
Nucleoside is
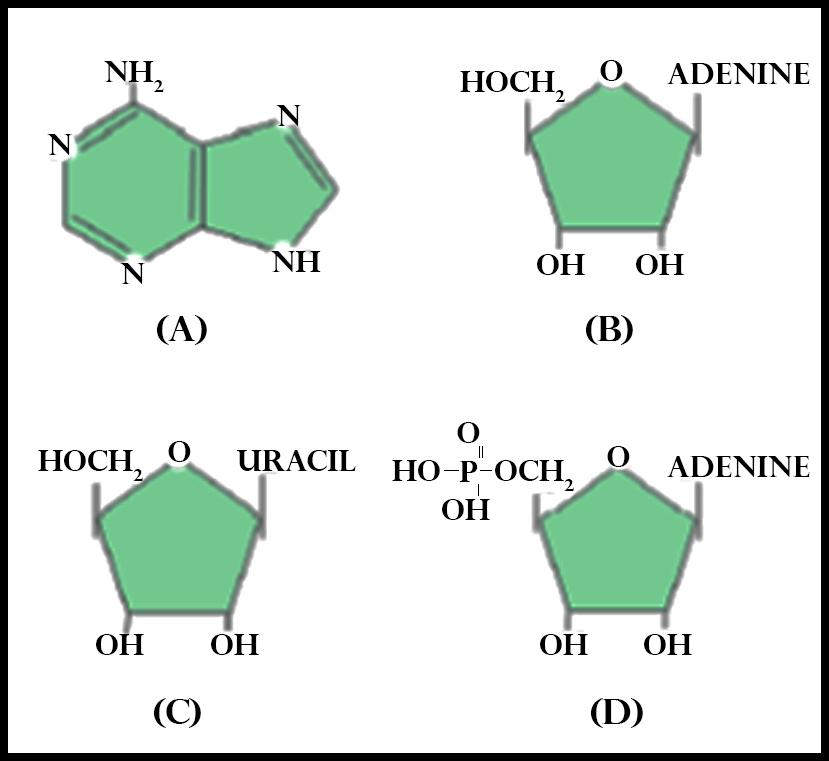
(a) A & B
(b) B & C
(c) C & D
(d) D & A

Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: These are glycosylamines without a phosphate group. A glycosylamine is a glycosyl group attached to an amino group.
Complete step by step answer:
In the figure given in the question, option B is adenosine, and option C is uridine, both of which are nucleosides.
A nucleoside is made up of a nucleobase of a nitrogenous base and has a five-carbon sugar that is ribose or 2'-deoxyribose attached to it. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon forms a nexus through a glycosidic bond to the N1 of a pyrimidine such as Cytosine, Thymine (in DNA) & Uracil (in RNA) , or the N9 of a purine that is Guanine & Adenine. Some examples of nucleosides are cytidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine, thymidine, and inosine.
Nucleosides can be produced from nucleotides anew, particularly in the liver, but they are more abundantly supplied via ingestion and digestion of nucleic acids in the diet. Nucleotidases break down nucleotides into nucleosides, such as the thymidine monophosphate into thymidine and phosphate. The nucleosides, in turn, are subsequently weakened within the lumen of the gastrointestinal system by nucleosidases into nucleobases and ribose or deoxyribose.
So, the correct answer is,’ B & C’.
Note:
- Additionally, nucleotides can be broken down inside the cell into nitrogenous bases, and deoxyribose-1-phosphate or ribose-1-phosphate.
- In medicine, several nucleotides are used as antiviral or anticancer agents. With non-canonical bases, these compounds are incorporated by the viral polymerase. These compounds are activated within the cells by being converted into nucleotides. Since charged nucleotides cannot easily cross cell membranes they are administered as nucleotides.
Complete step by step answer:
In the figure given in the question, option B is adenosine, and option C is uridine, both of which are nucleosides.
A nucleoside is made up of a nucleobase of a nitrogenous base and has a five-carbon sugar that is ribose or 2'-deoxyribose attached to it. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon forms a nexus through a glycosidic bond to the N1 of a pyrimidine such as Cytosine, Thymine (in DNA) & Uracil (in RNA) , or the N9 of a purine that is Guanine & Adenine. Some examples of nucleosides are cytidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine, thymidine, and inosine.
Nucleosides can be produced from nucleotides anew, particularly in the liver, but they are more abundantly supplied via ingestion and digestion of nucleic acids in the diet. Nucleotidases break down nucleotides into nucleosides, such as the thymidine monophosphate into thymidine and phosphate. The nucleosides, in turn, are subsequently weakened within the lumen of the gastrointestinal system by nucleosidases into nucleobases and ribose or deoxyribose.
So, the correct answer is,’ B & C’.
Note:
- Additionally, nucleotides can be broken down inside the cell into nitrogenous bases, and deoxyribose-1-phosphate or ribose-1-phosphate.
- In medicine, several nucleotides are used as antiviral or anticancer agents. With non-canonical bases, these compounds are incorporated by the viral polymerase. These compounds are activated within the cells by being converted into nucleotides. Since charged nucleotides cannot easily cross cell membranes they are administered as nucleotides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




