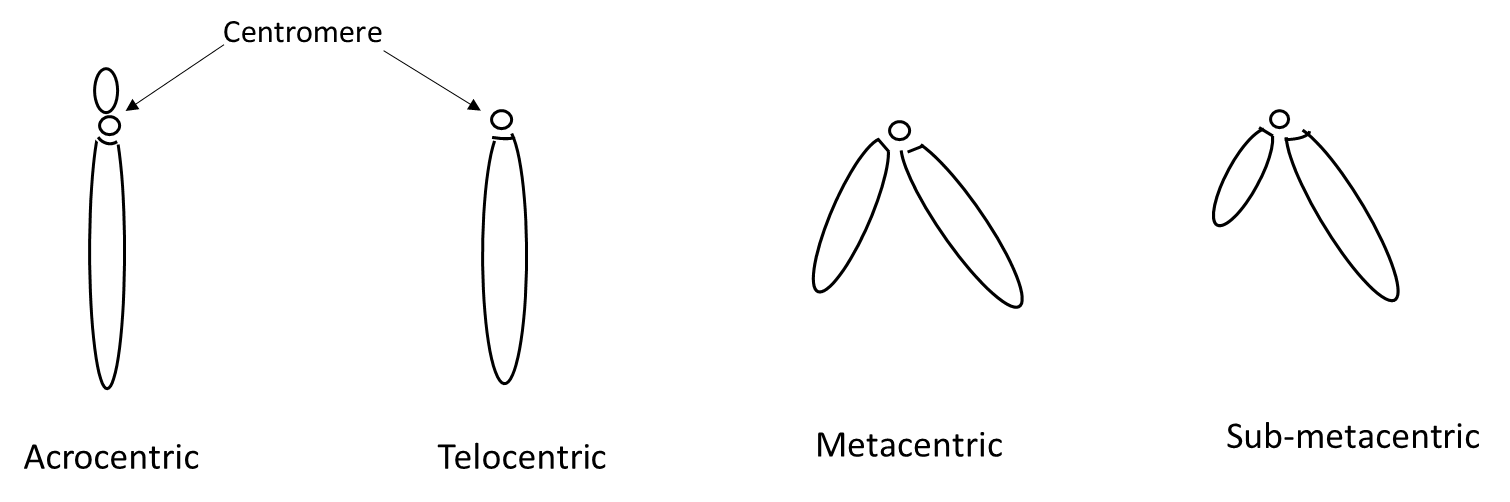
Figure: Types of chromosomes based on the position of the centromere
It is a DNA molecule with the genetic material of an organism. The morphological classification of an organism is an important karyotypic feature.
Complete answer:
In the different phases of the cell cycle, the size and shape of chromosomes changes like in interphase, they appear thin, coiled, and thread-like structures. However, in meiotic and mitotic cell division they appear thicker and shorter in length. Every chromosome has a primary constriction known as centromere that contains a disc-shaped structure on its side called kinetochores. The centromere divides the chromosome into two portions called chromosomes arms.
Based on the position of centromere and length of chromosomes arms, the chromosomes are divided into four group-
Metacentric: In this chromosome, the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome and divides it into equal arms. These chromosomes appear as ‘V’ shapes in the metaphase stage of cell division.
Sub-metacentric: This type of chromosome has a centromere nearer to one end of the chromosome that resulted in one shorter arm and one long arm. They appear in ‘L’ shape structure during cell division.
Acrocentric: In this type of chromosome, the centromere is located close to its end which resulted in one extremely short arm and one very long arm. Sat-chromosomes include all acrocentric chromosomes.
Telocentric: In this chromosome, the centromere is located at the proximal end that resulted in only one arm. The chromosomal tips are known as telomeres.
Note:
1. Few chromosomes possess non-staining secondary constrictions at a fixed place that shows a small fragment called the satellite.
2. Amphibians generally show metacentric chromosomes.
3. Most of the human chromosomes are considered as sub-metacentric chromosome

Figure: Types of chromosomes based on the position of the centromere
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




