
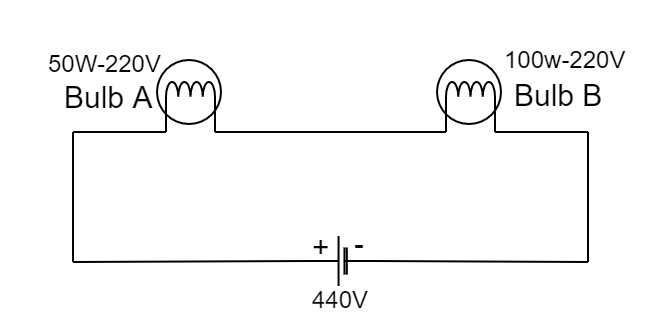
Observe the following figure which bulb gets fused?

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: In such types of questions firstly we compute the resistance of the bulb and the maximum current which can flow from the bulb. If the current flown in the entire circuit is larger than the maximum current of the bulb in that circumstance the bulb will fuse.
Formula used: The power consumed can be written as:
$P = VI = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
We first determine the current ratings for the two bulbs.
For the bulb of $\;50W$ power,
$I = \dfrac{P}{V} = \dfrac{{50}}{{220}}A$
$ \Rightarrow I = 0.227A$
For the bulb of $\;100W$ power,
$I = \dfrac{P}{V} = \dfrac{{100}}{{220}}$
On further solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{5}{{11}}A$
$ \Rightarrow I = 0.45A$
Now, we need to determine the current flowing in the condition when both the bulbs are connected in series.
As soon as the two bulbs are joined in series, their resistances simply add and when the equivalent is divided by the supply voltage, we get the current.
To get the resistance, we use the expression,
$R = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{P}$
Now in the series circuit, the equivalent resistance will be:
$R = \dfrac{{{{\left( {220} \right)}^2}}}{{50}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {220} \right)}^2}}}{{100}}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {220} \right)^2}\left( {\dfrac{{100 + 50}}{{50 \times 100}}} \right)$
On further solving we get,
$R = {\left( {220} \right)^2}\left( {\dfrac{{150}}{{5000}}} \right)$
Dividing this with the supply voltage, we get:
$I = \dfrac{{440}}{{{{\left( {220} \right)}^2}\left( {\dfrac{{150}}{{5000}}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{2 \times 5000}}{{220 \times 150}}$
On further solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{50}}{{165}}$
$ \Rightarrow I = 0.30A$
Now, compare this with the current ratings for the two bulbs. This current clearly exceeds the current rating of $\;50W$ bulb. Therefore, this bulb definitely fuses. The $\;100W$ bulb will not fuse though as the current rating for it is more than the current flowing in the series circuit.
Therefore, Bulb A will get a fuse.
Note: A bulb fuses when a current flows in it more than its rated capacity in the circuit. We went for comparing the currents everywhere because the definition of fusing is closely related to current flow, so that is the quantity to be compared. One should mind here that with the given ratings of power and voltage, we can only tell the limits for the quantities and not the exact quantities.
Formula used: The power consumed can be written as:
$P = VI = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
We first determine the current ratings for the two bulbs.
For the bulb of $\;50W$ power,
$I = \dfrac{P}{V} = \dfrac{{50}}{{220}}A$
$ \Rightarrow I = 0.227A$
For the bulb of $\;100W$ power,
$I = \dfrac{P}{V} = \dfrac{{100}}{{220}}$
On further solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{5}{{11}}A$
$ \Rightarrow I = 0.45A$
Now, we need to determine the current flowing in the condition when both the bulbs are connected in series.
As soon as the two bulbs are joined in series, their resistances simply add and when the equivalent is divided by the supply voltage, we get the current.
To get the resistance, we use the expression,
$R = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{P}$
Now in the series circuit, the equivalent resistance will be:
$R = \dfrac{{{{\left( {220} \right)}^2}}}{{50}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {220} \right)}^2}}}{{100}}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {220} \right)^2}\left( {\dfrac{{100 + 50}}{{50 \times 100}}} \right)$
On further solving we get,
$R = {\left( {220} \right)^2}\left( {\dfrac{{150}}{{5000}}} \right)$
Dividing this with the supply voltage, we get:
$I = \dfrac{{440}}{{{{\left( {220} \right)}^2}\left( {\dfrac{{150}}{{5000}}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{2 \times 5000}}{{220 \times 150}}$
On further solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{50}}{{165}}$
$ \Rightarrow I = 0.30A$
Now, compare this with the current ratings for the two bulbs. This current clearly exceeds the current rating of $\;50W$ bulb. Therefore, this bulb definitely fuses. The $\;100W$ bulb will not fuse though as the current rating for it is more than the current flowing in the series circuit.
Therefore, Bulb A will get a fuse.
Note: A bulb fuses when a current flows in it more than its rated capacity in the circuit. We went for comparing the currents everywhere because the definition of fusing is closely related to current flow, so that is the quantity to be compared. One should mind here that with the given ratings of power and voltage, we can only tell the limits for the quantities and not the exact quantities.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




