
How is the number of rings in Bohr's model of any element determined?
(A) Column number on the periodic table
(B) Atomic mass
(C) Row number on the periodic table
(D) Atomic number
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: Neil Bohr proposed a model of an atom. He agreed that the negatively charged electrons are revolving around the nucleus in the same way as the planets revolve around the sun. The electrons revolve in a fixed orbit which has fixed energy. Each electron in the orbits of the ring possesses fixed energy.
Complete step by step solution:
According to Bohr’s model of an atom, the electrons in the atom revolve around the nucleus only in a curtained circular orbit. As long as the electron remains in a particular orbit, it neither loses nor gains energy. In other words, the energy of electrons remains constant in a particular orbit. This leads to the idea that each orbit is associated with definite energy i.e. with a definite whole number of quanta of energy.
The orbits, therefore are also known as energy levels or energy shells. Bohr gave numbers such as 1, 2, 3, 4, etc. to these energy levels. These energy levels are termed as the principal quantum numbers. The various energy levels are also designated by letters K, L, M, N, etc.
We know that the principal quantum number is one of the quantum numbers which is used to describe the position of an electron in the atom.
Quantum number is used to describe the position and the energy of an electron in the atoms.
The principal quantum number is denoted by the symbol ‘n’. It is used to designate the shell number which accommodates the electron. The principal quantum number is the distance between the nucleus and the electron of the interest.
The Bohr model correctly depicts the energy levels of the electrons. We can say that the principal quantum number is used to represent the orbit of the atom.
Along the period, the electrons enter the same shell and thus the principal quantum number along the period is the same.
Along with the group, the principal quantum increases as we move down in the period. Each shell ‘n’ is nothing but a ring in Bohr's model.
The ring in Bohr's model determines the row number or the period in the periodic table. The Bohr ring model of the sodium is as shown below:
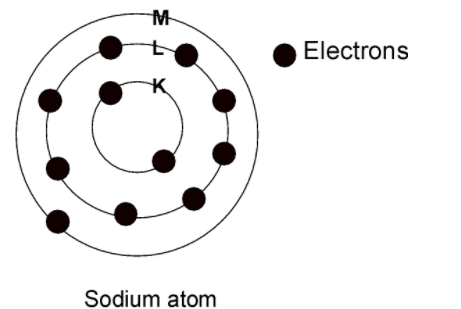
This ring or the n value or the principal quantum number corresponds to Row number on the periodic table.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note: According to the Bohr model of arrangements of electrons,
The first shell ($\text{ n = 1 }$ or K shell) the 2 elements are in the row and there are 2electrons in the orbit
The second shell ($\text{ n = 2 }$or L shell) the 8 elements are in the row such that the 8 electrons are in the second orbits.
In the third shell ($\text{ n = 3 }$or M shell) the 8 elements are in the row such that the 8 electrons are in the third orbit and this goes on.
Complete step by step solution:
According to Bohr’s model of an atom, the electrons in the atom revolve around the nucleus only in a curtained circular orbit. As long as the electron remains in a particular orbit, it neither loses nor gains energy. In other words, the energy of electrons remains constant in a particular orbit. This leads to the idea that each orbit is associated with definite energy i.e. with a definite whole number of quanta of energy.
The orbits, therefore are also known as energy levels or energy shells. Bohr gave numbers such as 1, 2, 3, 4, etc. to these energy levels. These energy levels are termed as the principal quantum numbers. The various energy levels are also designated by letters K, L, M, N, etc.
We know that the principal quantum number is one of the quantum numbers which is used to describe the position of an electron in the atom.
Quantum number is used to describe the position and the energy of an electron in the atoms.
The principal quantum number is denoted by the symbol ‘n’. It is used to designate the shell number which accommodates the electron. The principal quantum number is the distance between the nucleus and the electron of the interest.
The Bohr model correctly depicts the energy levels of the electrons. We can say that the principal quantum number is used to represent the orbit of the atom.
Along the period, the electrons enter the same shell and thus the principal quantum number along the period is the same.
Along with the group, the principal quantum increases as we move down in the period. Each shell ‘n’ is nothing but a ring in Bohr's model.
The ring in Bohr's model determines the row number or the period in the periodic table. The Bohr ring model of the sodium is as shown below:

This ring or the n value or the principal quantum number corresponds to Row number on the periodic table.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note: According to the Bohr model of arrangements of electrons,
The first shell ($\text{ n = 1 }$ or K shell) the 2 elements are in the row and there are 2electrons in the orbit
The second shell ($\text{ n = 2 }$or L shell) the 8 elements are in the row such that the 8 electrons are in the second orbits.
In the third shell ($\text{ n = 3 }$or M shell) the 8 elements are in the row such that the 8 electrons are in the third orbit and this goes on.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




