
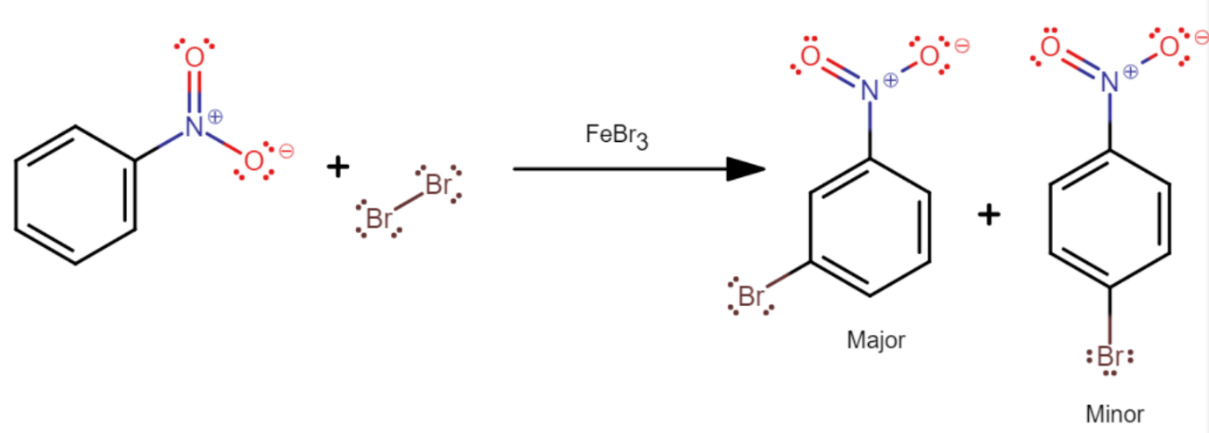
Nitrobenzene reacts with $B{{r}_{2}}$ in the presence of $FeB{{r}_{3}}$ to give m-bromonitrobenzene as major project. Which of the following provides the best reason for the formation of m-bromonitrobenzene as the major project?
(A) The electrons density at the meta position is greater than those at the ortho and para positions.
(B) Aromaticity is lost in the $\sigma $-complexes formed by the attack of $B{{r}^{+}}$ at the ortho and para positions but not at the meta position.
(C) The $\sigma $-complex formed by the attack of $B{{r}^{+}}$ at the meta position is the least destabilized and the most stable among the three $\sigma $-complexes.
(D) In the final step of regeneration of benzene ring by the loss of ${{H}^{+}}$ from the $\sigma $-complexes, the meta-oriented $\sigma $-complex loses ${{H}^{+}}$ most readily.
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: We first need to know what are ortho, para, and meta positions. When a group is substituted in a monosubstituted arene, it can occupy three positions as follows
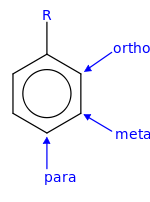
The positions of the substituted group relative to the position of the pre-existing substituted group are ortho, para, and meta positions.
Complete answer:
When a benzene ring that has one substituted group is treated with an electrophile, the electrophilic aromatic substitution could undergo in three ways giving three products in which the substituted electrophile is at ortho position, para position, and meta position.
When the products obtained of meta position is more than the product obtained of ortho and para positions, the substituent group is said to be meta directing and vice versa.
The substituent group which withdraws electrons are meta directing whereas the groups that donate electrons are ortho-para directing.
Now, the bromination of nitrobenzene in the presence of $FeB{{r}_{3}}$ to produce m-bromonitrobenzene as a major product is depicted as follows
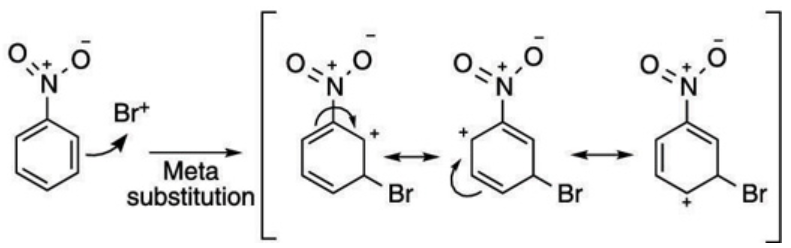
The resonating structure of nitrobenzene is as follows
From the resonance structures of nitrobenzene, we can see that there is electron deficiency at ortho and para positions. Since bromine is an electron-withdrawing group, the most stable resonance intermediates are formed when it is bonded at the meta position.
Hence the bromination of benzene results in a major m-bromonitrobenzene because of option (C).
Note:
It should be noted that the carbocation formed upon the attack of the substitution group determines the stability of the product formed. The more stable the intermediate carbocation, the more stable the product.

The positions of the substituted group relative to the position of the pre-existing substituted group are ortho, para, and meta positions.
Complete answer:
When a benzene ring that has one substituted group is treated with an electrophile, the electrophilic aromatic substitution could undergo in three ways giving three products in which the substituted electrophile is at ortho position, para position, and meta position.
When the products obtained of meta position is more than the product obtained of ortho and para positions, the substituent group is said to be meta directing and vice versa.
The substituent group which withdraws electrons are meta directing whereas the groups that donate electrons are ortho-para directing.
Now, the bromination of nitrobenzene in the presence of $FeB{{r}_{3}}$ to produce m-bromonitrobenzene as a major product is depicted as follows
The resonating structure of nitrobenzene is as follows

From the resonance structures of nitrobenzene, we can see that there is electron deficiency at ortho and para positions. Since bromine is an electron-withdrawing group, the most stable resonance intermediates are formed when it is bonded at the meta position.

Hence the bromination of benzene results in a major m-bromonitrobenzene because of option (C).
Note:
It should be noted that the carbocation formed upon the attack of the substitution group determines the stability of the product formed. The more stable the intermediate carbocation, the more stable the product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




